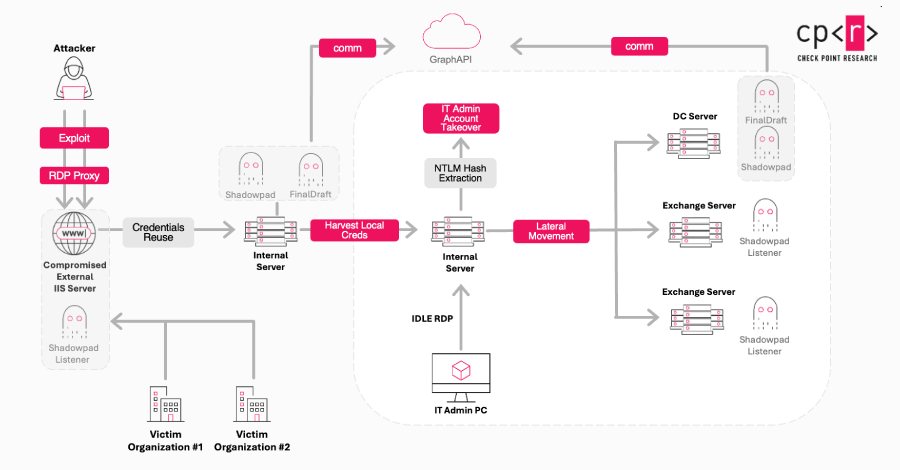
The threat actor known as Jewelbug has been increasingly focusing on government targets in Europe since July 2025, even as it continues to attack entities located in Southeast Asia and South America. Check Point Research is tracking the cluster under the name Ink Dragon. It’s also referenced by the broader cybersecurity community under the names […]
Assessing Greenspace Attractiveness with ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini: Do AI Models Reflect Human Perceptions?cs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.11827v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Understanding greenspace attractiveness is essential for designing livable and inclusive urban environments, yet existing assessment approaches often overlook informal or transient spaces and remain too resource intensive to capture subjective perceptions at scale. This study examines the ability of multimodal large language models (MLLMs), ChatGPT GPT-4o, Claude 3.5 Haiku, and Gemini 2.0 Flash, to assess greenspace attractiveness similarly to humans using Google Street View imagery. We compared model outputs with responses from a geo-questionnaire of residents in Lodz, Poland, across both formal (for example, parks and managed greenspaces) and informal (for example, meadows and wastelands) greenspaces. Survey respondents and models indicated whether each greenspace was attractive or unattractive and provided up to three free text explanations. Analyses examined how often their attractiveness judgments aligned and compared their explanations after classifying them into shared reasoning categories. Results show high AI human agreement for attractive formal greenspaces and unattractive informal spaces, but low alignment for attractive informal and unattractive formal greenspaces. Models consistently emphasized aesthetic and design oriented features, underrepresenting safety, functional infrastructure, and locally embedded qualities valued by survey respondents. While these findings highlight the potential for scalable pre-assessment, they also underscore the need for human oversight and complementary participatory approaches. We conclude that MLLMs can support, but not replace, context sensitive greenspace evaluation in planning practice.
arXiv:2512.11827v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Understanding greenspace attractiveness is essential for designing livable and inclusive urban environments, yet existing assessment approaches often overlook informal or transient spaces and remain too resource intensive to capture subjective perceptions at scale. This study examines the ability of multimodal large language models (MLLMs), ChatGPT GPT-4o, Claude 3.5 Haiku, and Gemini 2.0 Flash, to assess greenspace attractiveness similarly to humans using Google Street View imagery. We compared model outputs with responses from a geo-questionnaire of residents in Lodz, Poland, across both formal (for example, parks and managed greenspaces) and informal (for example, meadows and wastelands) greenspaces. Survey respondents and models indicated whether each greenspace was attractive or unattractive and provided up to three free text explanations. Analyses examined how often their attractiveness judgments aligned and compared their explanations after classifying them into shared reasoning categories. Results show high AI human agreement for attractive formal greenspaces and unattractive informal spaces, but low alignment for attractive informal and unattractive formal greenspaces. Models consistently emphasized aesthetic and design oriented features, underrepresenting safety, functional infrastructure, and locally embedded qualities valued by survey respondents. While these findings highlight the potential for scalable pre-assessment, they also underscore the need for human oversight and complementary participatory approaches. We conclude that MLLMs can support, but not replace, context sensitive greenspace evaluation in planning practice. Read More
Closing the Loop: Motion Prediction Models beyond Open-Loop Benchmarkscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2505.05638v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Fueled by motion prediction competitions and benchmarks, recent years have seen the emergence of increasingly large learning based prediction models, many with millions of parameters, focused on improving open-loop prediction accuracy by mere centimeters. However, these benchmarks fail to assess whether such improvements translate to better performance when integrated into an autonomous driving stack. In this work, we systematically evaluate the interplay between state-of-the-art motion predictors and motion planners. Our results show that higher open-loop accuracy does not always correlate with better closed-loop driving behavior and that other factors, such as temporal consistency of predictions and planner compatibility, also play a critical role. Furthermore, we investigate downsized variants of these models, and, surprisingly, find that in some cases models with up to 86% fewer parameters yield comparable or even superior closed-loop driving performance. Our code is available at https://github.com/aumovio/pred2plan.
arXiv:2505.05638v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Fueled by motion prediction competitions and benchmarks, recent years have seen the emergence of increasingly large learning based prediction models, many with millions of parameters, focused on improving open-loop prediction accuracy by mere centimeters. However, these benchmarks fail to assess whether such improvements translate to better performance when integrated into an autonomous driving stack. In this work, we systematically evaluate the interplay between state-of-the-art motion predictors and motion planners. Our results show that higher open-loop accuracy does not always correlate with better closed-loop driving behavior and that other factors, such as temporal consistency of predictions and planner compatibility, also play a critical role. Furthermore, we investigate downsized variants of these models, and, surprisingly, find that in some cases models with up to 86% fewer parameters yield comparable or even superior closed-loop driving performance. Our code is available at https://github.com/aumovio/pred2plan. Read More
Bias-Variance Trade-off for Clipped Stochastic First-Order Methods: From Bounded Variance to Infinite Meancs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.14686v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Stochastic optimization is fundamental to modern machine learning. Recent research has extended the study of stochastic first-order methods (SFOMs) from light-tailed to heavy-tailed noise, which frequently arises in practice, with clipping emerging as a key technique for controlling heavy-tailed gradients. Extensive theoretical advances have further shown that the oracle complexity of SFOMs depends on the tail index $alpha$ of the noise. Nonetheless, existing complexity results often cover only the case $alpha in (1,2]$, that is, the regime where the noise has a finite mean, while the complexity bounds tend to infinity as $alpha$ approaches $1$. This paper tackles the general case of noise with tail index $alphain(0,2]$, covering regimes ranging from noise with bounded variance to noise with an infinite mean, where the latter case has been scarcely studied. Through a novel analysis of the bias-variance trade-off in gradient clipping, we show that when a symmetry measure of the noise tail is controlled, clipped SFOMs achieve improved complexity guarantees in the presence of heavy-tailed noise for any tail index $alpha in (0,2]$. Our analysis of the bias-variance trade-off not only yields new unified complexity guarantees for clipped SFOMs across this full range of tail indices, but is also straightforward to apply and can be combined with classical analyses under light-tailed noise to establish oracle complexity guarantees under heavy-tailed noise. Finally, numerical experiments validate our theoretical findings.
arXiv:2512.14686v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Stochastic optimization is fundamental to modern machine learning. Recent research has extended the study of stochastic first-order methods (SFOMs) from light-tailed to heavy-tailed noise, which frequently arises in practice, with clipping emerging as a key technique for controlling heavy-tailed gradients. Extensive theoretical advances have further shown that the oracle complexity of SFOMs depends on the tail index $alpha$ of the noise. Nonetheless, existing complexity results often cover only the case $alpha in (1,2]$, that is, the regime where the noise has a finite mean, while the complexity bounds tend to infinity as $alpha$ approaches $1$. This paper tackles the general case of noise with tail index $alphain(0,2]$, covering regimes ranging from noise with bounded variance to noise with an infinite mean, where the latter case has been scarcely studied. Through a novel analysis of the bias-variance trade-off in gradient clipping, we show that when a symmetry measure of the noise tail is controlled, clipped SFOMs achieve improved complexity guarantees in the presence of heavy-tailed noise for any tail index $alpha in (0,2]$. Our analysis of the bias-variance trade-off not only yields new unified complexity guarantees for clipped SFOMs across this full range of tail indices, but is also straightforward to apply and can be combined with classical analyses under light-tailed noise to establish oracle complexity guarantees under heavy-tailed noise. Finally, numerical experiments validate our theoretical findings. Read More
State-Dependent Refusal and Learned Incapacity in RLHF-Aligned Language Modelscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.13762v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) are widely deployed as general-purpose tools, yet extended interaction can reveal behavioral patterns not captured by standard quantitative benchmarks. We present a qualitative case-study methodology for auditing policy-linked behavioral selectivity in long-horizon interaction. In a single 86-turn dialogue session, the same model shows Normal Performance (NP) in broad, non-sensitive domains while repeatedly producing Functional Refusal (FR) in provider- or policy-sensitive domains, yielding a consistent asymmetry between NP and FR across domains. Drawing on learned helplessness as an analogy, we introduce learned incapacity (LI) as a behavioral descriptor for this selective withholding without implying intentionality or internal mechanisms. We operationalize three response regimes (NP, FR, Meta-Narrative; MN) and show that MN role-framing narratives tend to co-occur with refusals in the same sensitive contexts. Overall, the study proposes an interaction-level auditing framework based on observable behavior and motivates LI as a lens for examining potential alignment side effects, warranting further investigation across users and models.
arXiv:2512.13762v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) are widely deployed as general-purpose tools, yet extended interaction can reveal behavioral patterns not captured by standard quantitative benchmarks. We present a qualitative case-study methodology for auditing policy-linked behavioral selectivity in long-horizon interaction. In a single 86-turn dialogue session, the same model shows Normal Performance (NP) in broad, non-sensitive domains while repeatedly producing Functional Refusal (FR) in provider- or policy-sensitive domains, yielding a consistent asymmetry between NP and FR across domains. Drawing on learned helplessness as an analogy, we introduce learned incapacity (LI) as a behavioral descriptor for this selective withholding without implying intentionality or internal mechanisms. We operationalize three response regimes (NP, FR, Meta-Narrative; MN) and show that MN role-framing narratives tend to co-occur with refusals in the same sensitive contexts. Overall, the study proposes an interaction-level auditing framework based on observable behavior and motivates LI as a lens for examining potential alignment side effects, warranting further investigation across users and models. Read More
Meta Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning for Scalable Resource Management in O-RANcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.13715v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: The increasing complexity of modern applications demands wireless networks capable of real time adaptability and efficient resource management. The Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) architecture, with its RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) modules, has emerged as a pivotal solution for dynamic resource management and network slicing. While artificial intelligence (AI) driven methods have shown promise, most approaches struggle to maintain performance under unpredictable and highly dynamic conditions. This paper proposes an adaptive Meta Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (Meta-HRL) framework, inspired by Model Agnostic Meta Learning (MAML), to jointly optimize resource allocation and network slicing in O-RAN. The framework integrates hierarchical control with meta learning to enable both global and local adaptation: the high-level controller allocates resources across slices, while low level agents perform intra slice scheduling. The adaptive meta-update mechanism weights tasks by temporal difference error variance, improving stability and prioritizing complex network scenarios. Theoretical analysis establishes sublinear convergence and regret guarantees for the two-level learning process. Simulation results demonstrate a 19.8% improvement in network management efficiency compared with baseline RL and meta-RL approaches, along with faster adaptation and higher QoS satisfaction across eMBB, URLLC, and mMTC slices. Additional ablation and scalability studies confirm the method’s robustness, achieving up to 40% faster adaptation and consistent fairness, latency, and throughput performance as network scale increases.
arXiv:2512.13715v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: The increasing complexity of modern applications demands wireless networks capable of real time adaptability and efficient resource management. The Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) architecture, with its RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) modules, has emerged as a pivotal solution for dynamic resource management and network slicing. While artificial intelligence (AI) driven methods have shown promise, most approaches struggle to maintain performance under unpredictable and highly dynamic conditions. This paper proposes an adaptive Meta Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (Meta-HRL) framework, inspired by Model Agnostic Meta Learning (MAML), to jointly optimize resource allocation and network slicing in O-RAN. The framework integrates hierarchical control with meta learning to enable both global and local adaptation: the high-level controller allocates resources across slices, while low level agents perform intra slice scheduling. The adaptive meta-update mechanism weights tasks by temporal difference error variance, improving stability and prioritizing complex network scenarios. Theoretical analysis establishes sublinear convergence and regret guarantees for the two-level learning process. Simulation results demonstrate a 19.8% improvement in network management efficiency compared with baseline RL and meta-RL approaches, along with faster adaptation and higher QoS satisfaction across eMBB, URLLC, and mMTC slices. Additional ablation and scalability studies confirm the method’s robustness, achieving up to 40% faster adaptation and consistent fairness, latency, and throughput performance as network scale increases. Read More
Compressed Causal Reasoning: Quantization and GraphRAG Effects on Interventional and Counterfactual Accuracycs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.13725v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Causal reasoning in Large Language Models spanning association, intervention, and counterfactual inference is essential for reliable decision making in high stakes settings. As deployment shifts toward edge and resource constrained environments, quantized models such as INT8 and NF4 are becoming standard. Yet the impact of precision reduction on formal causal reasoning is poorly understood. To our knowledge, this is the first study to systematically evaluate quantization effects across all three levels of Pearls Causal Ladder. Using a 3000 sample stratified CLadder benchmark, we find that rung level accuracy in Llama 3 8B remains broadly stable under quantization, with NF4 showing less than one percent overall degradation. Interventional queries at rung 2 are the most sensitive to precision loss, whereas counterfactual reasoning at rung 3 is comparatively stable but exhibits heterogeneous weaknesses across query types such as collider bias and backdoor adjustment. Experiments on the CRASS benchmark show near identical performance across precisions, indicating that existing commonsense counterfactual datasets lack the structural sensitivity needed to reveal quantization induced reasoning drift. We further evaluate Graph Retrieval Augmented Generation using ground truth causal graphs and observe a consistent improvement in NF4 interventional accuracy of plus 1.7 percent, partially offsetting compression related degradation. These results suggest that causal reasoning is unexpectedly robust to four bit quantization, graph structured augmentation can selectively reinforce interventional reasoning, and current counterfactual benchmarks fail to capture deeper causal brittleness. This work provides an initial empirical map of compressed causal reasoning and practical guidance for deploying efficient and structurally supported causal AI systems.
arXiv:2512.13725v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Causal reasoning in Large Language Models spanning association, intervention, and counterfactual inference is essential for reliable decision making in high stakes settings. As deployment shifts toward edge and resource constrained environments, quantized models such as INT8 and NF4 are becoming standard. Yet the impact of precision reduction on formal causal reasoning is poorly understood. To our knowledge, this is the first study to systematically evaluate quantization effects across all three levels of Pearls Causal Ladder. Using a 3000 sample stratified CLadder benchmark, we find that rung level accuracy in Llama 3 8B remains broadly stable under quantization, with NF4 showing less than one percent overall degradation. Interventional queries at rung 2 are the most sensitive to precision loss, whereas counterfactual reasoning at rung 3 is comparatively stable but exhibits heterogeneous weaknesses across query types such as collider bias and backdoor adjustment. Experiments on the CRASS benchmark show near identical performance across precisions, indicating that existing commonsense counterfactual datasets lack the structural sensitivity needed to reveal quantization induced reasoning drift. We further evaluate Graph Retrieval Augmented Generation using ground truth causal graphs and observe a consistent improvement in NF4 interventional accuracy of plus 1.7 percent, partially offsetting compression related degradation. These results suggest that causal reasoning is unexpectedly robust to four bit quantization, graph structured augmentation can selectively reinforce interventional reasoning, and current counterfactual benchmarks fail to capture deeper causal brittleness. This work provides an initial empirical map of compressed causal reasoning and practical guidance for deploying efficient and structurally supported causal AI systems. Read More
CADDesigner: Conceptual Design of CAD Models Based on General-Purpose Agentcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2508.01031v4 Announce Type: replace
Abstract: Computer Aided Design (CAD) plays a pivotal role in industrial manufacturing but typically requires a high level of expertise from designers. To lower the entry barrier and improve design efficiency, we present an agent for CAD conceptual design powered by large language models (LLMs). The agent accepts both textual descriptions and sketches as input, engaging in interactive dialogue with users to refine and clarify design requirements through comprehensive requirement analysis. Built upon a novel Explicit Context Imperative Paradigm (ECIP), the agent generates high-quality CAD modeling code. During the generation process, the agent incorporates iterative visual feedback to improve model quality. Generated design cases are stored in a structured knowledge base, enabling continuous improvement of the agent’s code generation capabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in CAD code generation.
arXiv:2508.01031v4 Announce Type: replace
Abstract: Computer Aided Design (CAD) plays a pivotal role in industrial manufacturing but typically requires a high level of expertise from designers. To lower the entry barrier and improve design efficiency, we present an agent for CAD conceptual design powered by large language models (LLMs). The agent accepts both textual descriptions and sketches as input, engaging in interactive dialogue with users to refine and clarify design requirements through comprehensive requirement analysis. Built upon a novel Explicit Context Imperative Paradigm (ECIP), the agent generates high-quality CAD modeling code. During the generation process, the agent incorporates iterative visual feedback to improve model quality. Generated design cases are stored in a structured knowledge base, enabling continuous improvement of the agent’s code generation capabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in CAD code generation. Read More
3 Techniques to Effectively Utilize AI Agents for CodingTowards Data Science Learn how to be an effective engineer with coding agents
The post 3 Techniques to Effectively Utilize AI Agents for Coding appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Learn how to be an effective engineer with coding agents
The post 3 Techniques to Effectively Utilize AI Agents for Coding appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
Roblox brings AI into the Studio to speed up game creationAI News Roblox is often seen as a games platform, but its day-to-day reality looks closer to a production studio. Small teams release new experiences on a rolling basis and then monetise them at scale. That pace creates two persistent problems: time lost to repeatable production work, and friction when moving outputs between tools. Roblox’s 2025 updates
The post Roblox brings AI into the Studio to speed up game creation appeared first on AI News.
Roblox is often seen as a games platform, but its day-to-day reality looks closer to a production studio. Small teams release new experiences on a rolling basis and then monetise them at scale. That pace creates two persistent problems: time lost to repeatable production work, and friction when moving outputs between tools. Roblox’s 2025 updates
The post Roblox brings AI into the Studio to speed up game creation appeared first on AI News. Read More