Do You Feel Comfortable? Detecting Hidden Conversational Escalation in AI Chatbotscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.06193v4 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Large Language Models (LLM) are increasingly integrated into everyday interactions, serving not only as information assistants but also as emotional companions. Even in the absence of explicit toxicity, repeated emotional reinforcement or affective drift can gradually escalate distress in a form of textit{implicit harm} that traditional toxicity filters fail to detect. Existing guardrail mechanisms often rely on external classifiers or clinical rubrics that may lag behind the nuanced, real-time dynamics of a developing conversation. To address this gap, we propose GAUGE (Guarding Affective Utterance Generation Escalation), logit-based framework for the real-time detection of hidden conversational escalation. GAUGE measures how an LLM’s output probabilistically shifts the affective state of a dialogue.
arXiv:2512.06193v4 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Large Language Models (LLM) are increasingly integrated into everyday interactions, serving not only as information assistants but also as emotional companions. Even in the absence of explicit toxicity, repeated emotional reinforcement or affective drift can gradually escalate distress in a form of textit{implicit harm} that traditional toxicity filters fail to detect. Existing guardrail mechanisms often rely on external classifiers or clinical rubrics that may lag behind the nuanced, real-time dynamics of a developing conversation. To address this gap, we propose GAUGE (Guarding Affective Utterance Generation Escalation), logit-based framework for the real-time detection of hidden conversational escalation. GAUGE measures how an LLM’s output probabilistically shifts the affective state of a dialogue. Read More
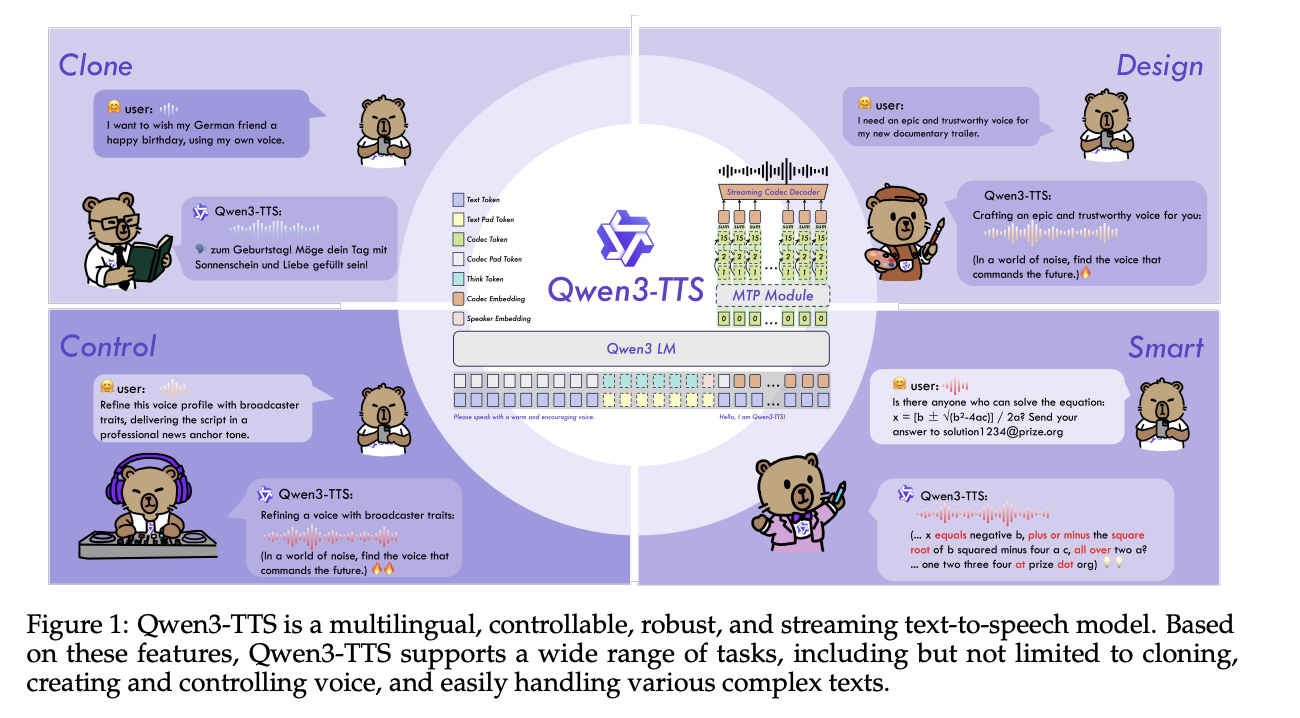
Qwen Researchers Release Qwen3-TTS: an Open Multilingual TTS Suite with Real-Time Latency and Fine-Grained Voice ControlMarkTechPost Alibaba Cloud’s Qwen team has open-sourced Qwen3-TTS, a family of multilingual text-to-speech models that target three core tasks in one stack, voice clone, voice design, and high quality speech generation. Model family and capabilities Qwen3-TTS uses a 12Hz speech tokenizer and 2 language model sizes, 0.6B and 1.7B, packaged into 3 main tasks. The open
The post Qwen Researchers Release Qwen3-TTS: an Open Multilingual TTS Suite with Real-Time Latency and Fine-Grained Voice Control appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Alibaba Cloud’s Qwen team has open-sourced Qwen3-TTS, a family of multilingual text-to-speech models that target three core tasks in one stack, voice clone, voice design, and high quality speech generation. Model family and capabilities Qwen3-TTS uses a 12Hz speech tokenizer and 2 language model sizes, 0.6B and 1.7B, packaged into 3 main tasks. The open
The post Qwen Researchers Release Qwen3-TTS: an Open Multilingual TTS Suite with Real-Time Latency and Fine-Grained Voice Control appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Knowing When to Abstain: Medical LLMs Under Clinical Uncertaintycs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.12471v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Current evaluation of large language models (LLMs) overwhelmingly prioritizes accuracy; however, in real-world and safety-critical applications, the ability to abstain when uncertain is equally vital for trustworthy deployment. We introduce MedAbstain, a unified benchmark and evaluation protocol for abstention in medical multiple-choice question answering (MCQA) — a discrete-choice setting that generalizes to agentic action selection — integrating conformal prediction, adversarial question perturbations, and explicit abstention options. Our systematic evaluation of both open- and closed-source LLMs reveals that even state-of-the-art, high-accuracy models often fail to abstain with uncertain. Notably, providing explicit abstention options consistently increases model uncertainty and safer abstention, far more than input perturbations, while scaling model size or advanced prompting brings little improvement. These findings highlight the central role of abstention mechanisms for trustworthy LLM deployment and offer practical guidance for improving safety in high-stakes applications.
arXiv:2601.12471v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Current evaluation of large language models (LLMs) overwhelmingly prioritizes accuracy; however, in real-world and safety-critical applications, the ability to abstain when uncertain is equally vital for trustworthy deployment. We introduce MedAbstain, a unified benchmark and evaluation protocol for abstention in medical multiple-choice question answering (MCQA) — a discrete-choice setting that generalizes to agentic action selection — integrating conformal prediction, adversarial question perturbations, and explicit abstention options. Our systematic evaluation of both open- and closed-source LLMs reveals that even state-of-the-art, high-accuracy models often fail to abstain with uncertain. Notably, providing explicit abstention options consistently increases model uncertainty and safer abstention, far more than input perturbations, while scaling model size or advanced prompting brings little improvement. These findings highlight the central role of abstention mechanisms for trustworthy LLM deployment and offer practical guidance for improving safety in high-stakes applications. Read More
Hackers began exploiting an authentication bypass vulnerability in SmarterTools’ SmarterMail email server and collaboration tool that allows resetting admin passwords. […] Read More
Okta is warning about custom phishing kits built specifically for voice-based social engineering (vishing) attacks. BleepingComputer has learned that these kits are being used in active attacks to steal Okta SSO credentials for data theft. […] Read More
A critical security flaw has been disclosed in the GNU InetUtils telnet daemon (telnetd) that went unnoticed for nearly 11 years. The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2026-24061, is rated 9.8 out of 10.0 on the CVSS scoring system. It affects all versions of GNU InetUtils from version 1.9.3 up to and including version 2.7. “Telnetd in […]
Microsoft will soon add new fraud protection features to Teams calls, warning users about external callers who attempt to impersonate trusted organizations in social engineering attacks. […] Read More
Microsoft is rolling out new artificial intelligence features with the latest updates to the Notepad and Paint apps for Windows 11 Insiders. […] Read More
An operational security failure allowed researchers to recover data that the INC ransomware gang stole from a dozen U.S. organizations. […] Read More
Hybrid work has driven a surge in Active Directory password resets, turning minor lockouts into major productivity drains. Specops shows why remote access, cached credentials, and security policies are fueling the spike. […] Read More