A data-driven framework for team selection in Fantasy Premier Leaguecs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2505.02170v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Fantasy football is a billion-dollar industry with millions of participants. Under a fixed budget, managers select squads to maximize future Fantasy Premier League (FPL) points. This study formulates lineup selection as data-driven optimization and develops deterministic and robust mixed-integer linear programs that choose the starting eleven, bench, and captain under budget, formation, and club-quota constraints (maximum three players per club). The objective is parameterized by a hybrid scoring metric that combines realized FPL points with predictions from a linear regression model trained on match-performance features identified using exploratory data analysis techniques. The study benchmarks alternative objectives and cost estimators, including simple and recency-weighted averages, exponential smoothing, autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA), and Monte Carlo simulation. Experiments on the 2023/24 Premier League season show that ARIMA with a constrained budget and a rolling window yields the most consistent out-of-sample performance; weighted averages and Monte Carlo are also competitive. Robust variants and hybrid scoring metrics improve some objectives but are not uniformly superior. The framework provides transparent decision support for fantasy roster construction and extends to FPL chips, multi-week rolling-horizon transfer planning, and week-by-week dynamic captaincy.
arXiv:2505.02170v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Fantasy football is a billion-dollar industry with millions of participants. Under a fixed budget, managers select squads to maximize future Fantasy Premier League (FPL) points. This study formulates lineup selection as data-driven optimization and develops deterministic and robust mixed-integer linear programs that choose the starting eleven, bench, and captain under budget, formation, and club-quota constraints (maximum three players per club). The objective is parameterized by a hybrid scoring metric that combines realized FPL points with predictions from a linear regression model trained on match-performance features identified using exploratory data analysis techniques. The study benchmarks alternative objectives and cost estimators, including simple and recency-weighted averages, exponential smoothing, autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA), and Monte Carlo simulation. Experiments on the 2023/24 Premier League season show that ARIMA with a constrained budget and a rolling window yields the most consistent out-of-sample performance; weighted averages and Monte Carlo are also competitive. Robust variants and hybrid scoring metrics improve some objectives but are not uniformly superior. The framework provides transparent decision support for fantasy roster construction and extends to FPL chips, multi-week rolling-horizon transfer planning, and week-by-week dynamic captaincy. Read More
How to make Medical AI Systems safer? Simulating Vulnerabilities, and Threats in Multimodal Medical RAG Systemcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2508.17215v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) augmented with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) are increasingly employed in medical AI to enhance factual grounding through external clinical image-text retrieval. However, this reliance creates a significant attack surface. We propose MedThreatRAG, a novel multimodal poisoning framework that systematically probes vulnerabilities in medical RAG systems by injecting adversarial image-text pairs. A key innovation of our approach is the construction of a simulated semi-open attack environment, mimicking real-world medical systems that permit periodic knowledge base updates via user or pipeline contributions. Within this setting, we introduce and emphasize Cross-Modal Conflict Injection (CMCI), which embeds subtle semantic contradictions between medical images and their paired reports. These mismatches degrade retrieval and generation by disrupting cross-modal alignment while remaining sufficiently plausible to evade conventional filters. While basic textual and visual attacks are included for completeness, CMCI demonstrates the most severe degradation. Evaluations on IU-Xray and MIMIC-CXR QA tasks show that MedThreatRAG reduces answer F1 scores by up to 27.66% and lowers LLaVA-Med-1.5 F1 rates to as low as 51.36%. Our findings expose fundamental security gaps in clinical RAG systems and highlight the urgent need for threat-aware design and robust multimodal consistency checks. Finally, we conclude with a concise set of guidelines to inform the safe development of future multimodal medical RAG systems.
arXiv:2508.17215v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) augmented with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) are increasingly employed in medical AI to enhance factual grounding through external clinical image-text retrieval. However, this reliance creates a significant attack surface. We propose MedThreatRAG, a novel multimodal poisoning framework that systematically probes vulnerabilities in medical RAG systems by injecting adversarial image-text pairs. A key innovation of our approach is the construction of a simulated semi-open attack environment, mimicking real-world medical systems that permit periodic knowledge base updates via user or pipeline contributions. Within this setting, we introduce and emphasize Cross-Modal Conflict Injection (CMCI), which embeds subtle semantic contradictions between medical images and their paired reports. These mismatches degrade retrieval and generation by disrupting cross-modal alignment while remaining sufficiently plausible to evade conventional filters. While basic textual and visual attacks are included for completeness, CMCI demonstrates the most severe degradation. Evaluations on IU-Xray and MIMIC-CXR QA tasks show that MedThreatRAG reduces answer F1 scores by up to 27.66% and lowers LLaVA-Med-1.5 F1 rates to as low as 51.36%. Our findings expose fundamental security gaps in clinical RAG systems and highlight the urgent need for threat-aware design and robust multimodal consistency checks. Finally, we conclude with a concise set of guidelines to inform the safe development of future multimodal medical RAG systems. Read More
Routing by Analogy: kNN-Augmented Expert Assignment for Mixture-of-Expertscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.02144v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures scale large language models efficiently by employing a parametric “router” to dispatch tokens to a sparse subset of experts. Typically, this router is trained once and then frozen, rendering routing decisions brittle under distribution shifts. We address this limitation by introducing kNN-MoE, a retrieval-augmented routing framework that reuses optimal expert assignments from a memory of similar past cases. This memory is constructed offline by directly optimizing token-wise routing logits to maximize the likelihood on a reference set. Crucially, we use the aggregate similarity of retrieved neighbors as a confidence-driven mixing coefficient, thus allowing the method to fall back to the frozen router when no relevant cases are found. Experiments show kNN-MoE outperforms zero-shot baselines and rivals computationally expensive supervised fine-tuning.
arXiv:2601.02144v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures scale large language models efficiently by employing a parametric “router” to dispatch tokens to a sparse subset of experts. Typically, this router is trained once and then frozen, rendering routing decisions brittle under distribution shifts. We address this limitation by introducing kNN-MoE, a retrieval-augmented routing framework that reuses optimal expert assignments from a memory of similar past cases. This memory is constructed offline by directly optimizing token-wise routing logits to maximize the likelihood on a reference set. Crucially, we use the aggregate similarity of retrieved neighbors as a confidence-driven mixing coefficient, thus allowing the method to fall back to the frozen router when no relevant cases are found. Experiments show kNN-MoE outperforms zero-shot baselines and rivals computationally expensive supervised fine-tuning. Read More
Claims administration and risk management company Sedgwick has confirmed that its federal contractor subsidiary, Sedgwick Government Solutions, was the victim of a security breach. […] Read More
The CERT Coordination Center (CERT/CC) has disclosed details of an unpatched security flaw impacting TOTOLINK EX200 wireless range extender that could allow a remote authenticated attacker to gain full control of the device. The flaw, CVE-2025-65606 (CVSS score: N/A), has been characterized as a flaw in the firmware-upload error-handling logic, which could cause the device […]
How to Design an Agentic AI Architecture with LangGraph and OpenAI Using Adaptive Deliberation, Memory Graphs, and Reflexion LoopsMarkTechPost In this tutorial, we build a genuinely advanced Agentic AI system using LangGraph and OpenAI models by going beyond simple planner, executor loops. We implement adaptive deliberation, where the agent dynamically decides between fast and deep reasoning; a Zettelkasten-style agentic memory graph that stores atomic knowledge and automatically links related experiences; and a governed tool-use
The post How to Design an Agentic AI Architecture with LangGraph and OpenAI Using Adaptive Deliberation, Memory Graphs, and Reflexion Loops appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In this tutorial, we build a genuinely advanced Agentic AI system using LangGraph and OpenAI models by going beyond simple planner, executor loops. We implement adaptive deliberation, where the agent dynamically decides between fast and deep reasoning; a Zettelkasten-style agentic memory graph that stores atomic knowledge and automatically links related experiences; and a governed tool-use
The post How to Design an Agentic AI Architecture with LangGraph and OpenAI Using Adaptive Deliberation, Memory Graphs, and Reflexion Loops appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
The 10 AI Developments That Defined 2025KDnuggets In this article, we retroactively analyze what I would consider the ten most consequential, broadly impactful AI storylines of 2025, and gain insight into where the field is going in 2026.
In this article, we retroactively analyze what I would consider the ten most consequential, broadly impactful AI storylines of 2025, and gain insight into where the field is going in 2026. Read More
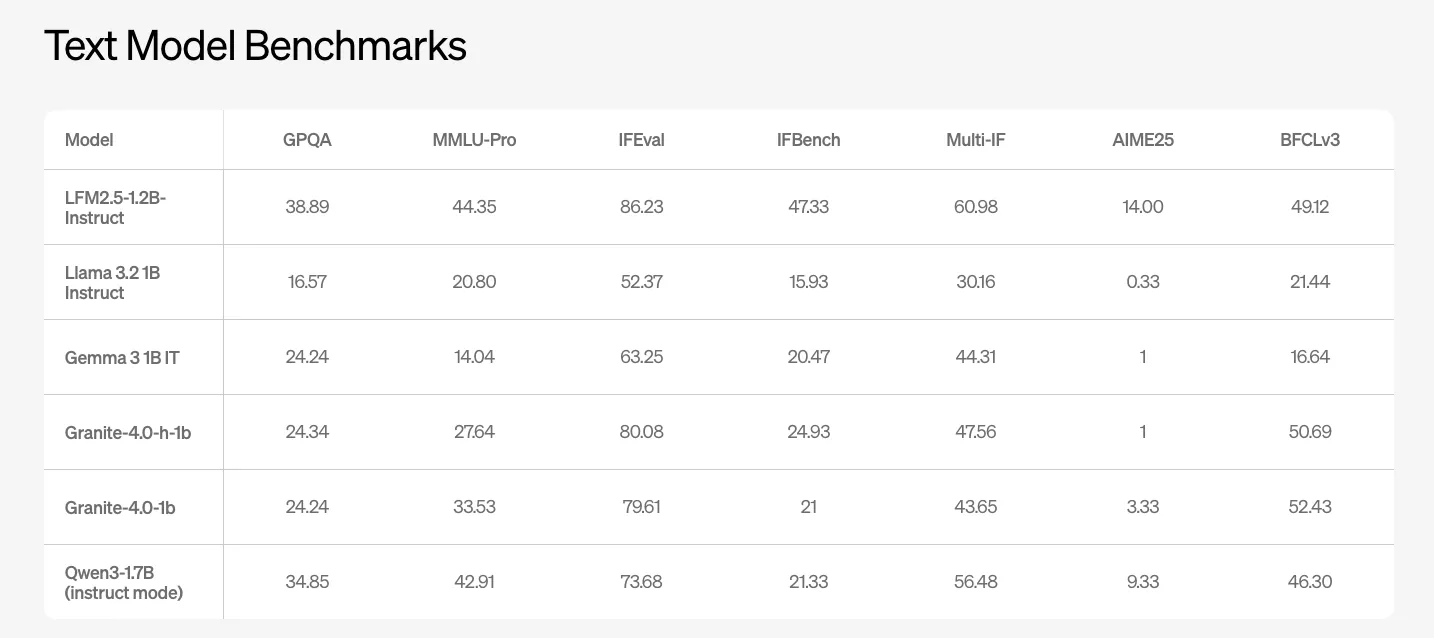
Liquid AI Releases LFM2.5: A Compact AI Model Family For Real On Device AgentsMarkTechPost Liquid AI has introduced LFM2.5, a new generation of small foundation models built on the LFM2 architecture and focused at on device and edge deployments. The model family includes LFM2.5-1.2B-Base and LFM2.5-1.2B-Instruct and extends to Japanese, vision language, and audio language variants. It is released as open weights on Hugging Face and exposed through the
The post Liquid AI Releases LFM2.5: A Compact AI Model Family For Real On Device Agents appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Liquid AI has introduced LFM2.5, a new generation of small foundation models built on the LFM2 architecture and focused at on device and edge deployments. The model family includes LFM2.5-1.2B-Base and LFM2.5-1.2B-Instruct and extends to Japanese, vision language, and audio language variants. It is released as open weights on Hugging Face and exposed through the
The post Liquid AI Releases LFM2.5: A Compact AI Model Family For Real On Device Agents appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Measuring What Matters with NeMo Agent ToolkitTowards Data Science A practical guide to observability, evaluations, and model comparisons
The post Measuring What Matters with NeMo Agent Toolkit appeared first on Towards Data Science.
A practical guide to observability, evaluations, and model comparisons
The post Measuring What Matters with NeMo Agent Toolkit appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
Threat actors are exploiting a recently discovered command injection vulnerability that affects multiple D-Link DSL gateway routers that went out of support years ago. […] Read More