A Novel Framework for Uncertainty-Driven Adaptive Explorationcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2509.03219v5 Announce Type: replace
Abstract: Adaptive exploration methods propose ways to learn complex policies via alternating between exploration and exploitation. An important question for such methods is to determine the appropriate moment to switch between exploration and exploitation and vice versa. This is critical in domains that require the learning of long and complex sequences of actions. In this work, we present a generic adaptive exploration framework that employs uncertainty to address this important issue in a principled manner. Our framework includes previous adaptive exploration approaches as special cases. Moreover, we can incorporate in our framework any uncertainty-measuring mechanism of choice, for instance mechanisms used in intrinsic motivation or epistemic uncertainty-based exploration methods. We experimentally demonstrate that our framework gives rise to adaptive exploration strategies that outperform standard ones across several environments.
arXiv:2509.03219v5 Announce Type: replace
Abstract: Adaptive exploration methods propose ways to learn complex policies via alternating between exploration and exploitation. An important question for such methods is to determine the appropriate moment to switch between exploration and exploitation and vice versa. This is critical in domains that require the learning of long and complex sequences of actions. In this work, we present a generic adaptive exploration framework that employs uncertainty to address this important issue in a principled manner. Our framework includes previous adaptive exploration approaches as special cases. Moreover, we can incorporate in our framework any uncertainty-measuring mechanism of choice, for instance mechanisms used in intrinsic motivation or epistemic uncertainty-based exploration methods. We experimentally demonstrate that our framework gives rise to adaptive exploration strategies that outperform standard ones across several environments. Read More
Today’s “AI everywhere” reality is woven into everyday workflows across the enterprise, embedded in SaaS platforms, browsers, copilots, extensions, and a rapidly expanding universe of shadow tools that appear faster than security teams can track. Yet most organizations still rely on legacy controls that operate far away from where AI interactions actually occur. The result […]
The elusive Iranian threat group known as Infy (aka Prince of Persia) has evolved its tactics as part of efforts to hide its tracks, even as it readied new command-and-control (C2) infrastructure coinciding with the end of the widespread internet blackout the regime imposed at the start of the month. “The threat actor stopped maintaining […]
A fresh wave of spam is hitting inboxes worldwide, with users reporting that they are once again being bombarded by automated emails generated through companies’ unsecured Zendesk support systems. Some recipients say they are receiving hundreds of messages with strange or alarming subject lines. such as ‘Activate account…’ […] Read More
Hackers stole email addresses and other personal information from 1.4 million accounts after breaching the systems of automated investment platform Betterment in January. […] Read More
Revisiting Prompt Sensitivity in Large Language Models for Text Classification: The Role of Prompt Underspecificationcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2602.04297v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) are widely used as zero-shot and few-shot classifiers, where task behaviour is largely controlled through prompting. A growing number of works have observed that LLMs are sensitive to prompt variations, with small changes leading to large changes in performance. However, in many cases, the investigation of sensitivity is performed using underspecified prompts that provide minimal task instructions and weakly constrain the model’s output space. In this work, we argue that a significant portion of the observed prompt sensitivity can be attributed to prompt underspecification. We systematically study and compare the sensitivity of underspecified prompts and prompts that provide specific instructions. Utilising performance analysis, logit analysis, and linear probing, we find that underspecified prompts exhibit higher performance variance and lower logit values for relevant tokens, while instruction-prompts suffer less from such problems. However, linear probing analysis suggests that the effects of prompt underspecification have only a marginal impact on the internal LLM representations, instead emerging in the final layers. Overall, our findings highlight the need for more rigour when investigating and mitigating prompt sensitivity.
arXiv:2602.04297v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) are widely used as zero-shot and few-shot classifiers, where task behaviour is largely controlled through prompting. A growing number of works have observed that LLMs are sensitive to prompt variations, with small changes leading to large changes in performance. However, in many cases, the investigation of sensitivity is performed using underspecified prompts that provide minimal task instructions and weakly constrain the model’s output space. In this work, we argue that a significant portion of the observed prompt sensitivity can be attributed to prompt underspecification. We systematically study and compare the sensitivity of underspecified prompts and prompts that provide specific instructions. Utilising performance analysis, logit analysis, and linear probing, we find that underspecified prompts exhibit higher performance variance and lower logit values for relevant tokens, while instruction-prompts suffer less from such problems. However, linear probing analysis suggests that the effects of prompt underspecification have only a marginal impact on the internal LLM representations, instead emerging in the final layers. Overall, our findings highlight the need for more rigour when investigating and mitigating prompt sensitivity. Read More
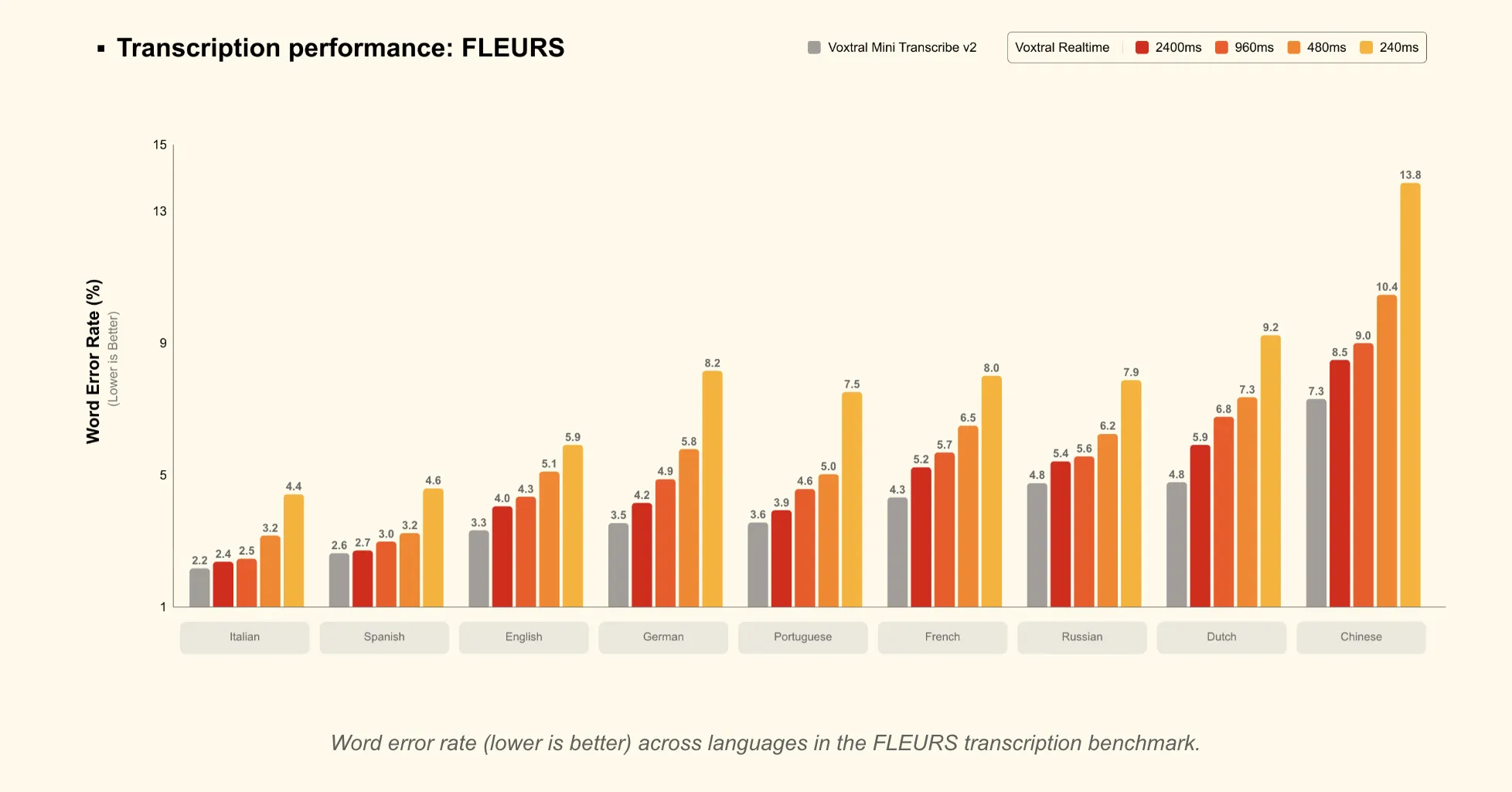
Mistral AI Launches Voxtral Transcribe 2: Pairing Batch Diarization And Open Realtime ASR For Multilingual Production Workloads At ScaleMarkTechPost Automatic speech recognition (ASR) is becoming a core building block for AI products, from meeting tools to voice agents. Mistral’s new Voxtral Transcribe 2 family targets this space with 2 models that split cleanly into batch and realtime use cases, while keeping cost, latency, and deployment constraints in focus. The release includes: Both models are
The post Mistral AI Launches Voxtral Transcribe 2: Pairing Batch Diarization And Open Realtime ASR For Multilingual Production Workloads At Scale appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Automatic speech recognition (ASR) is becoming a core building block for AI products, from meeting tools to voice agents. Mistral’s new Voxtral Transcribe 2 family targets this space with 2 models that split cleanly into batch and realtime use cases, while keeping cost, latency, and deployment constraints in focus. The release includes: Both models are
The post Mistral AI Launches Voxtral Transcribe 2: Pairing Batch Diarization And Open Realtime ASR For Multilingual Production Workloads At Scale appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
OpenAI’s enterprise push: The hidden story behind AI’s sales raceAI News As OpenAI races toward its ambitious US$100 billion revenue target by 2027, the ChatGPT maker is reportedly building an army of AI consultants to bridge the gap between cutting-edge technology and enterprise boardrooms—a move that signals a fundamental shift in how AI companies are approaching the notoriously difficult challenge of enterprise adoption. According to industry
The post OpenAI’s enterprise push: The hidden story behind AI’s sales race appeared first on AI News.
As OpenAI races toward its ambitious US$100 billion revenue target by 2027, the ChatGPT maker is reportedly building an army of AI consultants to bridge the gap between cutting-edge technology and enterprise boardrooms—a move that signals a fundamental shift in how AI companies are approaching the notoriously difficult challenge of enterprise adoption. According to industry
The post OpenAI’s enterprise push: The hidden story behind AI’s sales race appeared first on AI News. Read More
Microsoft unveils method to detect sleeper agent backdoorsAI News Researchers from Microsoft have unveiled a scanning method to identify poisoned models without knowing the trigger or intended outcome. Organisations integrating open-weight large language models (LLMs) face a specific supply chain vulnerability where distinct memory leaks and internal attention patterns expose hidden threats known as “sleeper agents”. These poisoned models contain backdoors that lie dormant
The post Microsoft unveils method to detect sleeper agent backdoors appeared first on AI News.
Researchers from Microsoft have unveiled a scanning method to identify poisoned models without knowing the trigger or intended outcome. Organisations integrating open-weight large language models (LLMs) face a specific supply chain vulnerability where distinct memory leaks and internal attention patterns expose hidden threats known as “sleeper agents”. These poisoned models contain backdoors that lie dormant
The post Microsoft unveils method to detect sleeper agent backdoors appeared first on AI News. Read More
The Rule Everyone Misses: How to Stop Confusing loc and iloc in PandasTowards Data Science A simple mental model to remember when each one works (with examples that finally click).
The post The Rule Everyone Misses: How to Stop Confusing loc and iloc in Pandas appeared first on Towards Data Science.
A simple mental model to remember when each one works (with examples that finally click).
The post The Rule Everyone Misses: How to Stop Confusing loc and iloc in Pandas appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More