How e& is using HR to bring AI into enterprise operationsAI News For many enterprises, the first real test of AI is not customer-facing products or flashy automation demos. It is the quiet machinery that runs the organisation itself. Human resources, with its mix of routine workflows, compliance needs, and large volumes of structured data, is emerging as one of the earliest areas where companies are pushing
The post How e& is using HR to bring AI into enterprise operations appeared first on AI News.
For many enterprises, the first real test of AI is not customer-facing products or flashy automation demos. It is the quiet machinery that runs the organisation itself. Human resources, with its mix of routine workflows, compliance needs, and large volumes of structured data, is emerging as one of the earliest areas where companies are pushing
The post How e& is using HR to bring AI into enterprise operations appeared first on AI News. Read More
Alibaba enters physical AI race with open-source robot model RynnBrainAI News Alibaba has entered the race to build AI that powers robots, not just chatbots. The Chinese tech giant this week unveiled RynnBrain, an open-source model designed to help robots perceive their environment and execute physical tasks. The move signals China’s accelerating push into physical AI as ageing populations and labour shortages drive demand for machines
The post Alibaba enters physical AI race with open-source robot model RynnBrain appeared first on AI News.
Alibaba has entered the race to build AI that powers robots, not just chatbots. The Chinese tech giant this week unveiled RynnBrain, an open-source model designed to help robots perceive their environment and execute physical tasks. The move signals China’s accelerating push into physical AI as ageing populations and labour shortages drive demand for machines
The post Alibaba enters physical AI race with open-source robot model RynnBrain appeared first on AI News. Read More
AI deployment in financial services hits an inflection point as Singapore leads the shift to productionAI News AI deployment in financial services has crossed a critical threshold, with only 2% of institutions globally reporting no AI use whatsoever—a dramatic indicator that the technology has moved decisively from boardroom discussion to operational reality. New research from Finastra surveying 1,509 senior leaders across 11 markets reveals that Singapore financial institutions are leading this transition,
The post AI deployment in financial services hits an inflection point as Singapore leads the shift to production appeared first on AI News.
AI deployment in financial services has crossed a critical threshold, with only 2% of institutions globally reporting no AI use whatsoever—a dramatic indicator that the technology has moved decisively from boardroom discussion to operational reality. New research from Finastra surveying 1,509 senior leaders across 11 markets reveals that Singapore financial institutions are leading this transition,
The post AI deployment in financial services hits an inflection point as Singapore leads the shift to production appeared first on AI News. Read More
Building Vertex AI Search Applications: A Comprehensive GuideKDnuggets This guide explores the essential components, implementation strategies, and best practices for building production-ready search applications using Vertex AI Search and AI Applications.
This guide explores the essential components, implementation strategies, and best practices for building production-ready search applications using Vertex AI Search and AI Applications. Read More
The Evolving Role of the ML EngineerTowards Data Science Stephanie Kirmer on the $200 billion investment bubble, how AI companies can rebuild trust, and how her day-to-day work changed with the rise of LLMs.
The post The Evolving Role of the ML Engineer appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Stephanie Kirmer on the $200 billion investment bubble, how AI companies can rebuild trust, and how her day-to-day work changed with the rise of LLMs.
The post The Evolving Role of the ML Engineer appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
12 Python Libraries You Need to Try in 2026KDnuggets These are 12 Python libraries that made waves in 2025, and that every developer should try in 2026.
These are 12 Python libraries that made waves in 2025, and that every developer should try in 2026. Read More
Microsoft has fixed a known issue causing its Family Safety parental control service to block Windows users from launching Google Chrome and other web browsers. […] Read More
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a malicious Google Chrome extension that’s designed to steal data associated with Meta Business Suite and Facebook Business Manager. The extension, named CL Suite by @CLMasters (ID: jkphinfhmfkckkcnifhjiplhfoiefffl), is marketed as a way to scrape Meta Business Suite data, remove verification pop-ups, and generate two-factor authentication (2FA) codes. Read More
Criminal IP now integrates with IBM QRadar SIEM and SOAR to bring external IP-based threat intelligence directly into detection and response workflows. See how risk scoring and automated enrichment help SOC teams prioritize high-risk IPs and accelerate investigations without leaving QRadar. […] Read More
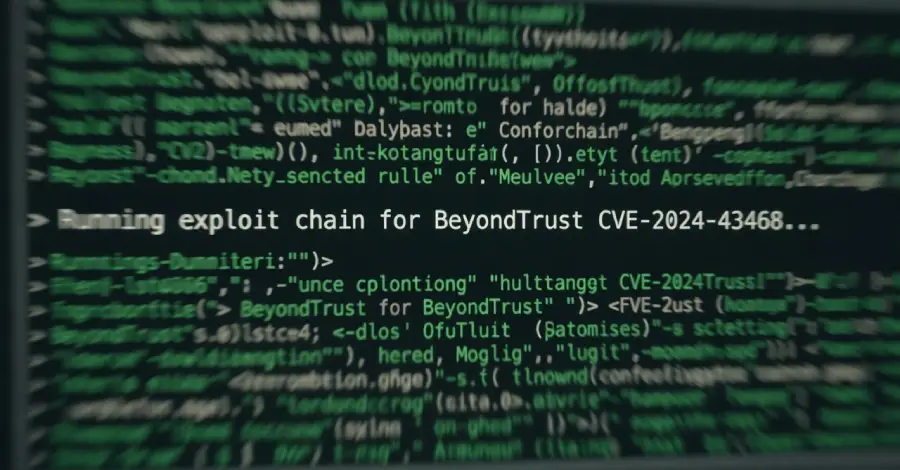
Threat actors have started to exploit a recently disclosed critical security flaw impacting BeyondTrust Remote Support (RS) and Privileged Remote Access (PRA) products, according to watchTowr. “Overnight we observed first in-the-wild exploitation of BeyondTrust across our global sensors,” Ryan Dewhurst, head of threat intelligence at watchTowr, said in a post on X. “Attackers are abusing Read […]