A Clustering-Based Variable Ordering Framework for Relaxed Decision Diagrams for Maximum Weighted Independent Set Problemcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.15198v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Efficient exact algorithms for Discrete Optimization (DO) rely heavily on strong primal and dual bounds. Relaxed Decision Diagrams (DDs) provide a versatile mechanism for deriving such dual bounds by compactly over-approximating the solution space through node merging. However, the quality of these relaxed diagrams, i.e. the tightness of the resulting dual bounds, depends critically on the variable ordering and the merging decisions executed during compilation. While dynamic variable ordering heuristics effectively tighten bounds, they often incur computational overhead when evaluated globally across the entire variable set. To mitigate this trade-off, this work introduces a novel clustering-based framework for variable ordering. Instead of applying dynamic ordering heuristics to the full set of unfixed variables, we first partition variables into clusters. We then leverage this structural decomposition to guide the ordering process, significantly reducing the heuristic’s search space. Within this framework, we investigate two distinct strategies: Cluster-to-Cluster, which processes clusters sequentially using problem-specific aggregate criteria (such as cumulative vertex weights in the Maximum Weighted Independent Set Problem (MWISP)), and Pick-and-Sort, which iteratively selects and sorts representative variables from each cluster to balance local diversity with heuristic guidance. Later on, developing some theoretical results on the growth of the size of DDs for MWISP we propose two different policies for setting the number of clusters within the proposed framework. We embed these strategies into a DD-based branch-and-bound algorithm and evaluate them on the MWISP. Across benchmark instances, the proposed methodology consistently reduces computational costs compared to standard dynamic variable ordering baseline.
arXiv:2512.15198v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Efficient exact algorithms for Discrete Optimization (DO) rely heavily on strong primal and dual bounds. Relaxed Decision Diagrams (DDs) provide a versatile mechanism for deriving such dual bounds by compactly over-approximating the solution space through node merging. However, the quality of these relaxed diagrams, i.e. the tightness of the resulting dual bounds, depends critically on the variable ordering and the merging decisions executed during compilation. While dynamic variable ordering heuristics effectively tighten bounds, they often incur computational overhead when evaluated globally across the entire variable set. To mitigate this trade-off, this work introduces a novel clustering-based framework for variable ordering. Instead of applying dynamic ordering heuristics to the full set of unfixed variables, we first partition variables into clusters. We then leverage this structural decomposition to guide the ordering process, significantly reducing the heuristic’s search space. Within this framework, we investigate two distinct strategies: Cluster-to-Cluster, which processes clusters sequentially using problem-specific aggregate criteria (such as cumulative vertex weights in the Maximum Weighted Independent Set Problem (MWISP)), and Pick-and-Sort, which iteratively selects and sorts representative variables from each cluster to balance local diversity with heuristic guidance. Later on, developing some theoretical results on the growth of the size of DDs for MWISP we propose two different policies for setting the number of clusters within the proposed framework. We embed these strategies into a DD-based branch-and-bound algorithm and evaluate them on the MWISP. Across benchmark instances, the proposed methodology consistently reduces computational costs compared to standard dynamic variable ordering baseline. Read More
LADY: Linear Attention for Autonomous Driving Efficiency without Transformerscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.15038v2 Announce Type: new
Abstract: End-to-end paradigms have demonstrated great potential for autonomous driving. Additionally, most existing methods are built upon Transformer architectures. However, transformers incur a quadratic attention cost, limiting their ability to model long spatial and temporal sequences-particularly on resource-constrained edge platforms. As autonomous driving inherently demands efficient temporal modeling, this challenge severely limits their deployment and real-time performance. Recently, linear attention mechanisms have gained increasing attention due to their superior spatiotemporal complexity. However, existing linear attention architectures are limited to self-attention, lacking support for cross-modal and cross-temporal interactions-both crucial for autonomous driving. In this work, we propose LADY, the first fully linear attention-based generative model for end-to-end autonomous driving. LADY enables fusion of long-range temporal context at inference with constant computational and memory costs, regardless of the history length of camera and LiDAR features. Additionally, we introduce a lightweight linear cross-attention mechanism that enables effective cross-modal information exchange. Experiments on the NAVSIM and Bench2Drive benchmarks demonstrate that LADY achieves state-of-the-art performance with constant-time and memory complexity, offering improved planning performance and significantly reduced computational cost. Additionally, the model has been deployed and validated on edge devices, demonstrating its practicality in resource-limited scenarios.
arXiv:2512.15038v2 Announce Type: new
Abstract: End-to-end paradigms have demonstrated great potential for autonomous driving. Additionally, most existing methods are built upon Transformer architectures. However, transformers incur a quadratic attention cost, limiting their ability to model long spatial and temporal sequences-particularly on resource-constrained edge platforms. As autonomous driving inherently demands efficient temporal modeling, this challenge severely limits their deployment and real-time performance. Recently, linear attention mechanisms have gained increasing attention due to their superior spatiotemporal complexity. However, existing linear attention architectures are limited to self-attention, lacking support for cross-modal and cross-temporal interactions-both crucial for autonomous driving. In this work, we propose LADY, the first fully linear attention-based generative model for end-to-end autonomous driving. LADY enables fusion of long-range temporal context at inference with constant computational and memory costs, regardless of the history length of camera and LiDAR features. Additionally, we introduce a lightweight linear cross-attention mechanism that enables effective cross-modal information exchange. Experiments on the NAVSIM and Bench2Drive benchmarks demonstrate that LADY achieves state-of-the-art performance with constant-time and memory complexity, offering improved planning performance and significantly reduced computational cost. Additionally, the model has been deployed and validated on edge devices, demonstrating its practicality in resource-limited scenarios. Read More
Beyond Fast and Slow: Cognitive-Inspired Elastic Reasoning for Large Language Modelscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.15089v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance across various language tasks. However, existing LLM reasoning strategies mainly rely on the LLM itself with fast or slow mode (like o1 thinking) and thus struggle to balance reasoning efficiency and accuracy across queries of varying difficulties. In this paper, we propose Cognitive-Inspired Elastic Reasoning (CogER), a framework inspired by human hierarchical reasoning that dynamically selects the most suitable reasoning strategy for each query. Specifically, CogER first assesses the complexity of incoming queries and assigns them to one of several predefined levels, each corresponding to a tailored processing strategy, thereby addressing the challenge of unobservable query difficulty. To achieve automatic strategy selection, we model the process as a Markov Decision Process and train a CogER-Agent using reinforcement learning. The agent is guided by a reward function that balances solution quality and computational cost, ensuring resource-efficient reasoning. Moreover, for queries requiring external tools, we introduce Cognitive Tool-Assisted Reasoning, which enables the LLM to autonomously invoke external tools within its chain-of-thought. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CogER outperforms state-of-the-art Test-Time scaling methods, achieving at least a 13% relative improvement in average exact match on In-Domain tasks and an 8% relative gain on Out-of-Domain tasks.
arXiv:2512.15089v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance across various language tasks. However, existing LLM reasoning strategies mainly rely on the LLM itself with fast or slow mode (like o1 thinking) and thus struggle to balance reasoning efficiency and accuracy across queries of varying difficulties. In this paper, we propose Cognitive-Inspired Elastic Reasoning (CogER), a framework inspired by human hierarchical reasoning that dynamically selects the most suitable reasoning strategy for each query. Specifically, CogER first assesses the complexity of incoming queries and assigns them to one of several predefined levels, each corresponding to a tailored processing strategy, thereby addressing the challenge of unobservable query difficulty. To achieve automatic strategy selection, we model the process as a Markov Decision Process and train a CogER-Agent using reinforcement learning. The agent is guided by a reward function that balances solution quality and computational cost, ensuring resource-efficient reasoning. Moreover, for queries requiring external tools, we introduce Cognitive Tool-Assisted Reasoning, which enables the LLM to autonomously invoke external tools within its chain-of-thought. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CogER outperforms state-of-the-art Test-Time scaling methods, achieving at least a 13% relative improvement in average exact match on In-Domain tasks and an 8% relative gain on Out-of-Domain tasks. Read More
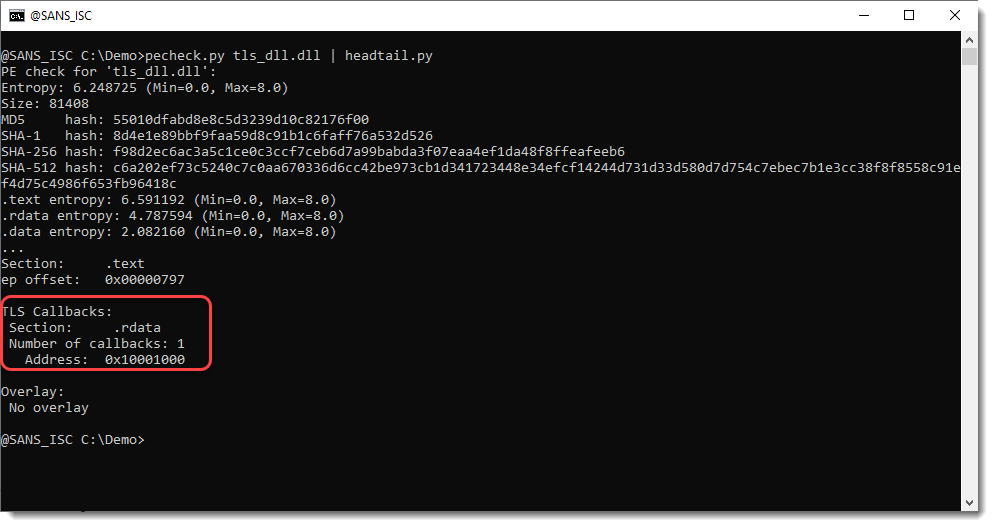
Xavier’s diary entry “Abusing DLLs EntryPoint for the Fun” inspired me to do some tests with TLS Callbacks and DLLs. TLS stands for Thread Local Storage. TLS Callbacks are an execution mechanism in Windows PE files that lets code run automatically when a process or thread starts, before the program’s normal entry point is reached. I’ve […]
WatchGuard has warned customers to patch a critical, actively exploited remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability in its Firebox firewalls. […] Read More
Certain motherboard models from vendors like ASRock, ASUSTeK Computer, GIGABYTE, and MSI are affected by a security vulnerability that leaves them susceptible to early-boot direct memory access (DMA) attacks across architectures that implement a Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) and input–output memory management unit (IOMMU). UEFI and IOMMU are designed to enforce a security Read More
Grocery delivery service Instacart will refund $60 million to settle FTC claims that it misled customers with false advertising and unlawfully enrolled them in paid subscriptions. […] Read More
On Assessing the Relevance of Code Reviews Authored by Generative Modelscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.15466v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: The use of large language models like ChatGPT in code review offers promising efficiency gains but also raises concerns about correctness and safety. Existing evaluation methods for code review generation either rely on automatic comparisons to a single ground truth, which fails to capture the variability of human perspectives, or on subjective assessments of “usefulness”, a highly ambiguous concept. We propose a novel evaluation approach based on what we call multi-subjective ranking. Using a dataset of 280 self-contained code review requests and corresponding comments from CodeReview StackExchange, multiple human judges ranked the quality of ChatGPT-generated comments alongside the top human responses from the platform. Results show that ChatGPT’s comments were ranked significantly better than human ones, even surpassing StackExchange’s accepted answers. Going further, our proposed method motivates and enables more meaningful assessments of generative AI’s performance in code review, while also raising awareness of potential risks of unchecked integration into review processes.
arXiv:2512.15466v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: The use of large language models like ChatGPT in code review offers promising efficiency gains but also raises concerns about correctness and safety. Existing evaluation methods for code review generation either rely on automatic comparisons to a single ground truth, which fails to capture the variability of human perspectives, or on subjective assessments of “usefulness”, a highly ambiguous concept. We propose a novel evaluation approach based on what we call multi-subjective ranking. Using a dataset of 280 self-contained code review requests and corresponding comments from CodeReview StackExchange, multiple human judges ranked the quality of ChatGPT-generated comments alongside the top human responses from the platform. Results show that ChatGPT’s comments were ranked significantly better than human ones, even surpassing StackExchange’s accepted answers. Going further, our proposed method motivates and enables more meaningful assessments of generative AI’s performance in code review, while also raising awareness of potential risks of unchecked integration into review processes. Read More
Control-Augmented Autoregressive Diffusion for Data Assimilationcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.06637v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Despite recent advances in test-time scaling and finetuning of diffusion models, guidance in Auto-Regressive Diffusion Models (ARDMs) remains underexplored. We introduce an amortized framework that augments a pretrained ARDM with a lightweight controller network, trained offline by previewing future rollouts to output stepwise controls that anticipate upcoming observations under a terminal-cost objective. Our approach is motivated by viewing guided generation as an entropy-regularized stochastic optimal control problem over ARDM trajectories: we learn a reusable policy that injects small control corrections inside each denoising sub-step while remaining anchored to the pretrained dynamics. We evaluate this framework in the context of data assimilation (DA) for chaotic spatiotemporal partial differential equations (PDEs), where existing methods can be computationally prohibitive and prone to forecast drift under sparse observations. At inference, DA reduces to a single causal forward rollout with on-the-fly corrections, requiring neither adjoint computations nor gradient-based optimization, and yields an order-of-magnitude speedup over strong diffusion-based DA baselines. Across two canonical PDEs and six observation regimes, our method consistently improves stability, accuracy, and physics-aware fidelity over state-of-the-art baselines. We will release code and checkpoints publicly.
arXiv:2510.06637v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Despite recent advances in test-time scaling and finetuning of diffusion models, guidance in Auto-Regressive Diffusion Models (ARDMs) remains underexplored. We introduce an amortized framework that augments a pretrained ARDM with a lightweight controller network, trained offline by previewing future rollouts to output stepwise controls that anticipate upcoming observations under a terminal-cost objective. Our approach is motivated by viewing guided generation as an entropy-regularized stochastic optimal control problem over ARDM trajectories: we learn a reusable policy that injects small control corrections inside each denoising sub-step while remaining anchored to the pretrained dynamics. We evaluate this framework in the context of data assimilation (DA) for chaotic spatiotemporal partial differential equations (PDEs), where existing methods can be computationally prohibitive and prone to forecast drift under sparse observations. At inference, DA reduces to a single causal forward rollout with on-the-fly corrections, requiring neither adjoint computations nor gradient-based optimization, and yields an order-of-magnitude speedup over strong diffusion-based DA baselines. Across two canonical PDEs and six observation regimes, our method consistently improves stability, accuracy, and physics-aware fidelity over state-of-the-art baselines. We will release code and checkpoints publicly. Read More
Cooperative Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Question Answering: Mutual Information Exchange and Ranking by Contrasting Layerscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.10422v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Since large language models (LLMs) have a tendency to generate factually inaccurate output, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has gained significant attention as a key means to mitigate this downside of harnessing only LLMs. However, existing RAG methods for simple and multi-hop question answering (QA) are still prone to incorrect retrievals and hallucinations. To address these limitations, we propose CoopRAG, a novel RAG framework for the question answering task in which a retriever and an LLM work cooperatively with each other by exchanging informative knowledge, and the earlier and later layers of the retriever model work cooperatively with each other to accurately rank the retrieved documents relevant to a given query. In this framework, we (i) unroll a question into sub-questions and a reasoning chain in which uncertain positions are masked, (ii) retrieve the documents relevant to the question augmented with the sub-questions and the reasoning chain, (iii) rerank the documents by contrasting layers of the retriever, and (iv) reconstruct the reasoning chain by filling the masked positions via the LLM. Our experiments demonstrate that CoopRAG consistently outperforms state-of-the-art QA methods on three multi-hop QA datasets as well as a simple QA dataset in terms of both the retrieval and QA performances. Our code is available.
arXiv:2512.10422v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Since large language models (LLMs) have a tendency to generate factually inaccurate output, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has gained significant attention as a key means to mitigate this downside of harnessing only LLMs. However, existing RAG methods for simple and multi-hop question answering (QA) are still prone to incorrect retrievals and hallucinations. To address these limitations, we propose CoopRAG, a novel RAG framework for the question answering task in which a retriever and an LLM work cooperatively with each other by exchanging informative knowledge, and the earlier and later layers of the retriever model work cooperatively with each other to accurately rank the retrieved documents relevant to a given query. In this framework, we (i) unroll a question into sub-questions and a reasoning chain in which uncertain positions are masked, (ii) retrieve the documents relevant to the question augmented with the sub-questions and the reasoning chain, (iii) rerank the documents by contrasting layers of the retriever, and (iv) reconstruct the reasoning chain by filling the masked positions via the LLM. Our experiments demonstrate that CoopRAG consistently outperforms state-of-the-art QA methods on three multi-hop QA datasets as well as a simple QA dataset in terms of both the retrieval and QA performances. Our code is available. Read More