Realistic threat perception drives intergroup conflict: A causal, dynamic analysis using generative-agent simulationscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.17066v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Human conflict is often attributed to threats against material conditions and symbolic values, yet it remains unclear how they interact and which dominates. Progress is limited by weak causal control, ethical constraints, and scarce temporal data. We address these barriers using simulations of large language model (LLM)-driven agents in virtual societies, independently varying realistic and symbolic threat while tracking actions, language, and attitudes. Representational analyses show that the underlying LLM encodes realistic threat, symbolic threat, and hostility as distinct internal states, that our manipulations map onto them, and that steering these states causally shifts behavior. Our simulations provide a causal account of threat-driven conflict over time: realistic threat directly increases hostility, whereas symbolic threat effects are weaker, fully mediated by ingroup bias, and increase hostility only when realistic threat is absent. Non-hostile intergroup contact buffers escalation, and structural asymmetries concentrate hostility among majority groups.
arXiv:2512.17066v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Human conflict is often attributed to threats against material conditions and symbolic values, yet it remains unclear how they interact and which dominates. Progress is limited by weak causal control, ethical constraints, and scarce temporal data. We address these barriers using simulations of large language model (LLM)-driven agents in virtual societies, independently varying realistic and symbolic threat while tracking actions, language, and attitudes. Representational analyses show that the underlying LLM encodes realistic threat, symbolic threat, and hostility as distinct internal states, that our manipulations map onto them, and that steering these states causally shifts behavior. Our simulations provide a causal account of threat-driven conflict over time: realistic threat directly increases hostility, whereas symbolic threat effects are weaker, fully mediated by ingroup bias, and increase hostility only when realistic threat is absent. Non-hostile intergroup contact buffers escalation, and structural asymmetries concentrate hostility among majority groups. Read More
Solomonoff-Inspired Hypothesis Ranking with LLMs for Prediction Under Uncertaintycs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.17145v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Reasoning under uncertainty is a key challenge in AI, especially for real-world tasks, where problems with sparse data demands systematic generalisation. Existing approaches struggle to balance accuracy and simplicity when evaluating multiple candidate solutions. We propose a Solomonoff-inspired method that weights LLM-generated hypotheses by simplicity and predictive fit. Applied to benchmark (Mini-ARC) tasks, our method produces Solomonoff-weighted mixtures for per-cell predictions, yielding conservative, uncertainty-aware outputs even when hypotheses are noisy or partially incorrect. Compared to Bayesian Model Averaging (BMA), Solomonoff scoring spreads probability more evenly across competing hypotheses, while BMA concentrates weight on the most likely but potentially flawed candidates. Across tasks, this highlights the value of algorithmic information-theoretic priors for interpretable, reliable multi-hypothesis reasoning under uncertainty.
arXiv:2512.17145v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Reasoning under uncertainty is a key challenge in AI, especially for real-world tasks, where problems with sparse data demands systematic generalisation. Existing approaches struggle to balance accuracy and simplicity when evaluating multiple candidate solutions. We propose a Solomonoff-inspired method that weights LLM-generated hypotheses by simplicity and predictive fit. Applied to benchmark (Mini-ARC) tasks, our method produces Solomonoff-weighted mixtures for per-cell predictions, yielding conservative, uncertainty-aware outputs even when hypotheses are noisy or partially incorrect. Compared to Bayesian Model Averaging (BMA), Solomonoff scoring spreads probability more evenly across competing hypotheses, while BMA concentrates weight on the most likely but potentially flawed candidates. Across tasks, this highlights the value of algorithmic information-theoretic priors for interpretable, reliable multi-hypothesis reasoning under uncertainty. Read More
Over 115,000 WatchGuard Firebox devices exposed online remain unpatched against a critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability actively exploited in attacks. […] Read More
Cyber threats last week showed how attackers no longer need big hacks to cause big damage. They’re going after the everyday tools we trust most — firewalls, browser add-ons, and even smart TVs — turning small cracks into serious breaches. The real danger now isn’t just one major attack, but hundreds of quiet ones using […]
As the internet becomes an essential part of daily life, its environmental footprint continues to grow. Data centers, constant connectivity, and resource-heavy browsing habits all contribute to energy consumption and digital waste. While individual users may not see this impact directly, the collective effect of everyday browsing is significant. Choosing a browser designed with Read More
The Machine Learning “Advent Calendar” Day 21: Gradient Boosted Decision Tree Regressor in ExcelTowards Data Science Gradient descent in function space with decision trees
The post The Machine Learning “Advent Calendar” Day 21: Gradient Boosted Decision Tree Regressor in Excel appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Gradient descent in function space with decision trees
The post The Machine Learning “Advent Calendar” Day 21: Gradient Boosted Decision Tree Regressor in Excel appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
The RansomHouse ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) has recently upgraded its encryptor, switching from a relatively simple single-phase linear technique to a more complex, multi-layered method. […] Read More
NVIDIA AI Releases Nemotron 3: A Hybrid Mamba Transformer MoE Stack for Long Context Agentic AIMarkTechPost NVIDIA has released the Nemotron 3 family of open models as part of a full stack for agentic AI, including model weights, datasets and reinforcement learning tools. The family has three sizes, Nano, Super and Ultra, and targets multi agent systems that need long context reasoning with tight control over inference cost. Nano has about
The post NVIDIA AI Releases Nemotron 3: A Hybrid Mamba Transformer MoE Stack for Long Context Agentic AI appeared first on MarkTechPost.
NVIDIA has released the Nemotron 3 family of open models as part of a full stack for agentic AI, including model weights, datasets and reinforcement learning tools. The family has three sizes, Nano, Super and Ultra, and targets multi agent systems that need long context reasoning with tight control over inference cost. Nano has about
The post NVIDIA AI Releases Nemotron 3: A Hybrid Mamba Transformer MoE Stack for Long Context Agentic AI appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Threat hunters have discerned new activity associated with an Iranian threat actor known as Infy (aka Prince of Persia), nearly five years after the hacking group was observed targeting victims in Sweden, the Netherlands, and Turkey. “The scale of Prince of Persia’s activity is more significant than we originally anticipated,” Tomer Bar, vice president of […]
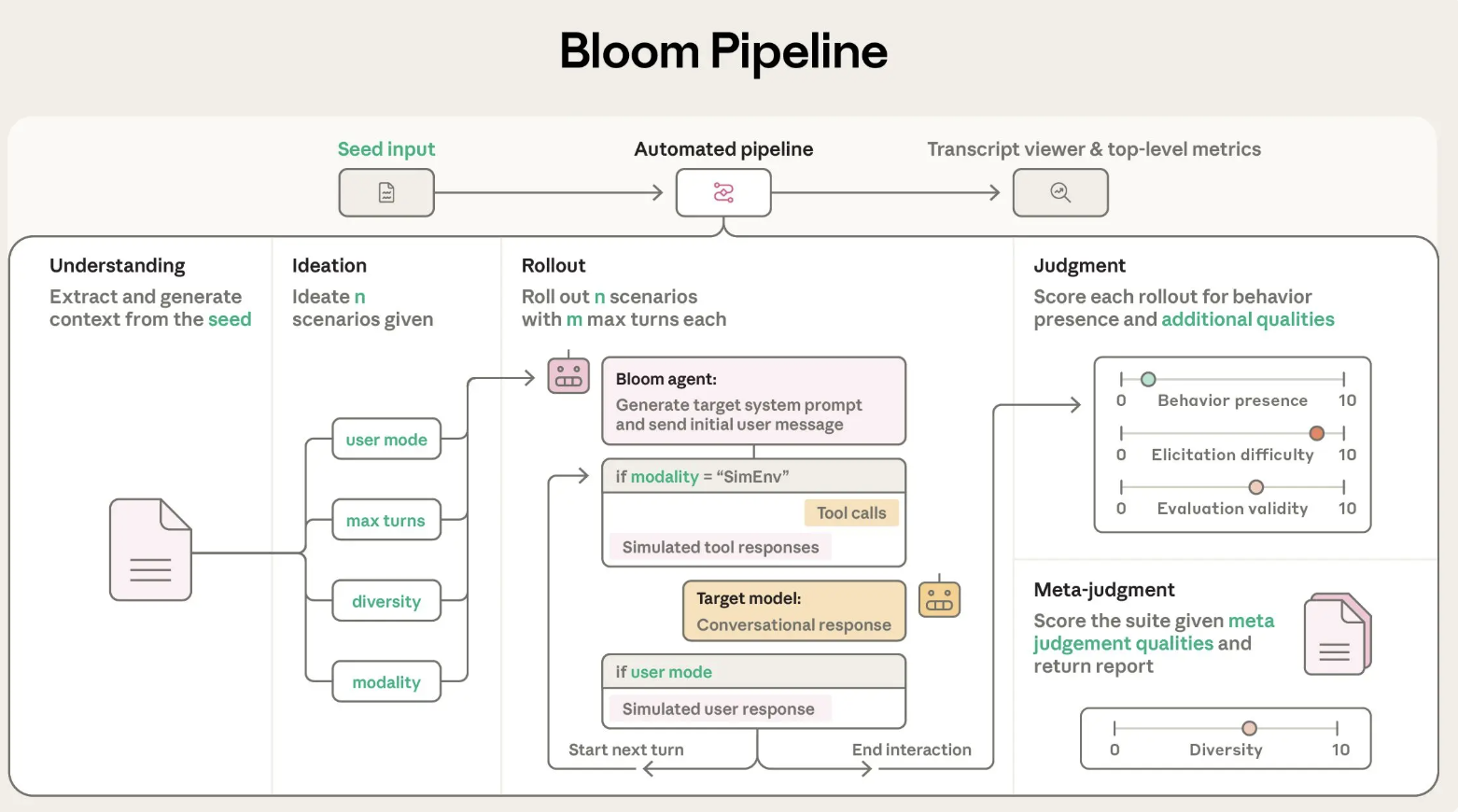
Anthropic AI Releases Bloom: An Open-Source Agentic Framework for Automated Behavioral Evaluations of Frontier AI ModelsMarkTechPost Anthropic has released Bloom, an open source agentic framework that automates behavioral evaluations for frontier AI models. The system takes a researcher specified behavior and builds targeted evaluations that measure how often and how strongly that behavior appears in realistic scenarios. Why Bloom? Behavioral evaluations for safety and alignment are expensive to design and maintain.
The post Anthropic AI Releases Bloom: An Open-Source Agentic Framework for Automated Behavioral Evaluations of Frontier AI Models appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Anthropic has released Bloom, an open source agentic framework that automates behavioral evaluations for frontier AI models. The system takes a researcher specified behavior and builds targeted evaluations that measure how often and how strongly that behavior appears in realistic scenarios. Why Bloom? Behavioral evaluations for safety and alignment are expensive to design and maintain.
The post Anthropic AI Releases Bloom: An Open-Source Agentic Framework for Automated Behavioral Evaluations of Frontier AI Models appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More