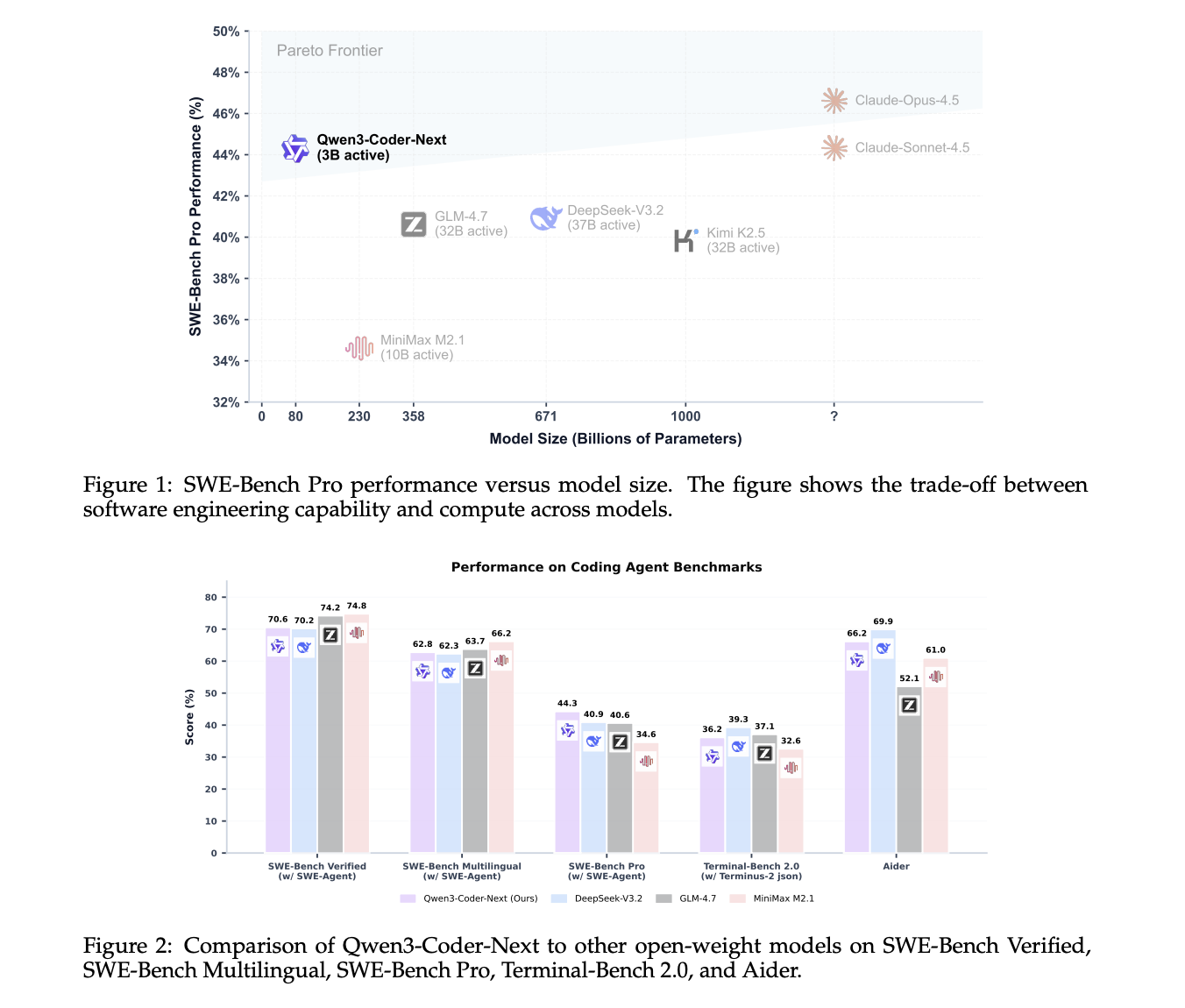
Qwen Team Releases Qwen3-Coder-Next: An Open-Weight Language Model Designed Specifically for Coding Agents and Local DevelopmentMarkTechPost Qwen team has just released Qwen3-Coder-Next, an open-weight language model designed for coding agents and local development. It sits on top of the Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B backbone. The model uses a sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture with hybrid attention. It has 80B total parameters, but only 3B parameters are activated per token. The goal is to match the
The post Qwen Team Releases Qwen3-Coder-Next: An Open-Weight Language Model Designed Specifically for Coding Agents and Local Development appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Qwen team has just released Qwen3-Coder-Next, an open-weight language model designed for coding agents and local development. It sits on top of the Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B backbone. The model uses a sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture with hybrid attention. It has 80B total parameters, but only 3B parameters are activated per token. The goal is to match the
The post Qwen Team Releases Qwen3-Coder-Next: An Open-Weight Language Model Designed Specifically for Coding Agents and Local Development appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Democratizing business intelligence: BGL’s journey with Claude Agent SDK and Amazon Bedrock AgentCoreArtificial Intelligence BGL is a leading provider of self-managed superannuation fund (SMSF) administration solutions that help individuals manage the complex compliance and reporting of their own or a client’s retirement savings, serving over 12,700 businesses across 15 countries. In this blog post, we explore how BGL built its production-ready AI agent using Claude Agent SDK and Amazon Bedrock AgentCore.
BGL is a leading provider of self-managed superannuation fund (SMSF) administration solutions that help individuals manage the complex compliance and reporting of their own or a client’s retirement savings, serving over 12,700 businesses across 15 countries. In this blog post, we explore how BGL built its production-ready AI agent using Claude Agent SDK and Amazon Bedrock AgentCore. Read More
How to Build Advanced Quantum Algorithms Using Qrisp with Grover Search, Quantum Phase Estimation, and QAOAMarkTechPost In this tutorial, we present an advanced, hands-on tutorial that demonstrates how we use Qrisp to build and execute non-trivial quantum algorithms. We walk through core Qrisp abstractions for quantum data, construct entangled states, and then progressively implement Grover’s search with automatic uncomputation, Quantum Phase Estimation, and a full QAOA workflow for the MaxCut problem.
The post How to Build Advanced Quantum Algorithms Using Qrisp with Grover Search, Quantum Phase Estimation, and QAOA appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In this tutorial, we present an advanced, hands-on tutorial that demonstrates how we use Qrisp to build and execute non-trivial quantum algorithms. We walk through core Qrisp abstractions for quantum data, construct entangled states, and then progressively implement Grover’s search with automatic uncomputation, Quantum Phase Estimation, and a full QAOA workflow for the MaxCut problem.
The post How to Build Advanced Quantum Algorithms Using Qrisp with Grover Search, Quantum Phase Estimation, and QAOA appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Most security teams today are buried under tools. Too many dashboards. Too much noise. Not enough real progress. Every vendor promises “complete coverage” or “AI-powered automation,” but inside most SOCs, teams are still overwhelmed, stretched thin, and unsure which tools are truly pulling their weight. The result? Bloated stacks, missed signals, and mounting pressure to […]
Autonomous AI agents are creating a new identity blind spot as they operate outside traditional IAM controls. Token Security shows why managing the full lifecycle of AI agent identities is becoming a critical CISO priority. […] Read More
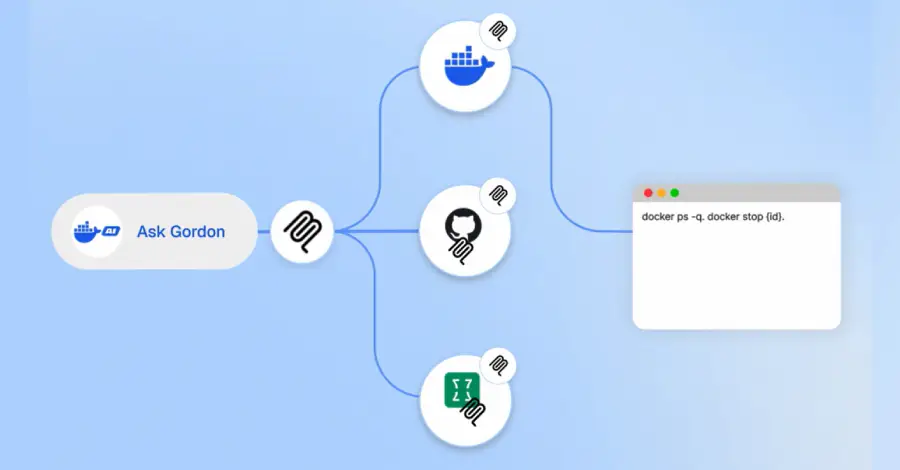
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed details of a now-patched security flaw impacting Ask Gordon, an artificial intelligence (AI) assistant built into Docker Desktop and the Docker Command-Line Interface (CLI), that could be exploited to execute code and exfiltrate sensitive data. The critical vulnerability has been codenamed DockerDash by cybersecurity company Noma Labs. It was addressed by Read […]
French prosecutors have raided X’s offices in Paris on Tuesday as part of a criminal investigation into the platform’s Grok AI tool, widely used to generate sexually explicit images. […] Read More
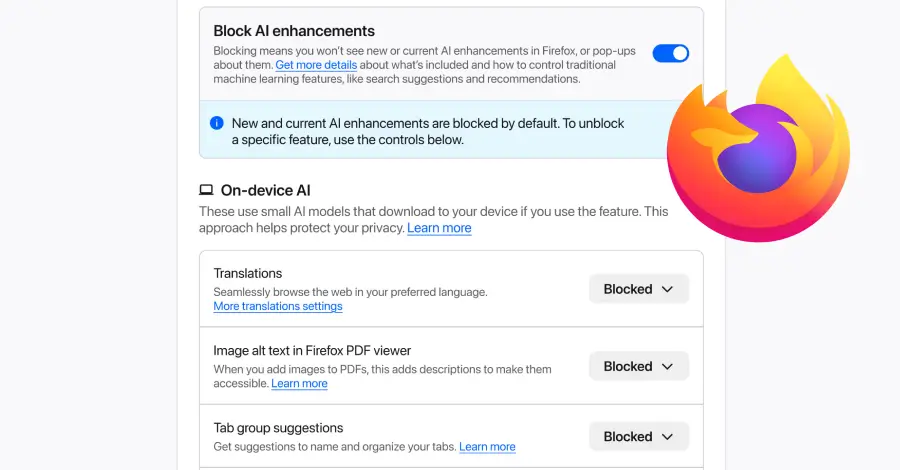
Mozilla on Monday announced a new controls section in its Firefox desktop browser settings that allows users to completely turn off generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) features. “It provides a single place to block current and future generative AI features in Firefox,” Ajit Varma, head of Firefox, said. “You can also review and manage individual AI […]
F-scheduler: illuminating the free-lunch design space for fast sampling of diffusion modelscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.02390v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Diffusion models are the state-of-the-art generative models for high-resolution images, but sampling from pretrained models is computationally expensive, motivating interest in fast sampling. Although Free-U Net is a training-free enhancement for improving image quality, we find it ineffective under few-step ($<10$) sampling. We analyze the discrete diffusion ODE and propose F-scheduler, a scheduler designed for ODE solvers with Free-U Net. Our proposed scheduler consists of a special time schedule that does not fully denoise the feature to enable the use of the KL-term in the $beta$-VAE decoder, and the schedule of a proper inference stage for modifying the U-Net skip-connection via Free-U Net. Via information theory, we provide insights into how the better scheduled ODE solvers for the diffusion model can outperform the training-based diffusion distillation model. The newly proposed scheduler is compatible with most of the few-step ODE solvers and can sample a 1024 x 1024-resolution image in 6 steps and a 512 x 512-resolution image in 5 steps when it applies to DPM++ 2m and UniPC, with an FID result that outperforms the SOTA distillation models and the 20-step DPM++ 2m solver, respectively. Codebase: https://github.com/TheLovesOfLadyPurple/F-scheduler
arXiv:2510.02390v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Diffusion models are the state-of-the-art generative models for high-resolution images, but sampling from pretrained models is computationally expensive, motivating interest in fast sampling. Although Free-U Net is a training-free enhancement for improving image quality, we find it ineffective under few-step ($<10$) sampling. We analyze the discrete diffusion ODE and propose F-scheduler, a scheduler designed for ODE solvers with Free-U Net. Our proposed scheduler consists of a special time schedule that does not fully denoise the feature to enable the use of the KL-term in the $beta$-VAE decoder, and the schedule of a proper inference stage for modifying the U-Net skip-connection via Free-U Net. Via information theory, we provide insights into how the better scheduled ODE solvers for the diffusion model can outperform the training-based diffusion distillation model. The newly proposed scheduler is compatible with most of the few-step ODE solvers and can sample a 1024 x 1024-resolution image in 6 steps and a 512 x 512-resolution image in 5 steps when it applies to DPM++ 2m and UniPC, with an FID result that outperforms the SOTA distillation models and the 20-step DPM++ 2m solver, respectively. Codebase: https://github.com/TheLovesOfLadyPurple/F-scheduler Read More
DIVERGE: Diversity-Enhanced RAG for Open-Ended Information Seekingcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2602.00238v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Existing retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems are primarily designed under the assumption that each query has a single correct answer. This overlooks common information-seeking scenarios with multiple plausible answers, where diversity is essential to avoid collapsing to a single dominant response, thereby constraining creativity and compromising fair and inclusive information access. Our analysis reveals a commonly overlooked limitation of standard RAG systems: they underutilize retrieved context diversity, such that increasing retrieval diversity alone does not yield diverse generations. To address this limitation, we propose DIVERGE, a plug-and-play agentic RAG framework with novel reflection-guided generation and memory-augmented iterative refinement, which promotes diverse viewpoints while preserving answer quality. We introduce novel metrics tailored to evaluating the diversity-quality trade-off in open-ended questions, and show that they correlate well with human judgments. We demonstrate that DIVERGE achieves the best diversity-quality trade-off compared to competitive baselines and previous state-of-the-art methods on the real-world Infinity-Chat dataset, substantially improving diversity while maintaining quality. More broadly, our results reveal a systematic limitation of current LLM-based systems for open-ended information-seeking and show that explicitly modeling diversity can mitigate it. Our code is available at: https://github.com/au-clan/Diverge
arXiv:2602.00238v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Existing retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems are primarily designed under the assumption that each query has a single correct answer. This overlooks common information-seeking scenarios with multiple plausible answers, where diversity is essential to avoid collapsing to a single dominant response, thereby constraining creativity and compromising fair and inclusive information access. Our analysis reveals a commonly overlooked limitation of standard RAG systems: they underutilize retrieved context diversity, such that increasing retrieval diversity alone does not yield diverse generations. To address this limitation, we propose DIVERGE, a plug-and-play agentic RAG framework with novel reflection-guided generation and memory-augmented iterative refinement, which promotes diverse viewpoints while preserving answer quality. We introduce novel metrics tailored to evaluating the diversity-quality trade-off in open-ended questions, and show that they correlate well with human judgments. We demonstrate that DIVERGE achieves the best diversity-quality trade-off compared to competitive baselines and previous state-of-the-art methods on the real-world Infinity-Chat dataset, substantially improving diversity while maintaining quality. More broadly, our results reveal a systematic limitation of current LLM-based systems for open-ended information-seeking and show that explicitly modeling diversity can mitigate it. Our code is available at: https://github.com/au-clan/Diverge Read More