Bridging Visual and Wireless Sensing: A Unified Radiation Field for 3D Radio Map Constructioncs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.19216v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: The emerging applications of next-generation wireless networks (e.g., immersive 3D communication, low-altitude networks, and integrated sensing and communication) necessitate high-fidelity environmental intelligence. 3D radio maps have emerged as a critical tool for this purpose, enabling spectrum-aware planning and environment-aware sensing by bridging the gap between physical environments and electromagnetic signal propagation. However, constructing accurate 3D radio maps requires fine-grained 3D geometric information and a profound understanding of electromagnetic wave propagation. Existing approaches typically treat optical and wireless knowledge as distinct modalities, failing to exploit the fundamental physical principles governing both light and electromagnetic propagation. To bridge this gap, we propose URF-GS, a unified radio-optical radiation field representation framework for accurate and generalizable 3D radio map construction based on 3D Gaussian splatting (3D-GS) and inverse rendering. By fusing visual and wireless sensing observations, URF-GS recovers scene geometry and material properties while accurately predicting radio signal behavior at arbitrary transmitter-receiver (Tx-Rx) configurations. Experimental results demonstrate that URF-GS achieves up to a 24.7% improvement in spatial spectrum prediction accuracy and a 10x increase in sample efficiency for 3D radio map construction compared with neural radiance field (NeRF)-based methods. This work establishes a foundation for next-generation wireless networks by integrating perception, interaction, and communication through holistic radiation field reconstruction.
arXiv:2601.19216v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: The emerging applications of next-generation wireless networks (e.g., immersive 3D communication, low-altitude networks, and integrated sensing and communication) necessitate high-fidelity environmental intelligence. 3D radio maps have emerged as a critical tool for this purpose, enabling spectrum-aware planning and environment-aware sensing by bridging the gap between physical environments and electromagnetic signal propagation. However, constructing accurate 3D radio maps requires fine-grained 3D geometric information and a profound understanding of electromagnetic wave propagation. Existing approaches typically treat optical and wireless knowledge as distinct modalities, failing to exploit the fundamental physical principles governing both light and electromagnetic propagation. To bridge this gap, we propose URF-GS, a unified radio-optical radiation field representation framework for accurate and generalizable 3D radio map construction based on 3D Gaussian splatting (3D-GS) and inverse rendering. By fusing visual and wireless sensing observations, URF-GS recovers scene geometry and material properties while accurately predicting radio signal behavior at arbitrary transmitter-receiver (Tx-Rx) configurations. Experimental results demonstrate that URF-GS achieves up to a 24.7% improvement in spatial spectrum prediction accuracy and a 10x increase in sample efficiency for 3D radio map construction compared with neural radiance field (NeRF)-based methods. This work establishes a foundation for next-generation wireless networks by integrating perception, interaction, and communication through holistic radiation field reconstruction. Read More
From Observations to Events: Event-Aware World Model for Reinforcement Learningcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.19336v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: While model-based reinforcement learning (MBRL) improves sample efficiency by learning world models from raw observations, existing methods struggle to generalize across structurally similar scenes and remain vulnerable to spurious variations such as textures or color shifts. From a cognitive science perspective, humans segment continuous sensory streams into discrete events and rely on these key events for decision-making. Motivated by this principle, we propose the Event-Aware World Model (EAWM), a general framework that learns event-aware representations to streamline policy learning without requiring handcrafted labels. EAWM employs an automated event generator to derive events from raw observations and introduces a Generic Event Segmentor (GES) to identify event boundaries, which mark the start and end time of event segments. Through event prediction, the representation space is shaped to capture meaningful spatio-temporal transitions. Beyond this, we present a unified formulation of seemingly distinct world model architectures and show the broad applicability of our methods. Experiments on Atari 100K, Craftax 1M, and DeepMind Control 500K, DMC-GB2 500K demonstrate that EAWM consistently boosts the performance of strong MBRL baselines by 10%-45%, setting new state-of-the-art results across benchmarks. Our code is released at https://github.com/MarquisDarwin/EAWM.
arXiv:2601.19336v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: While model-based reinforcement learning (MBRL) improves sample efficiency by learning world models from raw observations, existing methods struggle to generalize across structurally similar scenes and remain vulnerable to spurious variations such as textures or color shifts. From a cognitive science perspective, humans segment continuous sensory streams into discrete events and rely on these key events for decision-making. Motivated by this principle, we propose the Event-Aware World Model (EAWM), a general framework that learns event-aware representations to streamline policy learning without requiring handcrafted labels. EAWM employs an automated event generator to derive events from raw observations and introduces a Generic Event Segmentor (GES) to identify event boundaries, which mark the start and end time of event segments. Through event prediction, the representation space is shaped to capture meaningful spatio-temporal transitions. Beyond this, we present a unified formulation of seemingly distinct world model architectures and show the broad applicability of our methods. Experiments on Atari 100K, Craftax 1M, and DeepMind Control 500K, DMC-GB2 500K demonstrate that EAWM consistently boosts the performance of strong MBRL baselines by 10%-45%, setting new state-of-the-art results across benchmarks. Our code is released at https://github.com/MarquisDarwin/EAWM. Read More
GradPruner: Gradient-Guided Layer Pruning Enabling Efficient Fine-Tuning and Inference for LLMscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.19503v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs) with downstream data is often considered time-consuming and expensive. Structured pruning methods are primarily employed to improve the inference efficiency of pre-trained models. Meanwhile, they often require additional time and memory for training, knowledge distillation, structure search, and other strategies, making efficient model fine-tuning challenging to achieve. To simultaneously enhance the training and inference efficiency of downstream task fine-tuning, we introduce GradPruner, which can prune layers of LLMs guided by gradients in the early stages of fine-tuning. GradPruner uses the cumulative gradients of each parameter during the initial phase of fine-tuning to compute the Initial Gradient Information Accumulation Matrix (IGIA-Matrix) to assess the importance of layers and perform pruning. We sparsify the pruned layers based on the IGIA-Matrix and merge them with the remaining layers. Only elements with the same sign are merged to reduce interference from sign variations. We conducted extensive experiments on two LLMs across eight downstream datasets. Including medical, financial, and general benchmark tasks. The results demonstrate that GradPruner has achieved a parameter reduction of 40% with only a 0.99% decrease in accuracy. Our code is publicly available.
arXiv:2601.19503v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs) with downstream data is often considered time-consuming and expensive. Structured pruning methods are primarily employed to improve the inference efficiency of pre-trained models. Meanwhile, they often require additional time and memory for training, knowledge distillation, structure search, and other strategies, making efficient model fine-tuning challenging to achieve. To simultaneously enhance the training and inference efficiency of downstream task fine-tuning, we introduce GradPruner, which can prune layers of LLMs guided by gradients in the early stages of fine-tuning. GradPruner uses the cumulative gradients of each parameter during the initial phase of fine-tuning to compute the Initial Gradient Information Accumulation Matrix (IGIA-Matrix) to assess the importance of layers and perform pruning. We sparsify the pruned layers based on the IGIA-Matrix and merge them with the remaining layers. Only elements with the same sign are merged to reduce interference from sign variations. We conducted extensive experiments on two LLMs across eight downstream datasets. Including medical, financial, and general benchmark tasks. The results demonstrate that GradPruner has achieved a parameter reduction of 40% with only a 0.99% decrease in accuracy. Our code is publicly available. Read More
Tencent Hunyuan Releases HPC-Ops: A High Performance LLM Inference Operator LibraryMarkTechPost Tencent Hunyuan has open sourced HPC-Ops, a production grade operator library for large language model inference architecture devices. HPC-Ops focuses on low level CUDA kernels for core operators such as Attention, Grouped GEMM, and Fused MoE, and exposes them through a compact-C and Python API for integration into existing inference stacks. HPC-Ops runs in large
The post Tencent Hunyuan Releases HPC-Ops: A High Performance LLM Inference Operator Library appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Tencent Hunyuan has open sourced HPC-Ops, a production grade operator library for large language model inference architecture devices. HPC-Ops focuses on low level CUDA kernels for core operators such as Attention, Grouped GEMM, and Fused MoE, and exposes them through a compact-C and Python API for integration into existing inference stacks. HPC-Ops runs in large
The post Tencent Hunyuan Releases HPC-Ops: A High Performance LLM Inference Operator Library appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
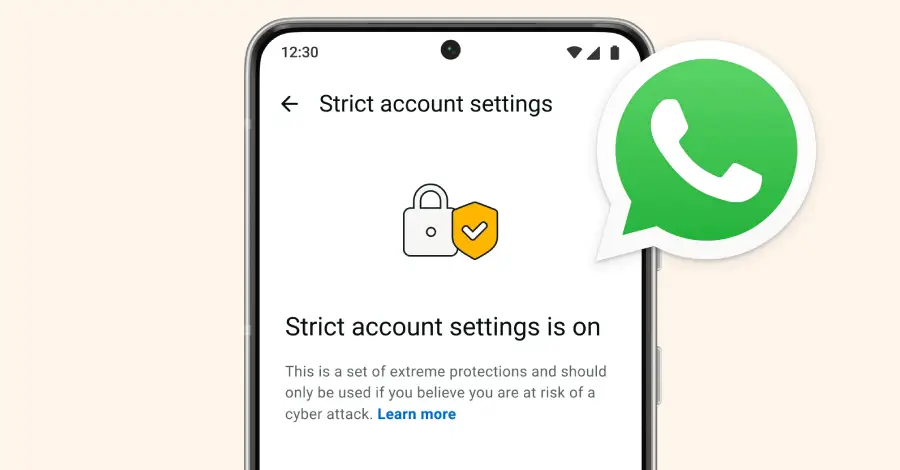
Meta on Tuesday announced it’s adding Strict Account Settings on WhatsApp to secure certain users against advanced cyber attacks because of who they are and what they do. The feature, similar to Lockdown Mode in Apple iOS and Advanced Protection in Android, aims to protect individuals, such as journalists or public-facing figures, from sophisticated spyware […]
Fortinet has begun releasing security updates to address a critical flaw impacting FortiOS that has come under active exploitation in the wild. The vulnerability, assigned the CVE identifier CVE-2026-24858 (CVSS score: 9.4), has been described as an authentication bypass related to FortiOS single sign-on (SSO). The flaw also affects FortiManager and FortiAnalyzer. The company said […]
Moonshot AI Releases Kimi K2.5: An Open Source Visual Agentic Intelligence Model with Native Swarm ExecutionMarkTechPost Moonshot AI has released Kimi K2.5 as an open source visual agentic intelligence model. It combines a large Mixture of Experts language backbone, a native vision encoder, and a parallel multi agent system called Agent Swarm. The model targets coding, multimodal reasoning, and deep web research with strong benchmark results on agentic, vision, and coding
The post Moonshot AI Releases Kimi K2.5: An Open Source Visual Agentic Intelligence Model with Native Swarm Execution appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Moonshot AI has released Kimi K2.5 as an open source visual agentic intelligence model. It combines a large Mixture of Experts language backbone, a native vision encoder, and a parallel multi agent system called Agent Swarm. The model targets coding, multimodal reasoning, and deep web research with strong benchmark results on agentic, vision, and coding
The post Moonshot AI Releases Kimi K2.5: An Open Source Visual Agentic Intelligence Model with Native Swarm Execution appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Nike is investigating what it described as a “potential cyber security incident” after the World Leaks ransomware gang leaked 1.4 TB of files allegedly stolen from the sportswear giant. […] Read More
Indian government entities have been targeted in two campaigns undertaken by a threat actor that operates in Pakistan using previously undocumented tradecraft. The campaigns have been codenamed Gopher Strike and Sheet Attack by Zscaler ThreatLabz, which identified them in September 2025. “While these campaigns share some similarities with the Pakistan-linked Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Read More
Multiple threat actors, both state-sponsored and financially motivated, are exploiting the CVE-2025-8088 high-severity vulnerability in WinRAR for initial access and to deliver various malicious payloads. […] Read More