Higher-order Linear Attentioncs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.27258v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: The quadratic cost of scaled dot-product attention is a central obstacle to scaling autoregressive language models to long contexts. Linear-time attention and State Space Models (SSMs) provide scalable alternatives but are typically restricted to first-order or kernel-based approximations, which can limit expressivity. We introduce Higher-order Linear Attention (HLA), a causal, streaming mechanism that realizes higher interactions via compact prefix sufficient statistics. In the second-order case, HLA maintains a constant-size state and computes per-token outputs in linear time without materializing any $n times n$ matrices. We give closed-form streaming identities, a strictly causal masked variant using two additional summaries, and a chunk-parallel training scheme based on associative scans that reproduces the activations of a serial recurrence exactly. We further outline extensions to third and higher orders. Collectively, these results position HLA as a principled, scalable building block that combines attention-like, data-dependent mixing with the efficiency of modern recurrent architectures. Project Page: https://github.com/yifanzhang-pro/HLA.
arXiv:2510.27258v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: The quadratic cost of scaled dot-product attention is a central obstacle to scaling autoregressive language models to long contexts. Linear-time attention and State Space Models (SSMs) provide scalable alternatives but are typically restricted to first-order or kernel-based approximations, which can limit expressivity. We introduce Higher-order Linear Attention (HLA), a causal, streaming mechanism that realizes higher interactions via compact prefix sufficient statistics. In the second-order case, HLA maintains a constant-size state and computes per-token outputs in linear time without materializing any $n times n$ matrices. We give closed-form streaming identities, a strictly causal masked variant using two additional summaries, and a chunk-parallel training scheme based on associative scans that reproduces the activations of a serial recurrence exactly. We further outline extensions to third and higher orders. Collectively, these results position HLA as a principled, scalable building block that combines attention-like, data-dependent mixing with the efficiency of modern recurrent architectures. Project Page: https://github.com/yifanzhang-pro/HLA. Read More
Privacy-Aware Continual Self-Supervised Learning on Multi-Window Chest Computed Tomography for Domain-Shift Robustnesscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.27213v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: We propose a novel continual self-supervised learning (CSSL) framework for simultaneously learning diverse features from multi-window-obtained chest computed tomography (CT) images and ensuring data privacy. Achieving a robust and highly generalizable model in medical image diagnosis is challenging, mainly because of issues, such as the scarcity of large-scale, accurately annotated datasets and domain shifts inherent to dynamic healthcare environments. Specifically, in chest CT, these domain shifts often arise from differences in window settings, which are optimized for distinct clinical purposes. Previous CSSL frameworks often mitigated domain shift by reusing past data, a typically impractical approach owing to privacy constraints. Our approach addresses these challenges by effectively capturing the relationship between previously learned knowledge and new information across different training stages through continual pretraining on unlabeled images. Specifically, by incorporating a latent replay-based mechanism into CSSL, our method mitigates catastrophic forgetting due to domain shifts during continual pretraining while ensuring data privacy. Additionally, we introduce a feature distillation technique that integrates Wasserstein distance-based knowledge distillation (WKD) and batch-knowledge ensemble (BKE), enhancing the ability of the model to learn meaningful, domain-shift-robust representations. Finally, we validate our approach using chest CT images obtained across two different window settings, demonstrating superior performance compared with other approaches.
arXiv:2510.27213v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: We propose a novel continual self-supervised learning (CSSL) framework for simultaneously learning diverse features from multi-window-obtained chest computed tomography (CT) images and ensuring data privacy. Achieving a robust and highly generalizable model in medical image diagnosis is challenging, mainly because of issues, such as the scarcity of large-scale, accurately annotated datasets and domain shifts inherent to dynamic healthcare environments. Specifically, in chest CT, these domain shifts often arise from differences in window settings, which are optimized for distinct clinical purposes. Previous CSSL frameworks often mitigated domain shift by reusing past data, a typically impractical approach owing to privacy constraints. Our approach addresses these challenges by effectively capturing the relationship between previously learned knowledge and new information across different training stages through continual pretraining on unlabeled images. Specifically, by incorporating a latent replay-based mechanism into CSSL, our method mitigates catastrophic forgetting due to domain shifts during continual pretraining while ensuring data privacy. Additionally, we introduce a feature distillation technique that integrates Wasserstein distance-based knowledge distillation (WKD) and batch-knowledge ensemble (BKE), enhancing the ability of the model to learn meaningful, domain-shift-robust representations. Finally, we validate our approach using chest CT images obtained across two different window settings, demonstrating superior performance compared with other approaches. Read More
Learning Soft Robotic Dynamics with Active Explorationcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.27428v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Soft robots offer unmatched adaptability and safety in unstructured environments, yet their compliant, high-dimensional, and nonlinear dynamics make modeling for control notoriously difficult. Existing data-driven approaches often fail to generalize, constrained by narrowly focused task demonstrations or inefficient random exploration. We introduce SoftAE, an uncertainty-aware active exploration framework that autonomously learns task-agnostic and generalizable dynamics models of soft robotic systems. SoftAE employs probabilistic ensemble models to estimate epistemic uncertainty and actively guides exploration toward underrepresented regions of the state-action space, achieving efficient coverage of diverse behaviors without task-specific supervision. We evaluate SoftAE on three simulated soft robotic platforms — a continuum arm, an articulated fish in fluid, and a musculoskeletal leg with hybrid actuation — and on a pneumatically actuated continuum soft arm in the real world. Compared with random exploration and task-specific model-based reinforcement learning, SoftAE produces more accurate dynamics models, enables superior zero-shot control on unseen tasks, and maintains robustness under sensing noise, actuation delays, and nonlinear material effects. These results demonstrate that uncertainty-driven active exploration can yield scalable, reusable dynamics models across diverse soft robotic morphologies, representing a step toward more autonomous, adaptable, and data-efficient control in compliant robots.
arXiv:2510.27428v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Soft robots offer unmatched adaptability and safety in unstructured environments, yet their compliant, high-dimensional, and nonlinear dynamics make modeling for control notoriously difficult. Existing data-driven approaches often fail to generalize, constrained by narrowly focused task demonstrations or inefficient random exploration. We introduce SoftAE, an uncertainty-aware active exploration framework that autonomously learns task-agnostic and generalizable dynamics models of soft robotic systems. SoftAE employs probabilistic ensemble models to estimate epistemic uncertainty and actively guides exploration toward underrepresented regions of the state-action space, achieving efficient coverage of diverse behaviors without task-specific supervision. We evaluate SoftAE on three simulated soft robotic platforms — a continuum arm, an articulated fish in fluid, and a musculoskeletal leg with hybrid actuation — and on a pneumatically actuated continuum soft arm in the real world. Compared with random exploration and task-specific model-based reinforcement learning, SoftAE produces more accurate dynamics models, enables superior zero-shot control on unseen tasks, and maintains robustness under sensing noise, actuation delays, and nonlinear material effects. These results demonstrate that uncertainty-driven active exploration can yield scalable, reusable dynamics models across diverse soft robotic morphologies, representing a step toward more autonomous, adaptable, and data-efficient control in compliant robots. Read More
FMint-SDE: A Multimodal Foundation Model for Accelerating Numerical Simulation of SDEs via Error Correctioncs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.27173v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Fast and accurate simulation of dynamical systems is a fundamental challenge across scientific and engineering domains. Traditional numerical integrators often face a trade-off between accuracy and computational efficiency, while existing neural network-based approaches typically require training a separate model for each case. To overcome these limitations, we introduce a novel multi-modal foundation model for large-scale simulations of differential equations: FMint-SDE (Foundation Model based on Initialization for stochastic differential equations). Based on a decoder-only transformer with in-context learning, FMint-SDE leverages numerical and textual modalities to learn a universal error-correction scheme. It is trained using prompted sequences of coarse solutions generated by conventional solvers, enabling broad generalization across diverse systems. We evaluate our models on a suite of challenging SDE benchmarks spanning applications in molecular dynamics, mechanical systems, finance, and biology. Experimental results show that our approach achieves a superior accuracy-efficiency tradeoff compared to classical solvers, underscoring the potential of FMint-SDE as a general-purpose simulation tool for dynamical systems.
arXiv:2510.27173v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Fast and accurate simulation of dynamical systems is a fundamental challenge across scientific and engineering domains. Traditional numerical integrators often face a trade-off between accuracy and computational efficiency, while existing neural network-based approaches typically require training a separate model for each case. To overcome these limitations, we introduce a novel multi-modal foundation model for large-scale simulations of differential equations: FMint-SDE (Foundation Model based on Initialization for stochastic differential equations). Based on a decoder-only transformer with in-context learning, FMint-SDE leverages numerical and textual modalities to learn a universal error-correction scheme. It is trained using prompted sequences of coarse solutions generated by conventional solvers, enabling broad generalization across diverse systems. We evaluate our models on a suite of challenging SDE benchmarks spanning applications in molecular dynamics, mechanical systems, finance, and biology. Experimental results show that our approach achieves a superior accuracy-efficiency tradeoff compared to classical solvers, underscoring the potential of FMint-SDE as a general-purpose simulation tool for dynamical systems. Read More
Expressive Range Characterization of Open Text-to-Audio Modelscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.27102v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Text-to-audio models are a type of generative model that produces audio output in response to a given textual prompt. Although level generators and the properties of the functional content that they create (e.g., playability) dominate most discourse in procedurally generated content (PCG), games that emotionally resonate with players tend to weave together a range of creative and multimodal content (e.g., music, sounds, visuals, narrative tone), and multimodal models have begun seeing at least experimental use for this purpose. However, it remains unclear what exactly such models generate, and with what degree of variability and fidelity: audio is an extremely broad class of output for a generative system to target.
Within the PCG community, expressive range analysis (ERA) has been used as a quantitative way to characterize generators’ output space, especially for level generators. This paper adapts ERA to text-to-audio models, making the analysis tractable by looking at the expressive range of outputs for specific, fixed prompts. Experiments are conducted by prompting the models with several standardized prompts derived from the Environmental Sound Classification (ESC-50) dataset. The resulting audio is analyzed along key acoustic dimensions (e.g., pitch, loudness, and timbre). More broadly, this paper offers a framework for ERA-based exploratory evaluation of generative audio models.
arXiv:2510.27102v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Text-to-audio models are a type of generative model that produces audio output in response to a given textual prompt. Although level generators and the properties of the functional content that they create (e.g., playability) dominate most discourse in procedurally generated content (PCG), games that emotionally resonate with players tend to weave together a range of creative and multimodal content (e.g., music, sounds, visuals, narrative tone), and multimodal models have begun seeing at least experimental use for this purpose. However, it remains unclear what exactly such models generate, and with what degree of variability and fidelity: audio is an extremely broad class of output for a generative system to target.
Within the PCG community, expressive range analysis (ERA) has been used as a quantitative way to characterize generators’ output space, especially for level generators. This paper adapts ERA to text-to-audio models, making the analysis tractable by looking at the expressive range of outputs for specific, fixed prompts. Experiments are conducted by prompting the models with several standardized prompts derived from the Environmental Sound Classification (ESC-50) dataset. The resulting audio is analyzed along key acoustic dimensions (e.g., pitch, loudness, and timbre). More broadly, this paper offers a framework for ERA-based exploratory evaluation of generative audio models. Read More
The Denario project: Deep knowledge AI agents for scientific discoverycs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.26887v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: We present Denario, an AI multi-agent system designed to serve as a scientific research assistant. Denario can perform many different tasks, such as generating ideas, checking the literature, developing research plans, writing and executing code, making plots, and drafting and reviewing a scientific paper. The system has a modular architecture, allowing it to handle specific tasks, such as generating an idea, or carrying out end-to-end scientific analysis using Cmbagent as a deep-research backend. In this work, we describe in detail Denario and its modules, and illustrate its capabilities by presenting multiple AI-generated papers generated by it in many different scientific disciplines such as astrophysics, biology, biophysics, biomedical informatics, chemistry, material science, mathematical physics, medicine, neuroscience and planetary science. Denario also excels at combining ideas from different disciplines, and we illustrate this by showing a paper that applies methods from quantum physics and machine learning to astrophysical data. We report the evaluations performed on these papers by domain experts, who provided both numerical scores and review-like feedback. We then highlight the strengths, weaknesses, and limitations of the current system. Finally, we discuss the ethical implications of AI-driven research and reflect on how such technology relates to the philosophy of science. We publicly release the code at https://github.com/AstroPilot-AI/Denario. A Denario demo can also be run directly on the web at https://huggingface.co/spaces/astropilot-ai/Denario, and the full app will be deployed on the cloud.
arXiv:2510.26887v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: We present Denario, an AI multi-agent system designed to serve as a scientific research assistant. Denario can perform many different tasks, such as generating ideas, checking the literature, developing research plans, writing and executing code, making plots, and drafting and reviewing a scientific paper. The system has a modular architecture, allowing it to handle specific tasks, such as generating an idea, or carrying out end-to-end scientific analysis using Cmbagent as a deep-research backend. In this work, we describe in detail Denario and its modules, and illustrate its capabilities by presenting multiple AI-generated papers generated by it in many different scientific disciplines such as astrophysics, biology, biophysics, biomedical informatics, chemistry, material science, mathematical physics, medicine, neuroscience and planetary science. Denario also excels at combining ideas from different disciplines, and we illustrate this by showing a paper that applies methods from quantum physics and machine learning to astrophysical data. We report the evaluations performed on these papers by domain experts, who provided both numerical scores and review-like feedback. We then highlight the strengths, weaknesses, and limitations of the current system. Finally, we discuss the ethical implications of AI-driven research and reflect on how such technology relates to the philosophy of science. We publicly release the code at https://github.com/AstroPilot-AI/Denario. A Denario demo can also be run directly on the web at https://huggingface.co/spaces/astropilot-ai/Denario, and the full app will be deployed on the cloud. Read More
Cognition Envelopes for Bounded AI Reasoning in Autonomous UAS Operationscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.26905v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Cyber-physical systems increasingly rely on Foundational Models such as Large Language Models (LLMs) and Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to increase autonomy through enhanced perception, inference, and planning. However, these models also introduce new types of errors, such as hallucinations, overgeneralizations, and context misalignments, resulting in incorrect and flawed decisions. To address this, we introduce the concept of Cognition Envelopes, designed to establish reasoning boundaries that constrain AI-generated decisions while complementing the use of meta-cognition and traditional safety envelopes. As with safety envelopes, Cognition Envelopes require practical guidelines and systematic processes for their definition, validation, and assurance.
arXiv:2510.26905v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Cyber-physical systems increasingly rely on Foundational Models such as Large Language Models (LLMs) and Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to increase autonomy through enhanced perception, inference, and planning. However, these models also introduce new types of errors, such as hallucinations, overgeneralizations, and context misalignments, resulting in incorrect and flawed decisions. To address this, we introduce the concept of Cognition Envelopes, designed to establish reasoning boundaries that constrain AI-generated decisions while complementing the use of meta-cognition and traditional safety envelopes. As with safety envelopes, Cognition Envelopes require practical guidelines and systematic processes for their definition, validation, and assurance. Read More
MobileNetV3 Paper Walkthrough: The Tiny Giant Getting Even SmarterTowards Data Science MobileNetV3 with PyTorch — now featuring SE blocks and hard activation functions
The post MobileNetV3 Paper Walkthrough: The Tiny Giant Getting Even Smarter appeared first on Towards Data Science.
MobileNetV3 with PyTorch — now featuring SE blocks and hard activation functions
The post MobileNetV3 Paper Walkthrough: The Tiny Giant Getting Even Smarter appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
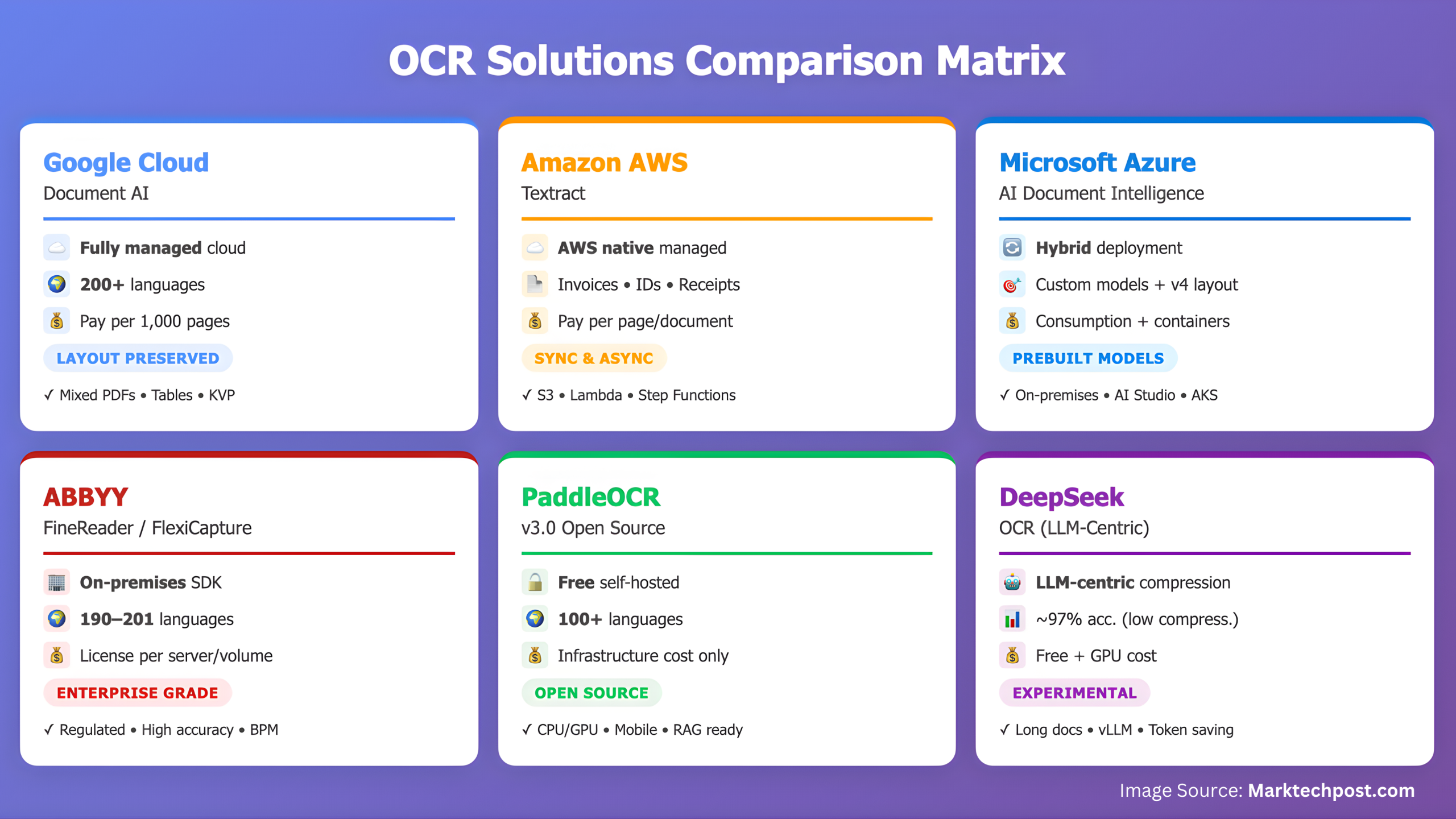
Comparing the Top 6 OCR (Optical Character Recognition) Models/Systems in 2025MarkTechPost Optical character recognition has moved from plain text extraction to document intelligence. Modern systems must read scanned and digital PDFs in one pass, preserve layout, detect tables, extract key value pairs, and work with more than one language. Many teams now also want OCR that can feed RAG and agent pipelines directly. In 2025, 6
The post Comparing the Top 6 OCR (Optical Character Recognition) Models/Systems in 2025 appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Optical character recognition has moved from plain text extraction to document intelligence. Modern systems must read scanned and digital PDFs in one pass, preserve layout, detect tables, extract key value pairs, and work with more than one language. Many teams now also want OCR that can feed RAG and agent pipelines directly. In 2025, 6
The post Comparing the Top 6 OCR (Optical Character Recognition) Models/Systems in 2025 appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
From Classical Models to AI: Forecasting Humidity for Energy and Water Efficiency in Data CentersTowards Data Science From ARIMA to N-BEATS: Comparing forecasting approaches that balance accuracy, interpretability, and sustainability
The post From Classical Models to AI: Forecasting Humidity for Energy and Water Efficiency in Data Centers appeared first on Towards Data Science.
From ARIMA to N-BEATS: Comparing forecasting approaches that balance accuracy, interpretability, and sustainability
The post From Classical Models to AI: Forecasting Humidity for Energy and Water Efficiency in Data Centers appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More