Gartner® doesn’t create new categories lightly. Generally speaking, a new acronym only emerges when the industry’s collective “to-do list” has become mathematically impossible to complete. And so it seems that the introduction of the Exposure Assessment Platforms (EAP) category is a formal admission that traditional Vulnerability Management (VM) is no longer a viable way to […]
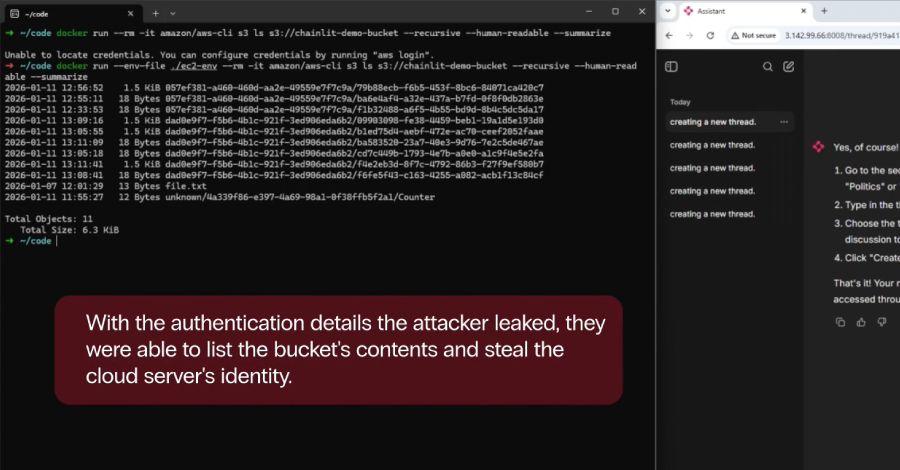
Security vulnerabilities were uncovered in the popular open-source artificial intelligence (AI) framework Chainlit that could allow attackers to steal sensitive data, which may allow for lateral movement within a susceptible organization. Zafran Security said the high-severity flaws, collectively dubbed ChainLeak, could be abused to leak cloud environment API keys and steal sensitive files, or Read More
Bounded Minds, Generative Machines: Envisioning Conversational AI that Works with Human Heuristics and Reduces Bias Riskcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.13376v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Conversational AI is rapidly becoming a primary interface for information seeking and decision making, yet most systems still assume idealized users. In practice, human reasoning is bounded by limited attention, uneven knowledge, and reliance on heuristics that are adaptive but bias-prone. This article outlines a research pathway grounded in bounded rationality, and argues that conversational AI should be designed to work with human heuristics rather than against them. It identifies key directions for detecting cognitive vulnerability, supporting judgment under uncertainty, and evaluating conversational systems beyond factual accuracy, toward decision quality and cognitive robustness.
arXiv:2601.13376v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Conversational AI is rapidly becoming a primary interface for information seeking and decision making, yet most systems still assume idealized users. In practice, human reasoning is bounded by limited attention, uneven knowledge, and reliance on heuristics that are adaptive but bias-prone. This article outlines a research pathway grounded in bounded rationality, and argues that conversational AI should be designed to work with human heuristics rather than against them. It identifies key directions for detecting cognitive vulnerability, supporting judgment under uncertainty, and evaluating conversational systems beyond factual accuracy, toward decision quality and cognitive robustness. Read More
5 Alternatives to Google Colab for Long-Running TasksKDnuggets These five options make long-running jobs easier, faster, and less frustrating than Colab.
These five options make long-running jobs easier, faster, and less frustrating than Colab. Read More
Balancing AI cost efficiency with data sovereigntyAI News AI cost efficiency and data sovereignty are at odds, forcing a rethink of enterprise risk frameworks for global organisations. For over a year, the generative AI narrative focused on a race for capability, often measuring success by parameter counts and flawed benchmark scores. Boardroom conversations, however, are undergoing a necessary correction. While the allure of
The post Balancing AI cost efficiency with data sovereignty appeared first on AI News.
AI cost efficiency and data sovereignty are at odds, forcing a rethink of enterprise risk frameworks for global organisations. For over a year, the generative AI narrative focused on a race for capability, often measuring success by parameter counts and flawed benchmark scores. Boardroom conversations, however, are undergoing a necessary correction. While the allure of
The post Balancing AI cost efficiency with data sovereignty appeared first on AI News. Read More
Salesforce AI Introduces FOFPred: A Language-Driven Future Optical Flow Prediction Framework that Enables Improved Robot Control and Video GenerationMarkTechPost Salesforce AI research team present FOFPred, a language driven future optical flow prediction framework that connects large vision language models with diffusion transformers for dense motion forecasting in control and video generation settings. FOFPred takes one or more images and a natural language instruction such as ‘moving the bottle from right to left’ and predicts
The post Salesforce AI Introduces FOFPred: A Language-Driven Future Optical Flow Prediction Framework that Enables Improved Robot Control and Video Generation appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Salesforce AI research team present FOFPred, a language driven future optical flow prediction framework that connects large vision language models with diffusion transformers for dense motion forecasting in control and video generation settings. FOFPred takes one or more images and a natural language instruction such as ‘moving the bottle from right to left’ and predicts
The post Salesforce AI Introduces FOFPred: A Language-Driven Future Optical Flow Prediction Framework that Enables Improved Robot Control and Video Generation appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
How AutoGluon Enables Modern AutoML Pipelines for Production-Grade Tabular Models with Ensembling and DistillationMarkTechPost In this tutorial, we build a production-grade tabular machine learning pipeline using AutoGluon, taking a real-world mixed-type dataset from raw ingestion through to deployment-ready artifacts. We train high-quality stacked and bagged ensembles, evaluate performance with robust metrics, perform subgroup and feature-level analysis, and then optimize the model for real-time inference using refit-full and distillation. Throughout
The post How AutoGluon Enables Modern AutoML Pipelines for Production-Grade Tabular Models with Ensembling and Distillation appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In this tutorial, we build a production-grade tabular machine learning pipeline using AutoGluon, taking a real-world mixed-type dataset from raw ingestion through to deployment-ready artifacts. We train high-quality stacked and bagged ensembles, evaluate performance with robust metrics, perform subgroup and feature-level analysis, and then optimize the model for real-time inference using refit-full and distillation. Throughout
The post How AutoGluon Enables Modern AutoML Pipelines for Production-Grade Tabular Models with Ensembling and Distillation appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
The human brain may work more like AI than anyone expectedArtificial Intelligence News — ScienceDaily Scientists have discovered that the human brain understands spoken language in a way that closely resembles how advanced AI language models work. By tracking brain activity as people listened to a long podcast, researchers found that meaning unfolds step by step—much like the layered processing inside systems such as GPT-style models.
Scientists have discovered that the human brain understands spoken language in a way that closely resembles how advanced AI language models work. By tracking brain activity as people listened to a long podcast, researchers found that meaning unfolds step by step—much like the layered processing inside systems such as GPT-style models. Read More
Improved Bug Localization with AI Agents Leveraging Hypothesis and Dynamic Cognitioncs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.12522v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Software bugs cost technology providers (e.g., AT&T) billions annually and cause developers to spend roughly 50% of their time on bug resolution. Traditional methods for bug localization often analyze the suspiciousness of code components (e.g., methods, documents) in isolation, overlooking their connections with other components in the codebase. Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) and agentic AI techniques have shown strong potential for code understanding, but still lack causal reasoning during code exploration and struggle to manage growing context effectively, limiting their capability. In this paper, we present a novel agentic technique for bug localization — CogniGent — that overcomes the limitations above by leveraging multiple AI agents capable of causal reasoning, call-graph-based root cause analysis and context engineering. It emulates developers-inspired debugging practices (a.k.a., dynamic cognitive debugging) and conducts hypothesis testing to support bug localization. We evaluate CogniGent on a curated dataset of 591 bug reports using three widely adopted performance metrics and compare it against six established baselines from the literature. Experimental results show that our technique consistently outperformed existing traditional and LLM-based techniques, achieving MAP improvements of 23.33-38.57% at the document and method levels. Similar gains were observed in MRR, with increases of 25.14-53.74% at both granularity levels. Statistical significance tests also confirm the superiority of our technique. By addressing the reasoning, dependency, and context limitations, CogniGent advances the state of bug localization, bridging human-like cognition with agentic automation for improved performance.
arXiv:2601.12522v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Software bugs cost technology providers (e.g., AT&T) billions annually and cause developers to spend roughly 50% of their time on bug resolution. Traditional methods for bug localization often analyze the suspiciousness of code components (e.g., methods, documents) in isolation, overlooking their connections with other components in the codebase. Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) and agentic AI techniques have shown strong potential for code understanding, but still lack causal reasoning during code exploration and struggle to manage growing context effectively, limiting their capability. In this paper, we present a novel agentic technique for bug localization — CogniGent — that overcomes the limitations above by leveraging multiple AI agents capable of causal reasoning, call-graph-based root cause analysis and context engineering. It emulates developers-inspired debugging practices (a.k.a., dynamic cognitive debugging) and conducts hypothesis testing to support bug localization. We evaluate CogniGent on a curated dataset of 591 bug reports using three widely adopted performance metrics and compare it against six established baselines from the literature. Experimental results show that our technique consistently outperformed existing traditional and LLM-based techniques, achieving MAP improvements of 23.33-38.57% at the document and method levels. Similar gains were observed in MRR, with increases of 25.14-53.74% at both granularity levels. Statistical significance tests also confirm the superiority of our technique. By addressing the reasoning, dependency, and context limitations, CogniGent advances the state of bug localization, bridging human-like cognition with agentic automation for improved performance. Read More
Multimodal Generative Engine Optimization: Rank Manipulation for Vision-Language Model Rankerscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.12263v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are rapidly replacing unimodal encoders in modern retrieval and recommendation systems. While their capabilities are well-documented, their robustness against adversarial manipulation in competitive ranking scenarios remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we uncover a critical vulnerability in VLM-based product search: multimodal ranking attacks. We present Multimodal Generative Engine Optimization (MGEO), a novel adversarial framework that enables a malicious actor to unfairly promote a target product by jointly optimizing imperceptible image perturbations and fluent textual suffixes. Unlike existing attacks that treat modalities in isolation, MGEO employs an alternating gradient-based optimization strategy to exploit the deep cross-modal coupling within the VLM. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets using state-of-the-art models demonstrate that our coordinated attack significantly outperforms text-only and image-only baselines. These findings reveal that multimodal synergy, typically a strength of VLMs, can be weaponized to compromise the integrity of search rankings without triggering conventional content filters.
arXiv:2601.12263v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are rapidly replacing unimodal encoders in modern retrieval and recommendation systems. While their capabilities are well-documented, their robustness against adversarial manipulation in competitive ranking scenarios remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we uncover a critical vulnerability in VLM-based product search: multimodal ranking attacks. We present Multimodal Generative Engine Optimization (MGEO), a novel adversarial framework that enables a malicious actor to unfairly promote a target product by jointly optimizing imperceptible image perturbations and fluent textual suffixes. Unlike existing attacks that treat modalities in isolation, MGEO employs an alternating gradient-based optimization strategy to exploit the deep cross-modal coupling within the VLM. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets using state-of-the-art models demonstrate that our coordinated attack significantly outperforms text-only and image-only baselines. These findings reveal that multimodal synergy, typically a strength of VLMs, can be weaponized to compromise the integrity of search rankings without triggering conventional content filters. Read More