Microsoft announced that it will disable the 30-year-old NTLM authentication protocol by default in upcoming Windows releases due to security vulnerabilities that expose organizations to cyberattacks. […] Read More
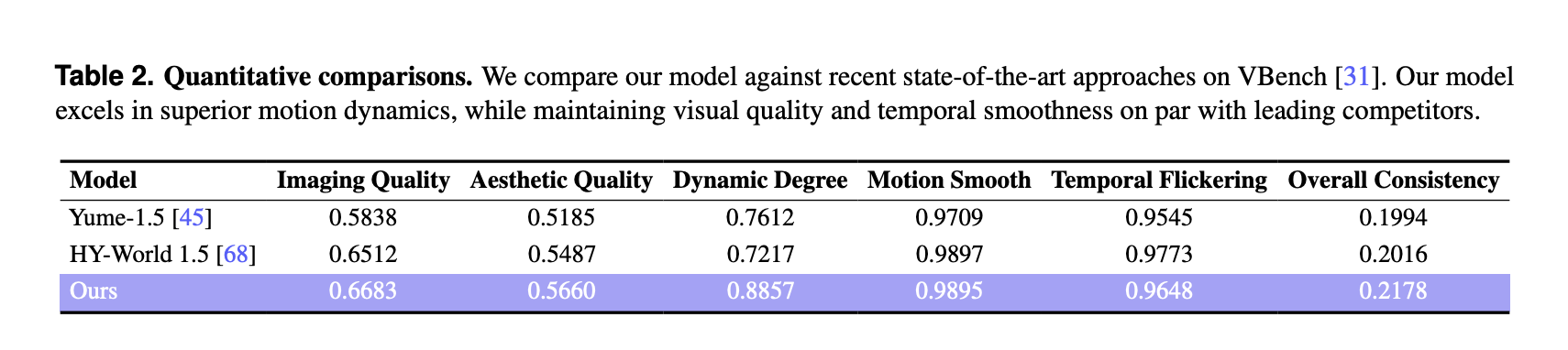
Robbyant Open Sources LingBot World: a Real Time World Model for Interactive Simulation and Embodied AIMarkTechPost Robbyant, the embodied AI unit inside Ant Group, has open sourced LingBot-World, a large scale world model that turns video generation into an interactive simulator for embodied agents, autonomous driving and games. The system is designed to render controllable environments with high visual fidelity, strong dynamics and long temporal horizons, while staying responsive enough for
The post Robbyant Open Sources LingBot World: a Real Time World Model for Interactive Simulation and Embodied AI appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Robbyant, the embodied AI unit inside Ant Group, has open sourced LingBot-World, a large scale world model that turns video generation into an interactive simulator for embodied agents, autonomous driving and games. The system is designed to render controllable environments with high visual fidelity, strong dynamics and long temporal horizons, while staying responsive enough for
The post Robbyant Open Sources LingBot World: a Real Time World Model for Interactive Simulation and Embodied AI appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
A Coding Implementation to Training, Optimizing, Evaluating, and Interpreting Knowledge Graph Embeddings with PyKEENMarkTechPost In this tutorial, we walk through an end-to-end, advanced workflow for knowledge graph embeddings using PyKEEN, actively exploring how modern embedding models are trained, evaluated, optimized, and interpreted in practice. We start by understanding the structure of a real knowledge graph dataset, then systematically train and compare multiple embedding models, tune their hyperparameters, and analyze
The post A Coding Implementation to Training, Optimizing, Evaluating, and Interpreting Knowledge Graph Embeddings with PyKEEN appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In this tutorial, we walk through an end-to-end, advanced workflow for knowledge graph embeddings using PyKEEN, actively exploring how modern embedding models are trained, evaluated, optimized, and interpreted in practice. We start by understanding the structure of a real knowledge graph dataset, then systematically train and compare multiple embedding models, tune their hyperparameters, and analyze
The post A Coding Implementation to Training, Optimizing, Evaluating, and Interpreting Knowledge Graph Embeddings with PyKEEN appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Evaluating generative AI models with Amazon Nova LLM-as-a-Judge on Amazon SageMaker AIArtificial Intelligence Evaluating the performance of large language models (LLMs) goes beyond statistical metrics like perplexity or bilingual evaluation understudy (BLEU) scores. For most real-world generative AI scenarios, it’s crucial to understand whether a model is producing better outputs than a baseline or an earlier iteration. This is especially important for applications such as summarization, content generation,
Evaluating the performance of large language models (LLMs) goes beyond statistical metrics like perplexity or bilingual evaluation understudy (BLEU) scores. For most real-world generative AI scenarios, it’s crucial to understand whether a model is producing better outputs than a baseline or an earlier iteration. This is especially important for applications such as summarization, content generation, Read More
The Tenable One AI Exposure add-on discovers unsanctioned AI use in the organization and enforces policy compliance with approved tools. Read More
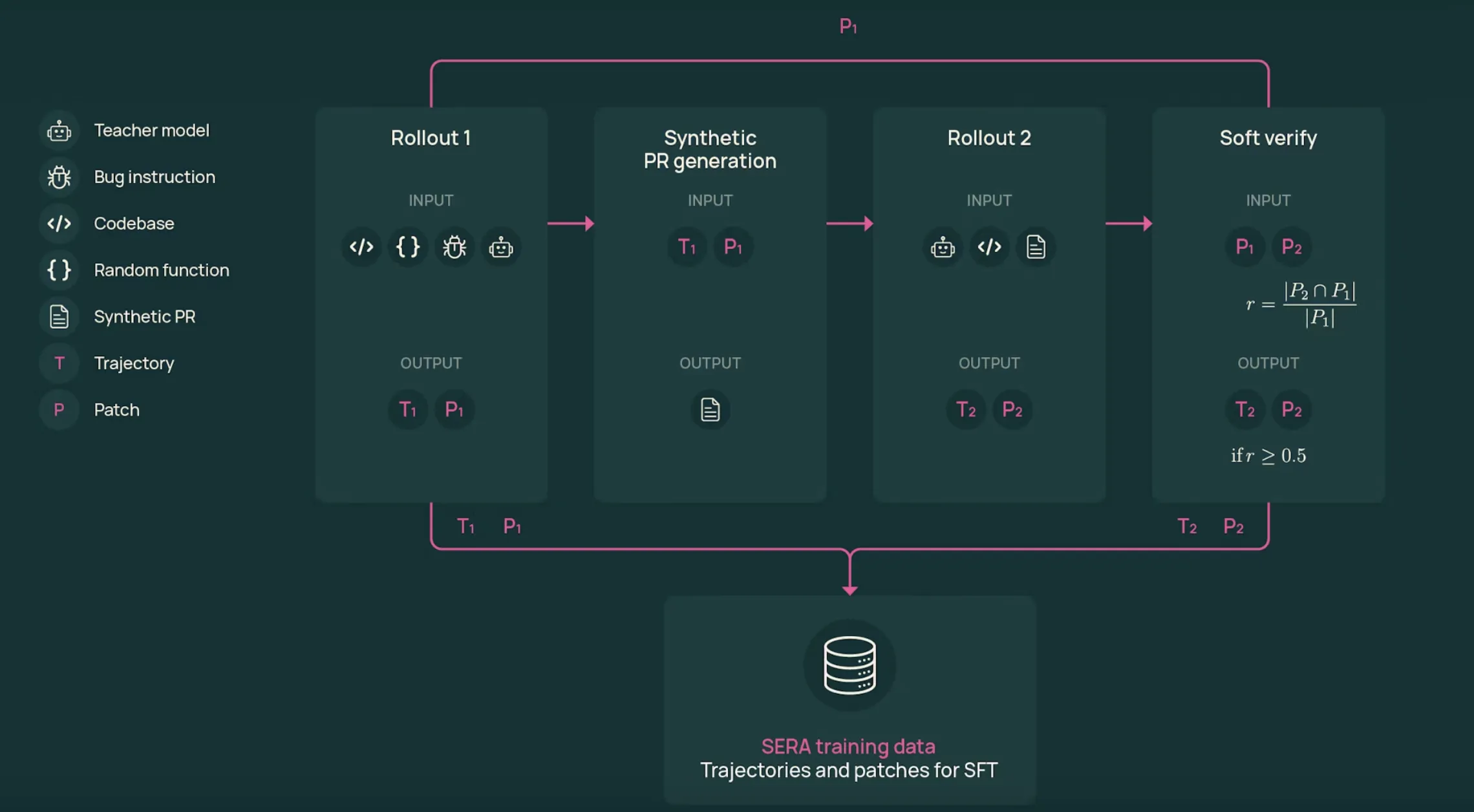
AI2 Releases SERA, Soft Verified Coding Agents Built with Supervised Training Only for Practical Repository Level Automation WorkflowsMarkTechPost Allen Institute for AI (AI2) Researchers introduce SERA, Soft Verified Efficient Repository Agents, as a coding agent family that aims to match much larger closed systems using only supervised training and synthetic trajectories. What is SERA? SERA is the first release in AI2’s Open Coding Agents series. The flagship model, SERA-32B, is built on the
The post AI2 Releases SERA, Soft Verified Coding Agents Built with Supervised Training Only for Practical Repository Level Automation Workflows appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Allen Institute for AI (AI2) Researchers introduce SERA, Soft Verified Efficient Repository Agents, as a coding agent family that aims to match much larger closed systems using only supervised training and synthetic trajectories. What is SERA? SERA is the first release in AI2’s Open Coding Agents series. The flagship model, SERA-32B, is built on the
The post AI2 Releases SERA, Soft Verified Coding Agents Built with Supervised Training Only for Practical Repository Level Automation Workflows appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
A former Google engineer accused of stealing thousands of the company’s confidential documents to build a startup in China has been convicted in the U.S., the Department of Justice (DoJ) announced Thursday. Linwei Ding (aka Leon Ding), 38, was convicted by a federal jury on seven counts of economic espionage and seven counts of theft […]
Large language models accurately predict public perceptions of support for climate action worldwidecs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.20141v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Although most people support climate action, widespread underestimation of others’ support stalls individual and systemic changes. In this preregistered experiment, we test whether large language models (LLMs) can reliably predict these perception gaps worldwide. Using country-level indicators and public opinion data from 125 countries, we benchmark four state-of-the-art LLMs against Gallup World Poll 2021/22 data and statistical regressions. LLMs, particularly Claude, accurately capture public perceptions of others’ willingness to contribute financially to climate action (MAE approximately 5 p.p.; r = .77), comparable to statistical models, though performance declines in less digitally connected, lower-GDP countries. Controlled tests show that LLMs capture the key psychological process – social projection with a systematic downward bias – and rely on structured reasoning rather than memorized values. Overall, LLMs provide a rapid tool for assessing perception gaps in climate action, serving as an alternative to costly surveys in resource-rich countries and as a complement in underrepresented populations.
arXiv:2601.20141v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Although most people support climate action, widespread underestimation of others’ support stalls individual and systemic changes. In this preregistered experiment, we test whether large language models (LLMs) can reliably predict these perception gaps worldwide. Using country-level indicators and public opinion data from 125 countries, we benchmark four state-of-the-art LLMs against Gallup World Poll 2021/22 data and statistical regressions. LLMs, particularly Claude, accurately capture public perceptions of others’ willingness to contribute financially to climate action (MAE approximately 5 p.p.; r = .77), comparable to statistical models, though performance declines in less digitally connected, lower-GDP countries. Controlled tests show that LLMs capture the key psychological process – social projection with a systematic downward bias – and rely on structured reasoning rather than memorized values. Overall, LLMs provide a rapid tool for assessing perception gaps in climate action, serving as an alternative to costly surveys in resource-rich countries and as a complement in underrepresented populations. Read More
Dynamics of Human-AI Collective Knowledge on the Web: A Scalable Model and Insights for Sustainable Growthcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.20099v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Humans and large language models (LLMs) now co-produce and co-consume the web’s shared knowledge archives. Such human-AI collective knowledge ecosystems contain feedback loops with both benefits (e.g., faster growth, easier learning) and systemic risks (e.g., quality dilution, skill reduction, model collapse). To understand such phenomena, we propose a minimal, interpretable dynamical model of the co-evolution of archive size, archive quality, model (LLM) skill, aggregate human skill, and query volume. The model captures two content inflows (human, LLM) controlled by a gate on LLM-content admissions, two learning pathways for humans (archive study vs. LLM assistance), and two LLM-training modalities (corpus-driven scaling vs. learning from human feedback). Through numerical experiments, we identify different growth regimes (e.g., healthy growth, inverted flow, inverted learning, oscillations), and show how platform and policy levers (gate strictness, LLM training, human learning pathways) shift the system across regime boundaries. Two domain configurations (PubMed, GitHub and Copilot) illustrate contrasting steady states under different growth rates and moderation norms. We also fit the model to Wikipedia’s knowledge flow during pre-ChatGPT and post-ChatGPT eras separately. We find a rise in LLM additions with a concurrent decline in human inflow, consistent with a regime identified by the model. Our model and analysis yield actionable insights for sustainable growth of human-AI collective knowledge on the Web.
arXiv:2601.20099v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Humans and large language models (LLMs) now co-produce and co-consume the web’s shared knowledge archives. Such human-AI collective knowledge ecosystems contain feedback loops with both benefits (e.g., faster growth, easier learning) and systemic risks (e.g., quality dilution, skill reduction, model collapse). To understand such phenomena, we propose a minimal, interpretable dynamical model of the co-evolution of archive size, archive quality, model (LLM) skill, aggregate human skill, and query volume. The model captures two content inflows (human, LLM) controlled by a gate on LLM-content admissions, two learning pathways for humans (archive study vs. LLM assistance), and two LLM-training modalities (corpus-driven scaling vs. learning from human feedback). Through numerical experiments, we identify different growth regimes (e.g., healthy growth, inverted flow, inverted learning, oscillations), and show how platform and policy levers (gate strictness, LLM training, human learning pathways) shift the system across regime boundaries. Two domain configurations (PubMed, GitHub and Copilot) illustrate contrasting steady states under different growth rates and moderation norms. We also fit the model to Wikipedia’s knowledge flow during pre-ChatGPT and post-ChatGPT eras separately. We find a rise in LLM additions with a concurrent decline in human inflow, consistent with a regime identified by the model. Our model and analysis yield actionable insights for sustainable growth of human-AI collective knowledge on the Web. Read More
How AI Impacts Skill Formationcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.20245v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: AI assistance produces significant productivity gains across professional domains, particularly for novice workers. Yet how this assistance affects the development of skills required to effectively supervise AI remains unclear. Novice workers who rely heavily on AI to complete unfamiliar tasks may compromise their own skill acquisition in the process. We conduct randomized experiments to study how developers gained mastery of a new asynchronous programming library with and without the assistance of AI. We find that AI use impairs conceptual understanding, code reading, and debugging abilities, without delivering significant efficiency gains on average. Participants who fully delegated coding tasks showed some productivity improvements, but at the cost of learning the library. We identify six distinct AI interaction patterns, three of which involve cognitive engagement and preserve learning outcomes even when participants receive AI assistance. Our findings suggest that AI-enhanced productivity is not a shortcut to competence and AI assistance should be carefully adopted into workflows to preserve skill formation — particularly in safety-critical domains.
arXiv:2601.20245v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: AI assistance produces significant productivity gains across professional domains, particularly for novice workers. Yet how this assistance affects the development of skills required to effectively supervise AI remains unclear. Novice workers who rely heavily on AI to complete unfamiliar tasks may compromise their own skill acquisition in the process. We conduct randomized experiments to study how developers gained mastery of a new asynchronous programming library with and without the assistance of AI. We find that AI use impairs conceptual understanding, code reading, and debugging abilities, without delivering significant efficiency gains on average. Participants who fully delegated coding tasks showed some productivity improvements, but at the cost of learning the library. We identify six distinct AI interaction patterns, three of which involve cognitive engagement and preserve learning outcomes even when participants receive AI assistance. Our findings suggest that AI-enhanced productivity is not a shortcut to competence and AI assistance should be carefully adopted into workflows to preserve skill formation — particularly in safety-critical domains. Read More