How to Run Coding Agents in ParallelTowards Data Science Get the most out of Claude Code
The post How to Run Coding Agents in Parallel appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Get the most out of Claude Code
The post How to Run Coding Agents in Parallel appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
Google Antigravity: AI-First Development with This New IDEKDnuggets Google Antigravity marks the beginning of the “agent-first” era, It isn’t just a Copilot, it’s a platform where you stop being the typist and start being the architect.
Google Antigravity marks the beginning of the “agent-first” era, It isn’t just a Copilot, it’s a platform where you stop being the typist and start being the architect. Read More
Scale creative asset discovery with Amazon Nova Multimodal Embeddings unified vector searchArtificial Intelligence In this post, we describe how you can use Amazon Nova Multimodal Embeddings to retrieve specific video segments. We also review a real-world use case in which Nova Multimodal Embeddings achieved a recall success rate of 96.7% and a high-precision recall of 73.3% (returning the target content in the top two results) when tested against a library of 170 gaming creative assets. The model also demonstrates strong cross-language capabilities with minimal performance degradation across multiple languages.
In this post, we describe how you can use Amazon Nova Multimodal Embeddings to retrieve specific video segments. We also review a real-world use case in which Nova Multimodal Embeddings achieved a recall success rate of 96.7% and a high-precision recall of 73.3% (returning the target content in the top two results) when tested against a library of 170 gaming creative assets. The model also demonstrates strong cross-language capabilities with minimal performance degradation across multiple languages. Read More
Safeguard generative AI applications with Amazon Bedrock GuardrailsArtificial Intelligence In this post, we demonstrate how you can address these challenges by adding centralized safeguards to a custom multi-provider generative AI gateway using Amazon Bedrock Guardrails.
In this post, we demonstrate how you can address these challenges by adding centralized safeguards to a custom multi-provider generative AI gateway using Amazon Bedrock Guardrails. Read More
Build a generative AI-powered business reporting solution with Amazon BedrockArtificial Intelligence This post introduces generative AI guided business reporting—with a focus on writing achievements & challenges about your business—providing a smart, practical solution that helps simplify and accelerate internal communication and reporting.
This post introduces generative AI guided business reporting—with a focus on writing achievements & challenges about your business—providing a smart, practical solution that helps simplify and accelerate internal communication and reporting. Read More
How the Amazon AMET Payments team accelerates test case generation with Strands AgentsArtificial Intelligence In this post, we explain how we overcame the limitations of single-agent AI systems through a human-centric approach, implemented structured outputs to significantly reduce hallucinations and built a scalable solution now positioned for expansion across the AMET QA team and later across other QA teams in International Emerging Stores and Payments (IESP) Org.
In this post, we explain how we overcame the limitations of single-agent AI systems through a human-centric approach, implemented structured outputs to significantly reduce hallucinations and built a scalable solution now positioned for expansion across the AMET QA team and later across other QA teams in International Emerging Stores and Payments (IESP) Org. Read More
When Shapley Values Break: A Guide to Robust Model ExplainabilityTowards Data Science Shapley Values are one of the most common methods for explainability, yet they can be misleading. Discover how to overcome these limitations to achieve better insights.
The post When Shapley Values Break: A Guide to Robust Model Explainability appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Shapley Values are one of the most common methods for explainability, yet they can be misleading. Discover how to overcome these limitations to achieve better insights.
The post When Shapley Values Break: A Guide to Robust Model Explainability appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
AI dominated the conversation in 2025, CIOs shift gears in 2026AI News Author: Richard Farrell, CIO at Netcall After a year of rapid adoption and high expectations surrounding artificial intelligence, 2026 is shaping up to be the year CIOs apply a more strategic lens. Not to slow progress, but to steer it in a smarter direction. In 2025, we saw the rise of AI copilots across almost
The post AI dominated the conversation in 2025, CIOs shift gears in 2026 appeared first on AI News.
Author: Richard Farrell, CIO at Netcall After a year of rapid adoption and high expectations surrounding artificial intelligence, 2026 is shaping up to be the year CIOs apply a more strategic lens. Not to slow progress, but to steer it in a smarter direction. In 2025, we saw the rise of AI copilots across almost
The post AI dominated the conversation in 2025, CIOs shift gears in 2026 appeared first on AI News. Read More
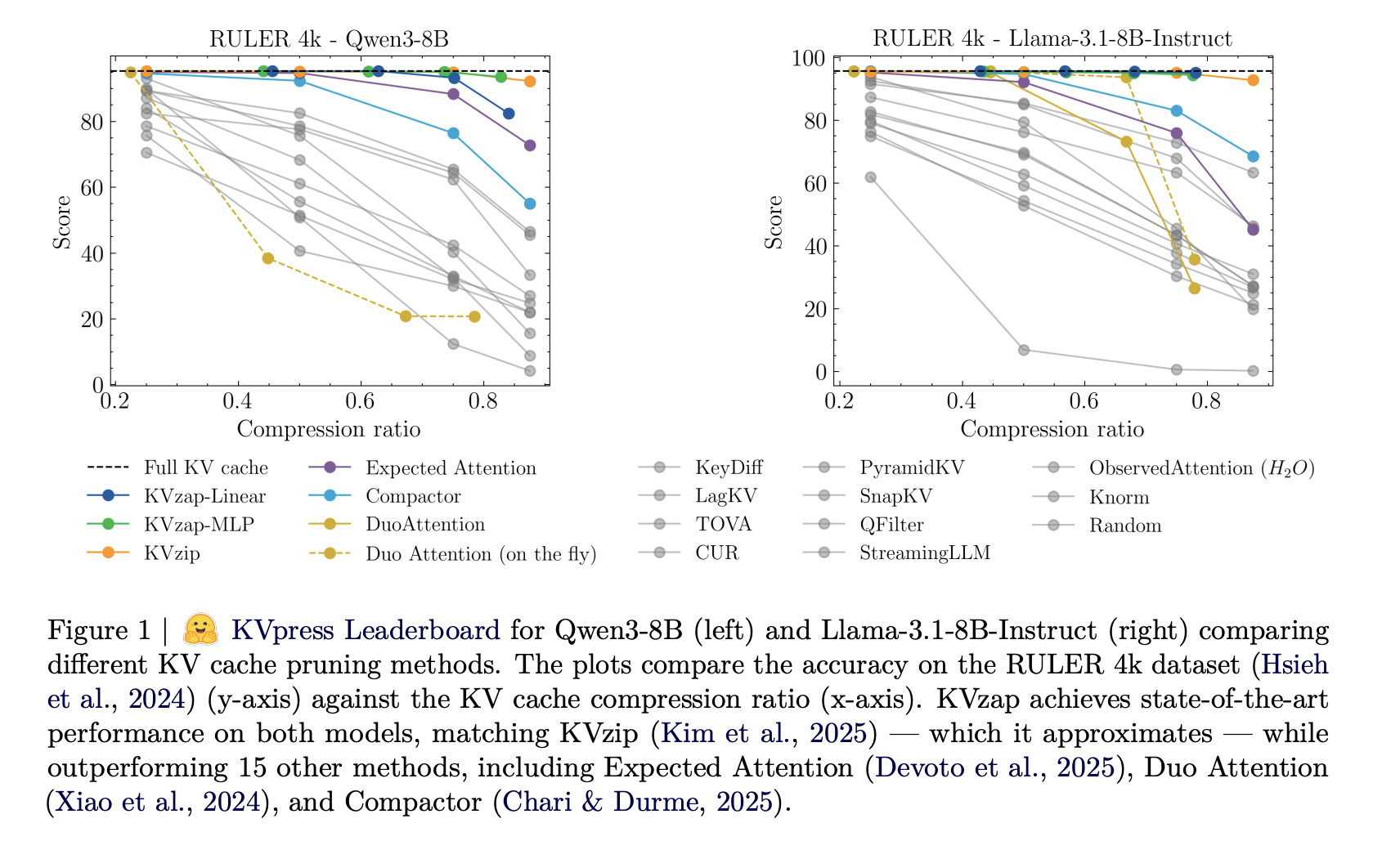
NVIDIA AI Open-Sourced KVzap: A SOTA KV Cache Pruning Method that Delivers near-Lossless 2x-4x CompressionMarkTechPost As context lengths move into tens and hundreds of thousands of tokens, the key value cache in transformer decoders becomes a primary deployment bottleneck. The cache stores keys and values for every layer and head with shape (2, L, H, T, D). For a vanilla transformer such as Llama1-65B, the cache reaches about 335 GB
The post NVIDIA AI Open-Sourced KVzap: A SOTA KV Cache Pruning Method that Delivers near-Lossless 2x-4x Compression appeared first on MarkTechPost.
As context lengths move into tens and hundreds of thousands of tokens, the key value cache in transformer decoders becomes a primary deployment bottleneck. The cache stores keys and values for every layer and head with shape (2, L, H, T, D). For a vanilla transformer such as Llama1-65B, the cache reaches about 335 GB
The post NVIDIA AI Open-Sourced KVzap: A SOTA KV Cache Pruning Method that Delivers near-Lossless 2x-4x Compression appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
PRISMA: Reinforcement Learning Guided Two-Stage Policy Optimization in Multi-Agent Architecture for Open-Domain Multi-Hop Question Answeringcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.05465v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Answering real-world open-domain multi-hop questions over massive corpora is a critical challenge in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. Recent research employs reinforcement learning (RL) to end-to-end optimize the retrieval-augmented reasoning process, directly enhancing its capacity to resolve complex queries. However, reliable deployment is hindered by two obstacles. 1) Retrieval Collapse: iterative retrieval over large corpora fails to locate intermediate evidence containing bridge answers without reasoning-guided planning, causing downstream reasoning to collapse. 2) Learning Instability: end-to-end trajectory training suffers from weak credit assignment across reasoning chains and poor error localization across modules, causing overfitting to benchmark-specific heuristics that limit transferability and stability. To address these problems, we propose PRISMA, a decoupled RL-guided framework featuring a Plan-Retrieve-Inspect-Solve-Memoize architecture. PRISMA’s strength lies in reasoning-guided collaboration: the Inspector provides reasoning-based feedback to refine the Planner’s decomposition and fine-grained retrieval, while enforcing evidence-grounded reasoning in the Solver. We optimize individual agent capabilities via Two-Stage Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). Stage I calibrates the Planner and Solver as specialized experts in planning and reasoning, while Stage II utilizes Observation-Aware Residual Policy Optimization (OARPO) to enhance the Inspector’s ability to verify context and trigger targeted recovery. Experiments show that PRISMA achieves state-of-the-art performance on ten benchmarks and can be deployed efficiently in real-world scenarios.
arXiv:2601.05465v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Answering real-world open-domain multi-hop questions over massive corpora is a critical challenge in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. Recent research employs reinforcement learning (RL) to end-to-end optimize the retrieval-augmented reasoning process, directly enhancing its capacity to resolve complex queries. However, reliable deployment is hindered by two obstacles. 1) Retrieval Collapse: iterative retrieval over large corpora fails to locate intermediate evidence containing bridge answers without reasoning-guided planning, causing downstream reasoning to collapse. 2) Learning Instability: end-to-end trajectory training suffers from weak credit assignment across reasoning chains and poor error localization across modules, causing overfitting to benchmark-specific heuristics that limit transferability and stability. To address these problems, we propose PRISMA, a decoupled RL-guided framework featuring a Plan-Retrieve-Inspect-Solve-Memoize architecture. PRISMA’s strength lies in reasoning-guided collaboration: the Inspector provides reasoning-based feedback to refine the Planner’s decomposition and fine-grained retrieval, while enforcing evidence-grounded reasoning in the Solver. We optimize individual agent capabilities via Two-Stage Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). Stage I calibrates the Planner and Solver as specialized experts in planning and reasoning, while Stage II utilizes Observation-Aware Residual Policy Optimization (OARPO) to enhance the Inspector’s ability to verify context and trigger targeted recovery. Experiments show that PRISMA achieves state-of-the-art performance on ten benchmarks and can be deployed efficiently in real-world scenarios. Read More