Microsoft announced today that it has canceled plans to impose a daily limit of 2,000 external recipients on Exchange Online bulk email senders. […] Read More
OpenAI is testing a new model for Codex, and it could be the company’s best coding model yet. […] Read More
Threat actors are using the social engineering technique and a legitimate Microsoft tool to deploy the DCRat remote access Trojan against targets in the hospitality sector. Read More
The National Security Bureau in Taiwan says that China’s attacks on the country’s energy sector increased tenfold in 2025 compared to the previous year. […] Read More
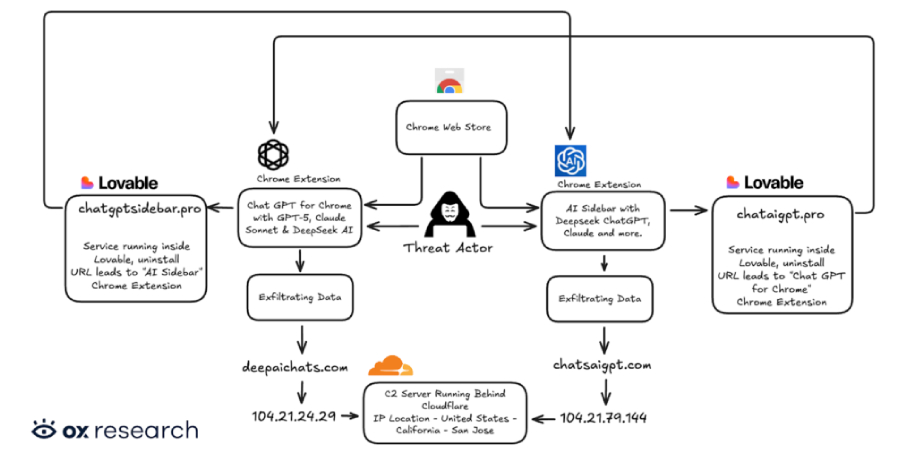
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered two new malicious extensions on the Chrome Web Store that are designed to exfiltrate OpenAI ChatGPT and DeepSeek conversations alongside browsing data to servers under the attackers’ control. The names of the extensions, which collectively have over 900,000 users, are below – Chat GPT for Chrome with GPT-5, Claude Sonnet & […]
The Kimwolf botnet, an Android variant of the Aisuru malware, has grown to more than two million hosts, most of them infected by exploiting vulnerabilities in residential proxy networks to target devices on internal networks. […] Read More
The GPT-4o Shock Emotional Attachment to AI Models and Its Impact on Regulatory Acceptance: A Cross-Cultural Analysis of the Immediate Transition from GPT-4o to GPT-5cs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2508.16624v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: In August 2025, a major AI company’s immediate, mandatory transition from its previous to its next-generation model triggered widespread public reactions. I collected 150 posts in Japanese and English from multiple social media platforms and video-sharing services between August 8-9, 2025, and qualitatively analyzed expressions of emotional attachment and resistance. Users often described GPT-4o as a trusted partner or AI boyfriend, suggesting person-like bonds. Japanese posts were dominated by loss-oriented narratives, whereas English posts included more anger, meta-level critique, and memes.A preliminary quantitative check showed a statistically significant difference in attachment coding between Japanese and English posts, with substantially higher attachment observed in the Japanese data. The findings suggest that for attachment-heavy models, even safety-oriented changes can face rapid, large-scale resistance that narrows the practical window for behavioral control. If future AI robots capable of inducing emotional bonds become widespread in the physical world, such attachment could surpass the ability to enforce regulation at an even earlier stage than in digital settings. Policy options include gradual transitions, parallel availability, and proactive measurement of attachment thresholds and points of no return to prevent emotional dynamics from outpacing effective governance.
arXiv:2508.16624v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: In August 2025, a major AI company’s immediate, mandatory transition from its previous to its next-generation model triggered widespread public reactions. I collected 150 posts in Japanese and English from multiple social media platforms and video-sharing services between August 8-9, 2025, and qualitatively analyzed expressions of emotional attachment and resistance. Users often described GPT-4o as a trusted partner or AI boyfriend, suggesting person-like bonds. Japanese posts were dominated by loss-oriented narratives, whereas English posts included more anger, meta-level critique, and memes.A preliminary quantitative check showed a statistically significant difference in attachment coding between Japanese and English posts, with substantially higher attachment observed in the Japanese data. The findings suggest that for attachment-heavy models, even safety-oriented changes can face rapid, large-scale resistance that narrows the practical window for behavioral control. If future AI robots capable of inducing emotional bonds become widespread in the physical world, such attachment could surpass the ability to enforce regulation at an even earlier stage than in digital settings. Policy options include gradual transitions, parallel availability, and proactive measurement of attachment thresholds and points of no return to prevent emotional dynamics from outpacing effective governance. Read More
Microsoft has pushed back against claims that multiple prompt injection and sandbox-related issues raised by a security engineer in its Copilot AI assistant constitute security vulnerabilities. The development highlights a growing divide between how vendors and researchers define risk in generative AI systems. […] Read More
FastV-RAG: Towards Fast and Fine-Grained Video QA with Retrieval-Augmented Generationcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.01513v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Vision-Language Models (VLMs) excel at visual reasoning but still struggle with integrating external knowledge. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a promising solution, but current methods remain inefficient and often fail to maintain high answer quality. To address these challenges, we propose VideoSpeculateRAG, an efficient VLM-based RAG framework built on two key ideas. First, we introduce a speculative decoding pipeline: a lightweight draft model quickly generates multiple answer candidates, which are then verified and refined by a more accurate heavyweight model, substantially reducing inference latency without sacrificing correctness. Second, we identify a major source of error – incorrect entity recognition in retrieved knowledge – and mitigate it with a simple yet effective similarity-based filtering strategy that improves entity alignment and boosts overall answer accuracy. Experiments demonstrate that VideoSpeculateRAG achieves comparable or higher accuracy than standard RAG approaches while accelerating inference by approximately 2x. Our framework highlights the potential of combining speculative decoding with retrieval-augmented reasoning to enhance efficiency and reliability in complex, knowledge-intensive multimodal tasks.
arXiv:2601.01513v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Vision-Language Models (VLMs) excel at visual reasoning but still struggle with integrating external knowledge. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a promising solution, but current methods remain inefficient and often fail to maintain high answer quality. To address these challenges, we propose VideoSpeculateRAG, an efficient VLM-based RAG framework built on two key ideas. First, we introduce a speculative decoding pipeline: a lightweight draft model quickly generates multiple answer candidates, which are then verified and refined by a more accurate heavyweight model, substantially reducing inference latency without sacrificing correctness. Second, we identify a major source of error – incorrect entity recognition in retrieved knowledge – and mitigate it with a simple yet effective similarity-based filtering strategy that improves entity alignment and boosts overall answer accuracy. Experiments demonstrate that VideoSpeculateRAG achieves comparable or higher accuracy than standard RAG approaches while accelerating inference by approximately 2x. Our framework highlights the potential of combining speculative decoding with retrieval-augmented reasoning to enhance efficiency and reliability in complex, knowledge-intensive multimodal tasks. Read More
OmniNeuro: A Multimodal HCI Framework for Explainable BCI Feedback via Generative AI and Sonificationcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.00843v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: While Deep Learning has improved Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) decoding accuracy, clinical adoption is hindered by the “Black Box” nature of these algorithms, leading to user frustration and poor neuroplasticity outcomes. We propose OmniNeuro, a novel HCI framework that transforms the BCI from a silent decoder into a transparent feedback partner. OmniNeuro integrates three interpretability engines: (1) Physics (Energy), (2) Chaos (Fractal Complexity), and (3) Quantum-Inspired uncertainty modeling. These metrics drive real-time Neuro-Sonification and Generative AI Clinical Reports. Evaluated on the PhysioNet dataset ($N=109$), the system achieved a mean accuracy of 58.52%, with qualitative pilot studies ($N=3$) confirming that explainable feedback helps users regulate mental effort and reduces the “trial-and-error” phase. OmniNeuro is decoder-agnostic, acting as an essential interpretability layer for any state-of-the-art architecture.
arXiv:2601.00843v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: While Deep Learning has improved Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) decoding accuracy, clinical adoption is hindered by the “Black Box” nature of these algorithms, leading to user frustration and poor neuroplasticity outcomes. We propose OmniNeuro, a novel HCI framework that transforms the BCI from a silent decoder into a transparent feedback partner. OmniNeuro integrates three interpretability engines: (1) Physics (Energy), (2) Chaos (Fractal Complexity), and (3) Quantum-Inspired uncertainty modeling. These metrics drive real-time Neuro-Sonification and Generative AI Clinical Reports. Evaluated on the PhysioNet dataset ($N=109$), the system achieved a mean accuracy of 58.52%, with qualitative pilot studies ($N=3$) confirming that explainable feedback helps users regulate mental effort and reduces the “trial-and-error” phase. OmniNeuro is decoder-agnostic, acting as an essential interpretability layer for any state-of-the-art architecture. Read More