Retrieval for Time-Series: How Looking Back Improves ForecastsTowards Data Science Why Retrieval Helps in Time Series Forecasting We all know how it goes: Time-series data is tricky. Traditional forecasting models are unprepared for incidents like sudden market crashes, black swan events, or rare weather patterns. Even large fancy models like Chronos sometimes struggle because they haven’t dealt with that kind of pattern before. We can
The post Retrieval for Time-Series: How Looking Back Improves Forecasts appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Why Retrieval Helps in Time Series Forecasting We all know how it goes: Time-series data is tricky. Traditional forecasting models are unprepared for incidents like sudden market crashes, black swan events, or rare weather patterns. Even large fancy models like Chronos sometimes struggle because they haven’t dealt with that kind of pattern before. We can
The post Retrieval for Time-Series: How Looking Back Improves Forecasts appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
Powerful Local AI Automations with n8n, MCP and OllamaKDnuggets The ultimate goal is to run these automations on a single workstation or small server, replacing fragile scripts and expensive API-based systems.
The ultimate goal is to run these automations on a single workstation or small server, replacing fragile scripts and expensive API-based systems. Read More
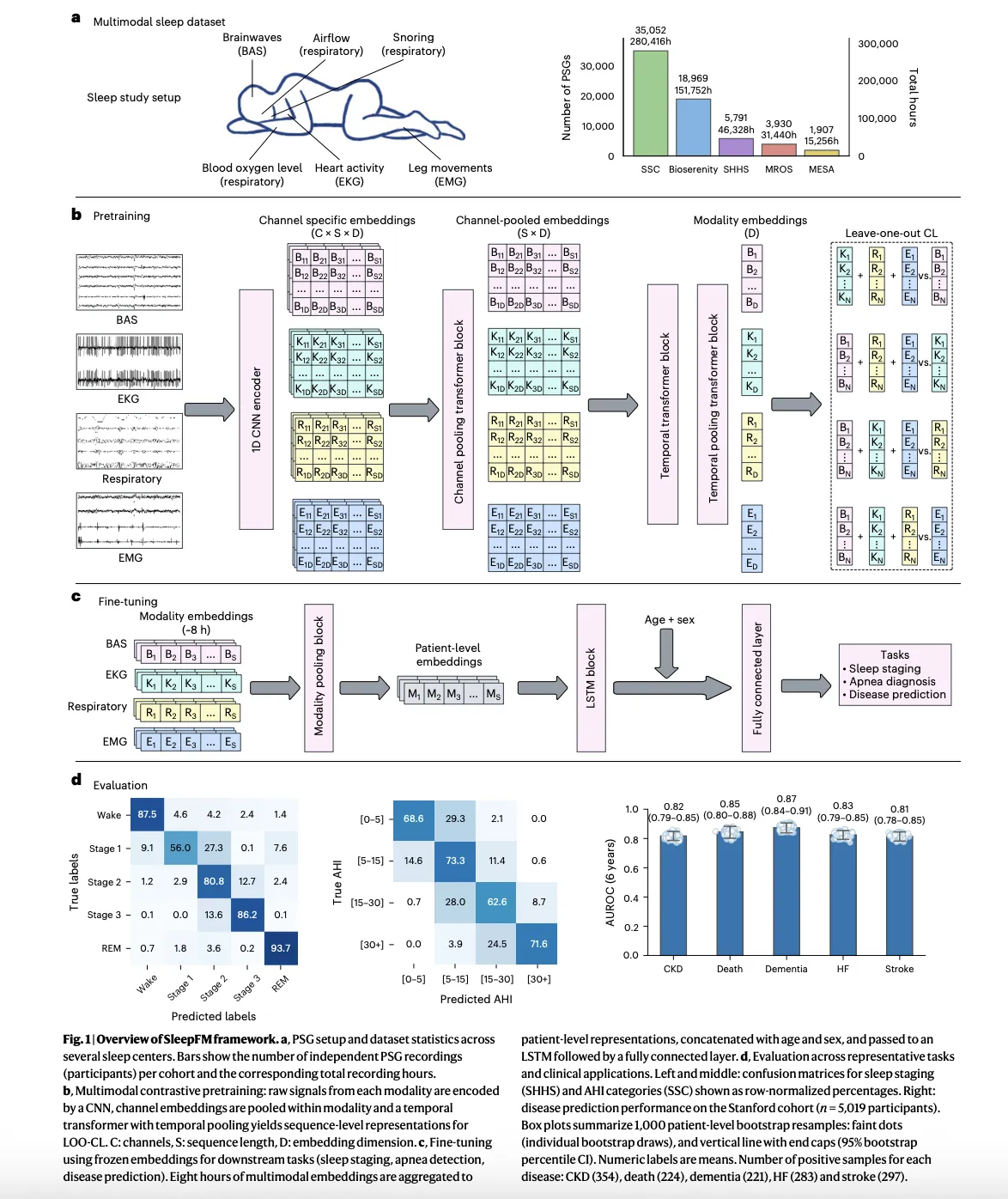
Stanford Researchers Build SleepFM Clinical: A Multimodal Sleep Foundation AI Model for 130+ Disease PredictionMarkTechPost A team of Stanford Medicine researchers have introduced SleepFM Clinical, a multimodal sleep foundation model that learns from clinical polysomnography and predicts long term disease risk from a single night of sleep. The research work is published in Nature Medicine and the team has released the clinical code as the open source sleepfm-clinical repository on
The post Stanford Researchers Build SleepFM Clinical: A Multimodal Sleep Foundation AI Model for 130+ Disease Prediction appeared first on MarkTechPost.
A team of Stanford Medicine researchers have introduced SleepFM Clinical, a multimodal sleep foundation model that learns from clinical polysomnography and predicts long term disease risk from a single night of sleep. The research work is published in Nature Medicine and the team has released the clinical code as the open source sleepfm-clinical repository on
The post Stanford Researchers Build SleepFM Clinical: A Multimodal Sleep Foundation AI Model for 130+ Disease Prediction appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Speed meets scale: Load testing SageMakerAI endpoints with Observe.AI’s testing toolArtificial Intelligence Observe.ai developed the One Load Audit Framework (OLAF), which integrates with SageMaker to identify bottlenecks and performance issues in ML services, offering latency and throughput measurements under both static and dynamic data loads. In this blog post, you will learn how to use the OLAF utility to test and validate your SageMaker endpoint.
Observe.ai developed the One Load Audit Framework (OLAF), which integrates with SageMaker to identify bottlenecks and performance issues in ML services, offering latency and throughput measurements under both static and dynamic data loads. In this blog post, you will learn how to use the OLAF utility to test and validate your SageMaker endpoint. Read More
Detect and redact personally identifiable information using Amazon Bedrock Data Automation and GuardrailsArtificial Intelligence This post shows an automated PII detection and redaction solution using Amazon Bedrock Data Automation and Amazon Bedrock Guardrails through a use case of processing text and image content in high volumes of incoming emails and attachments. The solution features a complete email processing workflow with a React-based user interface for authorized personnel to more securely manage and review redacted email communications and attachments. We walk through the step-by-step solution implementation procedures used to deploy this solution. Finally, we discuss the solution benefits, including operational efficiency, scalability, security and compliance, and adaptability.
This post shows an automated PII detection and redaction solution using Amazon Bedrock Data Automation and Amazon Bedrock Guardrails through a use case of processing text and image content in high volumes of incoming emails and attachments. The solution features a complete email processing workflow with a React-based user interface for authorized personnel to more securely manage and review redacted email communications and attachments. We walk through the step-by-step solution implementation procedures used to deploy this solution. Finally, we discuss the solution benefits, including operational efficiency, scalability, security and compliance, and adaptability. Read More
Beyond Prompting: The Power of Context EngineeringTowards Data Science Using ACE to create self-improving LLM workflows and structured playbooks
The post Beyond Prompting: The Power of Context Engineering appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Using ACE to create self-improving LLM workflows and structured playbooks
The post Beyond Prompting: The Power of Context Engineering appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
Scaling medical content review at Flo Health using Amazon Bedrock (Part 1)Artificial Intelligence This two-part series explores Flo Health’s journey with generative AI for medical content verification. Part 1 examines our proof of concept (PoC), including the initial solution, capabilities, and early results. Part 2 covers focusing on scaling challenges and real-world implementation. Each article stands alone while collectively showing how AI transforms medical content management at scale.
This two-part series explores Flo Health’s journey with generative AI for medical content verification. Part 1 examines our proof of concept (PoC), including the initial solution, capabilities, and early results. Part 2 covers focusing on scaling challenges and real-world implementation. Each article stands alone while collectively showing how AI transforms medical content management at scale. Read More
Artificial intelligence (AI) company OpenAI on Wednesday announced the launch of ChatGPT Health, a dedicated space that allows users to have conversations with the chatbot about their health. To that end, the sandboxed experience offers users the optional ability to securely connect medical records and wellness apps, including Apple Health, Function, MyFitnessPal, Weight Watchers, AllTrails, Read […]
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) on Wednesday added two security flaws impacting Microsoft Office and Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) OneView to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, citing evidence of active exploitation. The vulnerabilities are listed below – CVE-2009-0556 (CVSS score: 8.8) – A code injection vulnerability in Microsoft Office Read More
ALERT: Zero-shot LLM Jailbreak Detection via Internal Discrepancy Amplificationcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.03600v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Despite rich safety alignment strategies, large language models (LLMs) remain highly susceptible to jailbreak attacks, which compromise safety guardrails and pose serious security risks. Existing detection methods mainly detect jailbreak status relying on jailbreak templates present in the training data. However, few studies address the more realistic and challenging zero-shot jailbreak detection setting, where no jailbreak templates are available during training. This setting better reflects real-world scenarios where new attacks continually emerge and evolve. To address this challenge, we propose a layer-wise, module-wise, and token-wise amplification framework that progressively magnifies internal feature discrepancies between benign and jailbreak prompts. We uncover safety-relevant layers, identify specific modules that inherently encode zero-shot discriminative signals, and localize informative safety tokens. Building upon these insights, we introduce ALERT (Amplification-based Jailbreak Detector), an efficient and effective zero-shot jailbreak detector that introduces two independent yet complementary classifiers on amplified representations. Extensive experiments on three safety benchmarks demonstrate that ALERT achieves consistently strong zero-shot detection performance. Specifically, (i) across all datasets and attack strategies, ALERT reliably ranks among the top two methods, and (ii) it outperforms the second-best baseline by at least 10% in average Accuracy and F1-score, and sometimes by up to 40%.
arXiv:2601.03600v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Despite rich safety alignment strategies, large language models (LLMs) remain highly susceptible to jailbreak attacks, which compromise safety guardrails and pose serious security risks. Existing detection methods mainly detect jailbreak status relying on jailbreak templates present in the training data. However, few studies address the more realistic and challenging zero-shot jailbreak detection setting, where no jailbreak templates are available during training. This setting better reflects real-world scenarios where new attacks continually emerge and evolve. To address this challenge, we propose a layer-wise, module-wise, and token-wise amplification framework that progressively magnifies internal feature discrepancies between benign and jailbreak prompts. We uncover safety-relevant layers, identify specific modules that inherently encode zero-shot discriminative signals, and localize informative safety tokens. Building upon these insights, we introduce ALERT (Amplification-based Jailbreak Detector), an efficient and effective zero-shot jailbreak detector that introduces two independent yet complementary classifiers on amplified representations. Extensive experiments on three safety benchmarks demonstrate that ALERT achieves consistently strong zero-shot detection performance. Specifically, (i) across all datasets and attack strategies, ALERT reliably ranks among the top two methods, and (ii) it outperforms the second-best baseline by at least 10% in average Accuracy and F1-score, and sometimes by up to 40%. Read More