Microsoft has started rolling out built-in Sysmon functionality to some Windows 11 systems enrolled in the Windows Insider program. […] Read More
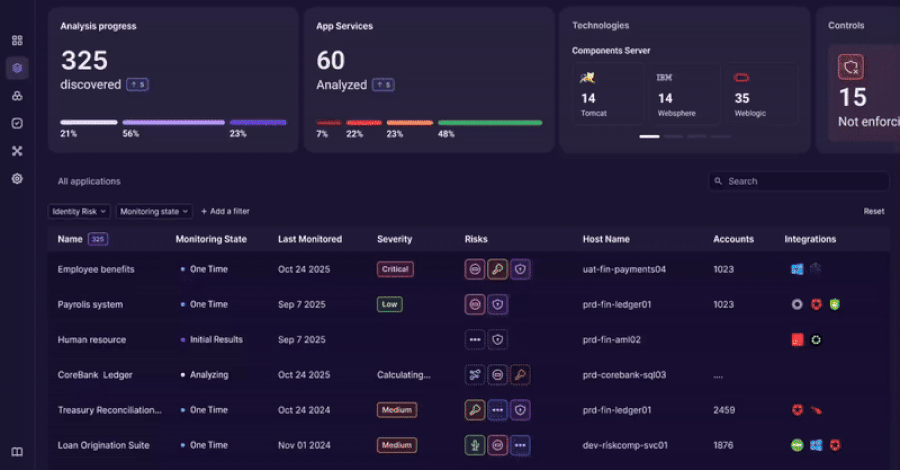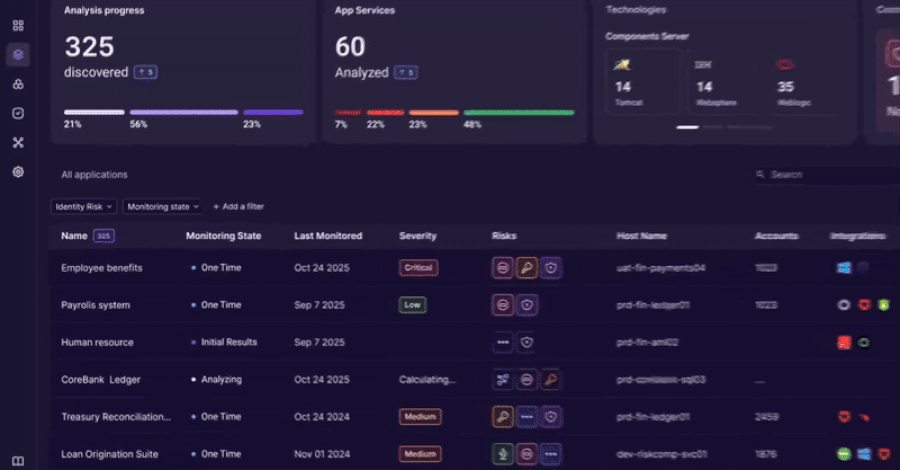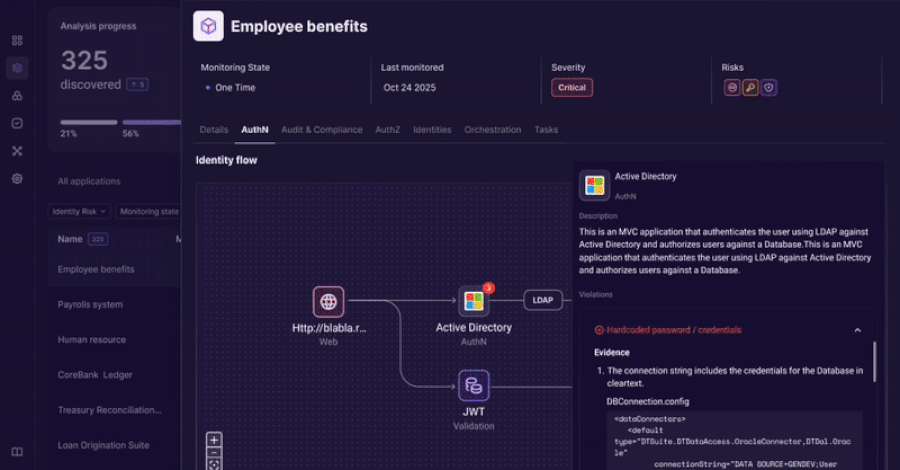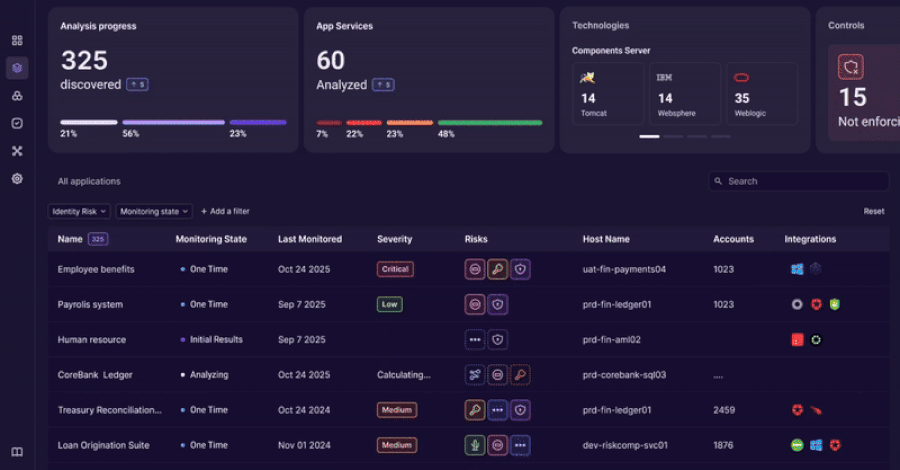
An innovative approach to discovering, analyzing, and governing identity usage beyond traditional IAM controls. The Challenge: Identity Lives Outside the Identity Stack Identity and access management tools were built to govern users and directories. Modern enterprises run on applications. Over time, identity logic has moved into application code, APIs, service accounts, and custom authentication Read More
Microsoft has warned that information-stealing attacks are “rapidly expanding” beyond Windows to target Apple macOS environments by leveraging cross-platform languages like Python and abusing trusted platforms for distribution at scale. The tech giant’s Defender Security Research Team said it observed macOS-targeted infostealer campaigns using social engineering techniques such as ClickFix since Read More
Complete Identification of Deep ReLU Neural Networks by Many-Valued Logiccs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2602.00266v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Deep ReLU neural networks admit nontrivial functional symmetries: vastly different architectures and parameters (weights and biases) can realize the same function. We address the complete identification problem — given a function f, deriving the architecture and parameters of all feedforward ReLU networks giving rise to f. We translate ReLU networks into Lukasiewicz logic formulae, and effect functional equivalent network transformations through algebraic rewrites governed by the logic axioms. A compositional norm form is proposed to facilitate the mapping from Lukasiewicz logic formulae back to ReLU networks. Using Chang’s completeness theorem, we show that for every functional equivalence class, all ReLU networks in that class are connected by a finite set of symmetries corresponding to the finite set of axioms of Lukasiewicz logic. This idea is reminiscent of Shannon’s seminal work on switching circuit design, where the circuits are translated into Boolean formulae, and synthesis is effected by algebraic rewriting governed by Boolean logic axioms.
arXiv:2602.00266v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Deep ReLU neural networks admit nontrivial functional symmetries: vastly different architectures and parameters (weights and biases) can realize the same function. We address the complete identification problem — given a function f, deriving the architecture and parameters of all feedforward ReLU networks giving rise to f. We translate ReLU networks into Lukasiewicz logic formulae, and effect functional equivalent network transformations through algebraic rewrites governed by the logic axioms. A compositional norm form is proposed to facilitate the mapping from Lukasiewicz logic formulae back to ReLU networks. Using Chang’s completeness theorem, we show that for every functional equivalence class, all ReLU networks in that class are connected by a finite set of symmetries corresponding to the finite set of axioms of Lukasiewicz logic. This idea is reminiscent of Shannon’s seminal work on switching circuit design, where the circuits are translated into Boolean formulae, and synthesis is effected by algebraic rewriting governed by Boolean logic axioms. Read More
FaithSCAN: Model-Driven Single-Pass Hallucination Detection for Faithful Visual Question Answeringcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.00269v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Faithfulness hallucinations in VQA occur when vision-language models produce fluent yet visually ungrounded answers, severely undermining their reliability in safety-critical applications. Existing detection methods mainly fall into two categories: external verification approaches relying on auxiliary models or knowledge bases, and uncertainty-driven approaches using repeated sampling or uncertainty estimates. The former suffer from high computational overhead and are limited by external resource quality, while the latter capture only limited facets of model uncertainty and fail to sufficiently explore the rich internal signals associated with the diverse failure modes. Both paradigms thus have inherent limitations in efficiency, robustness, and detection performance. To address these challenges, we propose FaithSCAN: a lightweight network that detects hallucinations by exploiting rich internal signals of VLMs, including token-level decoding uncertainty, intermediate visual representations, and cross-modal alignment features. These signals are fused via branch-wise evidence encoding and uncertainty-aware attention. We also extend the LLM-as-a-Judge paradigm to VQA hallucination and propose a low-cost strategy to automatically generate model-dependent supervision signals, enabling supervised training without costly human labels while maintaining high detection accuracy. Experiments on multiple VQA benchmarks show that FaithSCAN significantly outperforms existing methods in both effectiveness and efficiency. In-depth analysis shows hallucinations arise from systematic internal state variations in visual perception, cross-modal reasoning, and language decoding. Different internal signals provide complementary diagnostic cues, and hallucination patterns vary across VLM architectures, offering new insights into the underlying causes of multimodal hallucinations.
arXiv:2601.00269v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Faithfulness hallucinations in VQA occur when vision-language models produce fluent yet visually ungrounded answers, severely undermining their reliability in safety-critical applications. Existing detection methods mainly fall into two categories: external verification approaches relying on auxiliary models or knowledge bases, and uncertainty-driven approaches using repeated sampling or uncertainty estimates. The former suffer from high computational overhead and are limited by external resource quality, while the latter capture only limited facets of model uncertainty and fail to sufficiently explore the rich internal signals associated with the diverse failure modes. Both paradigms thus have inherent limitations in efficiency, robustness, and detection performance. To address these challenges, we propose FaithSCAN: a lightweight network that detects hallucinations by exploiting rich internal signals of VLMs, including token-level decoding uncertainty, intermediate visual representations, and cross-modal alignment features. These signals are fused via branch-wise evidence encoding and uncertainty-aware attention. We also extend the LLM-as-a-Judge paradigm to VQA hallucination and propose a low-cost strategy to automatically generate model-dependent supervision signals, enabling supervised training without costly human labels while maintaining high detection accuracy. Experiments on multiple VQA benchmarks show that FaithSCAN significantly outperforms existing methods in both effectiveness and efficiency. In-depth analysis shows hallucinations arise from systematic internal state variations in visual perception, cross-modal reasoning, and language decoding. Different internal signals provide complementary diagnostic cues, and hallucination patterns vary across VLM architectures, offering new insights into the underlying causes of multimodal hallucinations. Read More
ChipBench: A Next-Step Benchmark for Evaluating LLM Performance in AI-Aided Chip Designcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.21448v2 Announce Type: replace
Abstract: While Large Language Models (LLMs) show significant potential in hardware engineering, current benchmarks suffer from saturation and limited task diversity, failing to reflect LLMs’ performance in real industrial workflows. To address this gap, we propose a comprehensive benchmark for AI-aided chip design that rigorously evaluates LLMs across three critical tasks: Verilog generation, debugging, and reference model generation. Our benchmark features 44 realistic modules with complex hierarchical structures, 89 systematic debugging cases, and 132 reference model samples across Python, SystemC, and CXXRTL. Evaluation results reveal substantial performance gaps, with state-of-the-art Claude-4.5-opus achieving only 30.74% on Verilog generation and 13.33% on Python reference model generation, demonstrating significant challenges compared to existing saturated benchmarks where SOTA models achieve over 95% pass rates. Additionally, to help enhance LLM reference model generation, we provide an automated toolbox for high-quality training data generation, facilitating future research in this underexplored domain. Our code is available at https://github.com/zhongkaiyu/ChipBench.git.
arXiv:2601.21448v2 Announce Type: replace
Abstract: While Large Language Models (LLMs) show significant potential in hardware engineering, current benchmarks suffer from saturation and limited task diversity, failing to reflect LLMs’ performance in real industrial workflows. To address this gap, we propose a comprehensive benchmark for AI-aided chip design that rigorously evaluates LLMs across three critical tasks: Verilog generation, debugging, and reference model generation. Our benchmark features 44 realistic modules with complex hierarchical structures, 89 systematic debugging cases, and 132 reference model samples across Python, SystemC, and CXXRTL. Evaluation results reveal substantial performance gaps, with state-of-the-art Claude-4.5-opus achieving only 30.74% on Verilog generation and 13.33% on Python reference model generation, demonstrating significant challenges compared to existing saturated benchmarks where SOTA models achieve over 95% pass rates. Additionally, to help enhance LLM reference model generation, we provide an automated toolbox for high-quality training data generation, facilitating future research in this underexplored domain. Our code is available at https://github.com/zhongkaiyu/ChipBench.git. Read More
SoMA: A Real-to-Sim Neural Simulator for Robotic Soft-body Manipulationcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2602.02402v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Simulating deformable objects under rich interactions remains a fundamental challenge for real-to-sim robot manipulation, with dynamics jointly driven by environmental effects and robot actions. Existing simulators rely on predefined physics or data-driven dynamics without robot-conditioned control, limiting accuracy, stability, and generalization. This paper presents SoMA, a 3D Gaussian Splat simulator for soft-body manipulation. SoMA couples deformable dynamics, environmental forces, and robot joint actions in a unified latent neural space for end-to-end real-to-sim simulation. Modeling interactions over learned Gaussian splats enables controllable, stable long-horizon manipulation and generalization beyond observed trajectories without predefined physical models. SoMA improves resimulation accuracy and generalization on real-world robot manipulation by 20%, enabling stable simulation of complex tasks such as long-horizon cloth folding.
arXiv:2602.02402v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Simulating deformable objects under rich interactions remains a fundamental challenge for real-to-sim robot manipulation, with dynamics jointly driven by environmental effects and robot actions. Existing simulators rely on predefined physics or data-driven dynamics without robot-conditioned control, limiting accuracy, stability, and generalization. This paper presents SoMA, a 3D Gaussian Splat simulator for soft-body manipulation. SoMA couples deformable dynamics, environmental forces, and robot joint actions in a unified latent neural space for end-to-end real-to-sim simulation. Modeling interactions over learned Gaussian splats enables controllable, stable long-horizon manipulation and generalization beyond observed trajectories without predefined physical models. SoMA improves resimulation accuracy and generalization on real-world robot manipulation by 20%, enabling stable simulation of complex tasks such as long-horizon cloth folding. Read More
How to Build Your Own Custom LLM Memory Layer from ScratchTowards Data Science Step-by-step guide to building autonomous memory retrieval systems
The post How to Build Your Own Custom LLM Memory Layer from Scratch appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Step-by-step guide to building autonomous memory retrieval systems
The post How to Build Your Own Custom LLM Memory Layer from Scratch appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
Plan–Code–Execute: Designing Agents That Create Their Own ToolsTowards Data Science The case against pre-built tools in Agentic Architectures
The post Plan–Code–Execute: Designing Agents That Create Their Own Tools appeared first on Towards Data Science.
The case against pre-built tools in Agentic Architectures
The post Plan–Code–Execute: Designing Agents That Create Their Own Tools appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
How Cisco builds smart systems for the AI eraAI News Among the big players in technology, Cisco is one of the sector’s leaders that’s advancing operational deployments of AI internally to its own operations, and the tools it sells to its customers around the world. As a large company, its activities encompass many areas of the typical IT stack, including infrastructure, services, security, and the
The post How Cisco builds smart systems for the AI era appeared first on AI News.
Among the big players in technology, Cisco is one of the sector’s leaders that’s advancing operational deployments of AI internally to its own operations, and the tools it sells to its customers around the world. As a large company, its activities encompass many areas of the typical IT stack, including infrastructure, services, security, and the
The post How Cisco builds smart systems for the AI era appeared first on AI News. Read More