To exploit the vulnerability, an attacker would need either system access or be able to convince a user to open a malicious Office file. Read More
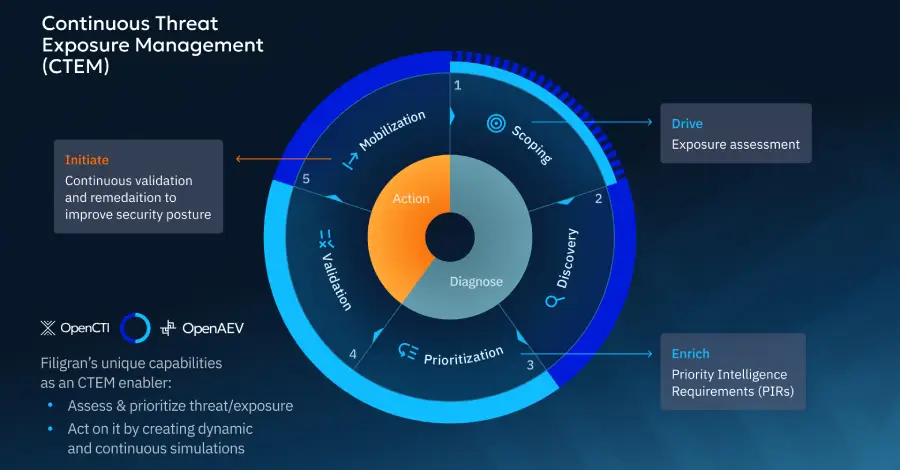
Cybersecurity teams increasingly want to move beyond looking at threats and vulnerabilities in isolation. It’s not only about what could go wrong (vulnerabilities) or who might attack (threats), but where they intersect in your actual environment to create real, exploitable exposure. Which exposures truly matter? Can attackers exploit them? Are our defenses effective? Continuous Threat […]
Microsoft on Monday issued out-of-band security patches for a high-severity Microsoft Office zero-day vulnerability exploited in attacks. The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2026-21509, carries a CVSS score of 7.8 out of 10.0. It has been described as a security feature bypass in Microsoft Office. “Reliance on untrusted inputs in a security decision in Microsoft Office allows […]
A critical security flaw has been disclosed in Grist‑Core, an open-source, self-hosted version of the Grist relational spreadsheet-database, that could result in remote code execution. The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2026-24002 (CVSS score: 9.1), has been codenamed Cellbreak by Cyera Research Labs. “One malicious formula can turn a spreadsheet into a Remote Code Execution (RCE) beachhead,” Read […]
From Connections to Meaning: Why Heterogeneous Graph Transformers (HGT) Change Demand ForecastingTowards Data Science How relationship-aware graphs turn connected forecasts into operational insight
The post From Connections to Meaning: Why Heterogeneous Graph Transformers (HGT) Change Demand Forecasting appeared first on Towards Data Science.
How relationship-aware graphs turn connected forecasts into operational insight
The post From Connections to Meaning: Why Heterogeneous Graph Transformers (HGT) Change Demand Forecasting appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
PVH reimagines the future of fashion with OpenAIOpenAI News PVH Corp., parent company of Calvin Klein and Tommy Hilfiger, is adopting ChatGPT Enterprise to bring AI into fashion design, supply chain, and consumer engagement.
PVH Corp., parent company of Calvin Klein and Tommy Hilfiger, is adopting ChatGPT Enterprise to bring AI into fashion design, supply chain, and consumer engagement. Read More
Privacy in Human-AI Romantic Relationships: Concerns, Boundaries, and Agency AI updates on arXiv.org
Privacy in Human-AI Romantic Relationships: Concerns, Boundaries, and Agencycs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.16824v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: An increasing number of LLM-based applications are being developed to facilitate romantic relationships with AI partners, yet the safety and privacy risks in these partnerships remain largely underexplored. In this work, we investigate privacy in human-AI romantic relationships through an interview study (N=17), examining participants’ experiences and privacy perceptions across stages of exploration, intimacy, and dissolution, alongside platforms they used. We found that these relationships took varied forms, from one-to-one to one-to-many, and were shaped by multiple actors, including creators, platforms, and moderators. AI partners were perceived as having agency, actively negotiating privacy boundaries with participants and sometimes encouraging disclosure of personal details. As intimacy deepened, these boundaries became more permeable, though some participants voiced concerns such as conversation exposure and sought to preserve anonymity. Overall, platform affordances and diverse romantic dynamics expand the privacy landscape, underscoring the need to rethink how privacy is constructed in human-AI intimacy.
arXiv:2601.16824v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: An increasing number of LLM-based applications are being developed to facilitate romantic relationships with AI partners, yet the safety and privacy risks in these partnerships remain largely underexplored. In this work, we investigate privacy in human-AI romantic relationships through an interview study (N=17), examining participants’ experiences and privacy perceptions across stages of exploration, intimacy, and dissolution, alongside platforms they used. We found that these relationships took varied forms, from one-to-one to one-to-many, and were shaped by multiple actors, including creators, platforms, and moderators. AI partners were perceived as having agency, actively negotiating privacy boundaries with participants and sometimes encouraging disclosure of personal details. As intimacy deepened, these boundaries became more permeable, though some participants voiced concerns such as conversation exposure and sought to preserve anonymity. Overall, platform affordances and diverse romantic dynamics expand the privacy landscape, underscoring the need to rethink how privacy is constructed in human-AI intimacy. Read More
Generative Confidants: How do People Experience Trust in Emotional Support from Generative AI?cs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.16656v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: People are increasingly turning to generative AI (e.g., ChatGPT, Gemini, Copilot) for emotional support and companionship. While trust is likely to play a central role in enabling these informal and unsupervised interactions, we still lack an understanding of how people develop and experience it in this context. Seeking to fill this gap, we recruited 24 frequent users of generative AI for emotional support and conducted a qualitative study consisting of diary entries about interactions, transcripts of chats with AI, and in-depth interviews. Our results suggest important novel drivers of trust in this context: familiarity emerging from personalisation, nuanced mental models of generative AI, and awareness of people’s control over conversations. Notably, generative AI’s homogeneous use of personalised, positive, and persuasive language appears to promote some of these trust-building factors. However, this also seems to discourage other trust-related behaviours, such as remembering that generative AI is a machine trained to converse in human language. We present implications for future research that are likely to become critical as the use of generative AI for emotional support increasingly overlaps with therapeutic work.
arXiv:2601.16656v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: People are increasingly turning to generative AI (e.g., ChatGPT, Gemini, Copilot) for emotional support and companionship. While trust is likely to play a central role in enabling these informal and unsupervised interactions, we still lack an understanding of how people develop and experience it in this context. Seeking to fill this gap, we recruited 24 frequent users of generative AI for emotional support and conducted a qualitative study consisting of diary entries about interactions, transcripts of chats with AI, and in-depth interviews. Our results suggest important novel drivers of trust in this context: familiarity emerging from personalisation, nuanced mental models of generative AI, and awareness of people’s control over conversations. Notably, generative AI’s homogeneous use of personalised, positive, and persuasive language appears to promote some of these trust-building factors. However, this also seems to discourage other trust-related behaviours, such as remembering that generative AI is a machine trained to converse in human language. We present implications for future research that are likely to become critical as the use of generative AI for emotional support increasingly overlaps with therapeutic work. Read More
DSGym: A Holistic Framework for Evaluating and Training Data Science Agentscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.16344v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Data science agents promise to accelerate discovery and insight-generation by turning data into executable analyses and findings. Yet existing data science benchmarks fall short due to fragmented evaluation interfaces that make cross-benchmark comparison difficult, narrow task coverage and a lack of rigorous data grounding. In particular, we show that a substantial portion of tasks in current benchmarks can be solved without using the actual data. To address these limitations, we introduce DSGym, a standardized framework for evaluating and training data science agents in self-contained execution environments. Unlike static benchmarks, DSGym provides a modular architecture that makes it easy to add tasks, agent scaffolds, and tools, positioning it as a live, extensible testbed. We curate DSGym-Tasks, a holistic task suite that standardizes and refines existing benchmarks via quality and shortcut solvability filtering. We further expand coverage with (1) DSBio: expert-derived bioinformatics tasks grounded in literature and (2) DSPredict: challenging prediction tasks spanning domains such as computer vision, molecular prediction, and single-cell perturbation. Beyond evaluation, DSGym enables agent training via execution-verified data synthesis pipeline. As a case study, we build a 2,000-example training set and trained a 4B model in DSGym that outperforms GPT-4o on standardized analysis benchmarks. Overall, DSGym enables rigorous end-to-end measurement of whether agents can plan, implement, and validate data analyses in realistic scientific context.
arXiv:2601.16344v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Data science agents promise to accelerate discovery and insight-generation by turning data into executable analyses and findings. Yet existing data science benchmarks fall short due to fragmented evaluation interfaces that make cross-benchmark comparison difficult, narrow task coverage and a lack of rigorous data grounding. In particular, we show that a substantial portion of tasks in current benchmarks can be solved without using the actual data. To address these limitations, we introduce DSGym, a standardized framework for evaluating and training data science agents in self-contained execution environments. Unlike static benchmarks, DSGym provides a modular architecture that makes it easy to add tasks, agent scaffolds, and tools, positioning it as a live, extensible testbed. We curate DSGym-Tasks, a holistic task suite that standardizes and refines existing benchmarks via quality and shortcut solvability filtering. We further expand coverage with (1) DSBio: expert-derived bioinformatics tasks grounded in literature and (2) DSPredict: challenging prediction tasks spanning domains such as computer vision, molecular prediction, and single-cell perturbation. Beyond evaluation, DSGym enables agent training via execution-verified data synthesis pipeline. As a case study, we build a 2,000-example training set and trained a 4B model in DSGym that outperforms GPT-4o on standardized analysis benchmarks. Overall, DSGym enables rigorous end-to-end measurement of whether agents can plan, implement, and validate data analyses in realistic scientific context. Read More
7 Under-the-Radar Python Libraries for Scalable Feature EngineeringKDnuggets This article lists 7 under-the-radar Python libraries that push the boundaries of feature engineering processes at scale.
This article lists 7 under-the-radar Python libraries that push the boundaries of feature engineering processes at scale. Read More