CPGPrompt: Translating Clinical Guidelines into LLM-Executable Decision Supportcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.03475v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) provide evidence-based recommendations for patient care; however, integrating them into Artificial Intelligence (AI) remains challenging. Previous approaches, such as rule-based systems, face significant limitations, including poor interpretability, inconsistent adherence to guidelines, and narrow domain applicability. To address this, we develop and validate CPGPrompt, an auto-prompting system that converts narrative clinical guidelines into large language models (LLMs).
Our framework translates CPGs into structured decision trees and utilizes an LLM to dynamically navigate them for patient case evaluation. Synthetic vignettes were generated across three domains (headache, lower back pain, and prostate cancer) and distributed into four categories to test different decision scenarios. System performance was assessed on both binary specialty-referral decisions and fine-grained pathway-classification tasks.
The binary specialty referral classification achieved consistently strong performance across all domains (F1: 0.85-1.00), with high recall (1.00 $pm$ 0.00). In contrast, multi-class pathway assignment showed reduced performance, with domain-specific variations: headache (F1: 0.47), lower back pain (F1: 0.72), and prostate cancer (F1: 0.77). Domain-specific performance differences reflected the structure of each guideline. The headache guideline highlighted challenges with negation handling. The lower back pain guideline required temporal reasoning. In contrast, prostate cancer pathways benefited from quantifiable laboratory tests, resulting in more reliable decision-making.
arXiv:2601.03475v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) provide evidence-based recommendations for patient care; however, integrating them into Artificial Intelligence (AI) remains challenging. Previous approaches, such as rule-based systems, face significant limitations, including poor interpretability, inconsistent adherence to guidelines, and narrow domain applicability. To address this, we develop and validate CPGPrompt, an auto-prompting system that converts narrative clinical guidelines into large language models (LLMs).
Our framework translates CPGs into structured decision trees and utilizes an LLM to dynamically navigate them for patient case evaluation. Synthetic vignettes were generated across three domains (headache, lower back pain, and prostate cancer) and distributed into four categories to test different decision scenarios. System performance was assessed on both binary specialty-referral decisions and fine-grained pathway-classification tasks.
The binary specialty referral classification achieved consistently strong performance across all domains (F1: 0.85-1.00), with high recall (1.00 $pm$ 0.00). In contrast, multi-class pathway assignment showed reduced performance, with domain-specific variations: headache (F1: 0.47), lower back pain (F1: 0.72), and prostate cancer (F1: 0.77). Domain-specific performance differences reflected the structure of each guideline. The headache guideline highlighted challenges with negation handling. The lower back pain guideline required temporal reasoning. In contrast, prostate cancer pathways benefited from quantifiable laboratory tests, resulting in more reliable decision-making. Read More
New data suggests that ChatGPT is losing its market share to Gemini on the web. It’s unclear if Gemini is also gaining ground in the mobile space. […] Read More
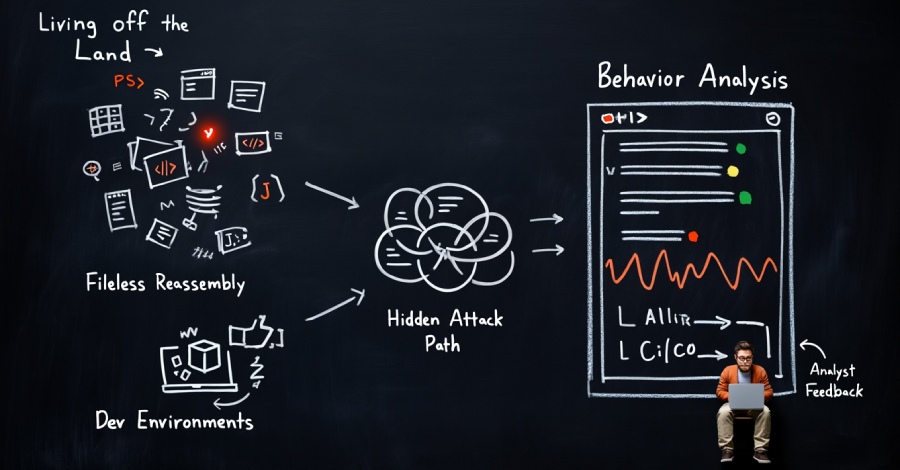
Security teams are still catching malware. The problem is what they’re not catching. More attacks today don’t arrive as files. They don’t drop binaries. They don’t trigger classic alerts. Instead, they run quietly through tools that already exist inside the environment — scripts, remote access, browsers, and developer workflows. That shift is creating a blind […]
AI, including AI Overviews on Google Search, can hallucinate and often make up stuff or offer contradicting answers when asked in two different ways. […] Read More
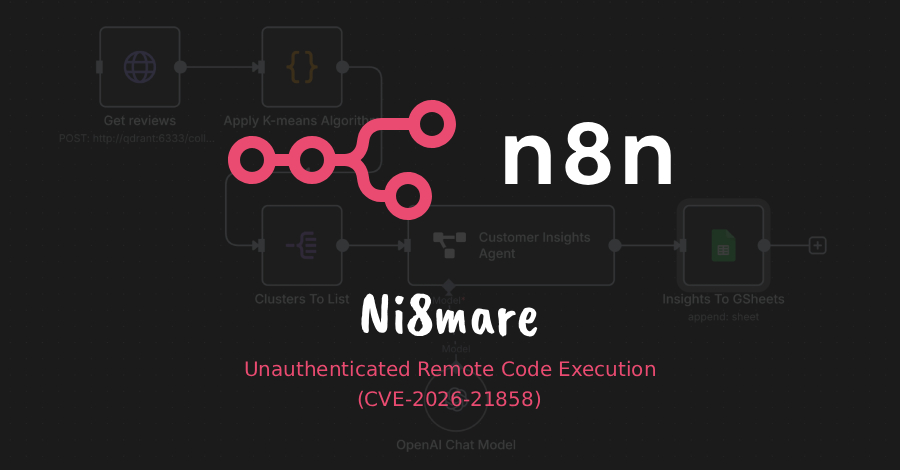
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed details of yet another maximum-severity security flaw in n8n, a popular workflow automation platform, that allows an unauthenticated remote attacker to gain complete control over susceptible instances. The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2026-21858 (CVSS score: 10.0), has been codenamed Ni8mare by Cyera Research Labs. Security researcher Dor Attias has been Read More
OpenAI is rolling out ChatGPT Health, which is a dedicated space for health conversations. Amidst privacy concerns, OpenAI said it won’t use your health data. […] Read More
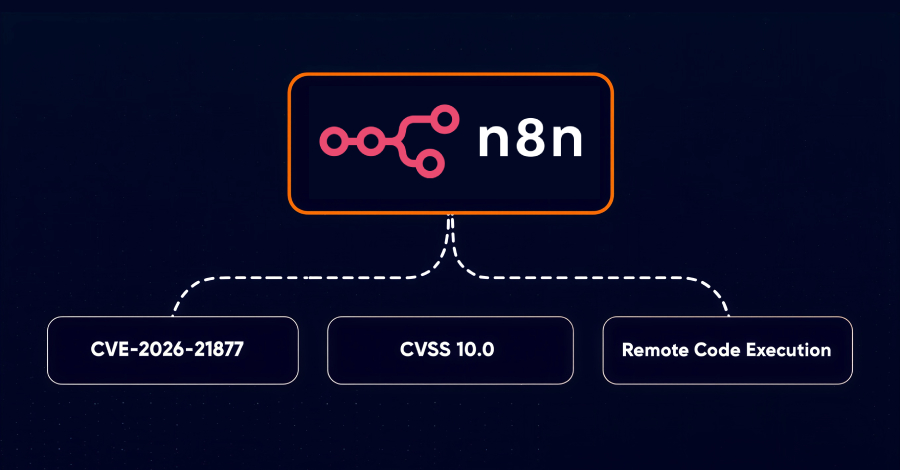
Open-source workflow automation platform n8n has warned of a maximum-severity security flaw that, if successfully exploited, could result in authenticated remote code execution (RCE). The vulnerability, which has been assigned the CVE identifier CVE-2026-21877, is rated 10.0 on the CVSS scoring system. “Under certain conditions, an authenticated user may be able to cause untrusted code […]
Why Supply Chain is the Best Domain for Data Scientists in 2026 (And How to Learn It)Towards Data Science My take after 10 years in Supply Chain on why this can be an excellent playground for data scientists who want to see their skills valued.
The post Why Supply Chain is the Best Domain for Data Scientists in 2026 (And How to Learn It) appeared first on Towards Data Science.
My take after 10 years in Supply Chain on why this can be an excellent playground for data scientists who want to see their skills valued.
The post Why Supply Chain is the Best Domain for Data Scientists in 2026 (And How to Learn It) appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
Agentic AI scaling requires new memory architectureAI News Agentic AI represents a distinct evolution from stateless chatbots toward complex workflows, and scaling it requires new memory architecture. As foundation models scale toward trillions of parameters and context windows reach millions of tokens, the computational cost of remembering history is rising faster than the ability to process it. Organisations deploying these systems now face
The post Agentic AI scaling requires new memory architecture appeared first on AI News.
Agentic AI represents a distinct evolution from stateless chatbots toward complex workflows, and scaling it requires new memory architecture. As foundation models scale toward trillions of parameters and context windows reach millions of tokens, the computational cost of remembering history is rising faster than the ability to process it. Organisations deploying these systems now face
The post Agentic AI scaling requires new memory architecture appeared first on AI News. Read More
Vibe Code Reality Check: What You Can Actually Build with Only AIKDnuggets This is an “expectations vs reality” approach to demystify, based on research of real success and failure stories, what are the capabilities and limits of vibe coding.
This is an “expectations vs reality” approach to demystify, based on research of real success and failure stories, what are the capabilities and limits of vibe coding. Read More