Author: Derrick D. Jackson
Title: Founder & Senior Director of Cloud Security Architecture & Risk
Credentials: CISSP, CRISC, CCSP
Last updated: January 8th, 2026
Table of Contents
Hello Everyone, Help us grow our community by sharing and/or supporting us on other platforms. This allow us to show verification that what we are doing is valued. It also allows us to plan and allocate resources to improve what we are doing, as we then know others are interested/supportive.
What is NIST AI RMF MANAGE?
NIST MANAGE in 60 Seconds: You’ve mapped your AI system’s context and measured its risks. Now what? NIST MANAGE is where you actually do something about it. It’s the fourth function of NIST’s AI Risk Management Framework, and it answers a straightforward question: how will you respond to the risks you’ve identified? Air Canada learned this lesson publicly when their chatbot gave a customer incorrect bereavement fare information. The airline argued the chatbot was a “separate legal entity” responsible for its own actions. A tribunal disagreed and ordered damages. NIST MANAGE won’t prevent every incident, but it creates the response mechanisms that separate “we hoped it would work” from “we had a plan.”
Who This Article Is For
- New to AI governance? Start here for foundational concepts in plain language.
- Compliance or security professional? You’ll find RACI matrices and framework crosswalks for implementation.
- Executive? Focus on the Business Impact section and the Executive Questions below.
This article covers NIST MANAGE at an introductory level. For risk assessment, see the NIST AI RMF MEASURE guide. For context-setting, review the MAP function.
Executive Summary
NIST MANAGE is the operational engine of NIST’s AI Risk Management Framework. Where MEASURE determines whether something is going wrong, NIST MANAGE determines what you’ll do about it. The function includes 13 subcategories across four categories.
It converts risk assessments into action through resource allocation, treatment plans, and response mechanisms. Key capabilities include go/no-go deployment decisions, deactivation protocols for malfunctioning systems, third-party component monitoring, and incident response processes. Skip this step and your risk identification becomes an academic exercise with no operational teeth.
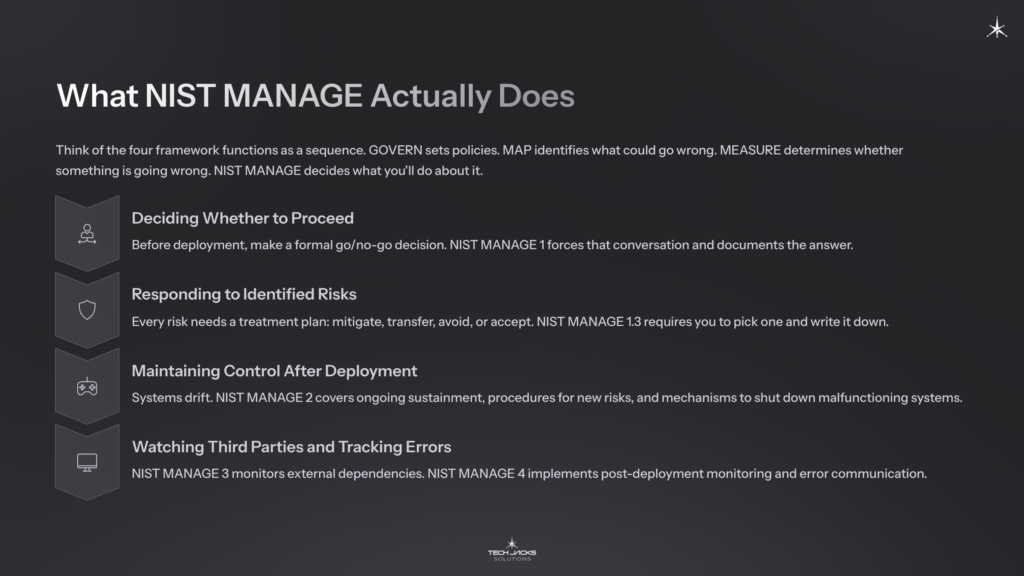
What NIST MANAGE Actually Does
Think of the four framework functions as a sequence. GOVERN sets policies. MAP identifies what could go wrong. MEASURE determines whether something is going wrong. NIST MANAGE decides what you’ll do about it.
The function breaks into four activities:
Deciding whether to proceed. Before deployment, someone needs to make a formal go/no-go decision. NIST MANAGE 1 forces that conversation and documents the answer.
Responding to identified risks. Every risk needs a treatment plan. Per NIST AI 100-1, you have four options: mitigate (reduce likelihood or impact), transfer (shift via insurance or contract), avoid (don’t deploy), or accept (document that the risk falls within tolerance). NIST MANAGE 1.3 requires you to pick one and write it down.
Maintaining control after deployment. Systems drift. NIST MANAGE 2 covers ongoing sustainment, procedures for new risks, and mechanisms to shut down systems that stop working as intended. That last part (NIST MANAGE 2.4) is sometimes called the “kill switch” requirement.
Watching third parties and tracking errors. Most AI deployments rely on external components. NIST MANAGE 3 monitors those dependencies. NIST MANAGE 4 implements post-deployment monitoring and ensures errors get communicated to affected parties.
Why NIST AI RMF MANAGE Matters: A Real Example
In November 2022, Jake Moffatt visited Air Canada’s website to book a flight following his grandmother’s death. The airline’s chatbot incorrectly advised he could book at full price and retroactively apply for a partial refund within 90 days. Moffatt followed this guidance, submitted documentation including a death certificate, and Air Canada denied his claim. Their actual policy required booking the bereavement fare before travel.
In February 2024, British Columbia’s Civil Resolution Tribunal ruled against Air Canada in Moffatt v. Air Canada, 2024 BCCRT 149, awarding approximately $812 CAD in damages.
Specific NIST MANAGE gaps illustrated by this case:
- NIST MANAGE 2.2 violated: No mechanisms sustained the accuracy of the deployed AI system
- NIST MANAGE 4.1 absent: No post-deployment monitoring caught the policy discrepancy
- NIST MANAGE 4.3 missing: No documented processes for tracking and responding to chatbot errors
Tribunal Member Christopher Rivers called Air Canada’s argument that the chatbot was “a separate legal entity responsible for its own actions” a “remarkable submission.” The ruling established that businesses bear responsibility for their AI agents.
Business Impact: Why Executives Should Care
The Air Canada case isn’t isolated. Organizations deploying AI without proper management controls face legal exposure from negligent misrepresentation claims, operational costs when errors surface publicly, and reputational damage when customers discover AI systems provide unreliable information.
NIST MANAGE creates documentation demonstrating due diligence. When regulators ask “what controls did you have?”, NIST MANAGE provides answers.
Five Questions Executives Should Ask Their Teams
- Do we have documented go/no-go criteria for AI deployments?
- Can we disable this AI system within 30 minutes if it malfunctions?
- Who owns third-party AI risk monitoring, and when did they last report?
- How quickly would we know if our AI system started producing errors?
- What residual risks have we formally accepted, and where is that documented?
If your teams can’t answer these questions clearly, you have NIST MANAGE gaps creating liability exposure.
The Four Categories of NIST AI RMF MANAGE
Each category addresses different management dimensions per NIST AI 100-1:
| Category | Focus | Subcategories |
| NIST MANAGE 1 | Risk prioritization and response | 4 |
| NIST MANAGE 2 | Strategies for benefits and impacts | 4 |
| NIST MANAGE 3 | Third-party risk management | 2 |
| NIST MANAGE 4 | Risk treatment monitoring | 3 |

How to Implement NIST AI RMF MANAGE: Top 5 Starting Points
Not all 13 subcategories require equal effort. Start here:
| Priority | Subcategory | Why Start Here |
| 1 | NIST MANAGE 1.1 (Go/No-Go Decision) | Foundation for all deployment decisions |
| 2 | NIST MANAGE 2.4 (Deactivation Mechanisms) | Non-negotiable safety control for high-risk systems |
| 3 | NIST MANAGE 1.3 (Risk Response Options) | Forces active treatment decisions |
| 4 | NIST MANAGE 4.1 (Post-Deployment Monitoring) | Catches drift and errors before customers do |
| 5 | NIST MANAGE 3.1 (Third-Party Monitoring) | Most AI deployments use external components |
RACI Matrix for NIST MANAGE Implementation
Who owns what? RACI clarifies accountability:
| Activity | Accountable | Responsible | Consulted | Informed |
| Risk Prioritization | Executive Leadership | AI Program Owner / CRO | Legal Counsel | Board |
| Risk Treatments | Product Owner | AI Developers, Security | Subject Matter Experts | End Users |
| Deactivation Mechanisms | Senior Management | MLOps Team | Business Continuity | Dependent Systems |
| Third-Party Management | Procurement Head | AI Security Lead | Data Scientists | Supply Chain Partners |
| Incident Response | CISO | Incident Response Team | PR/Communications | Affected Communities |
NIST emphasizes that risk treatment decisions require executive accountability, not just technical implementation.

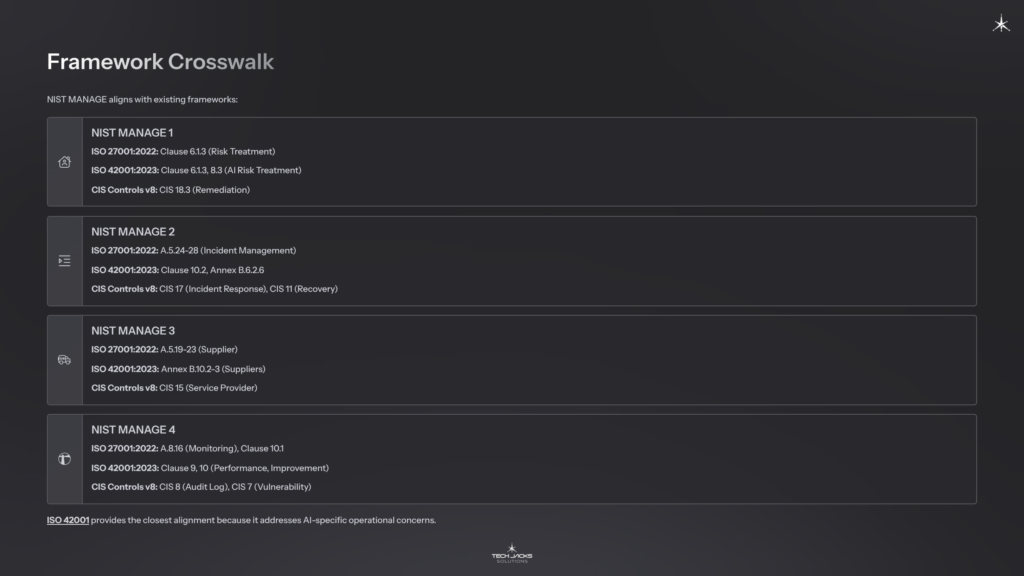
Framework Crosswalk
NIST MANAGE aligns with existing frameworks:
| NIST MANAGE Category | ISO 27001:2022 | ISO 42001:2023 | CIS Controls v8 |
| NIST MANAGE 1 | Clause 6.1.3 (Risk Treatment) | Clause 6.1.3, 8.3 (AI Risk Treatment) | CIS 18.3 (Remediation) |
| NIST MANAGE 2 | A.5.24-28 (Incident Management) | Clause 10.2, Annex B.6.2.6 | CIS 17 (Incident Response), CIS 11 (Recovery) |
| NIST MANAGE 3 | A.5.19-23 (Supplier) | Annex B.10.2-3 (Suppliers) | CIS 15 (Service Provider) |
| NIST MANAGE 4 | A.8.16 (Monitoring), Clause 10.1 | Clause 9, 10 (Performance, Improvement) | CIS 8 (Audit Log), CIS 7 (Vulnerability) |
ISO 42001 provides the closest alignment because it addresses AI-specific operational concerns. These mappings represent common alignment points for practitioners; verify specific requirements against current versions of each standard.
Warning Signs You Need NIST AI RMF MANAGE
These symptoms indicate gaps:
- No documented go/no-go decision process for AI deployments (missing NIST MANAGE 1.1)
- No ability to immediately disable an AI system if it malfunctions (missing NIST MANAGE 2.4)
- Third-party AI components used without ongoing risk monitoring (missing NIST MANAGE 3.1)
- AI errors discovered by customers before internal teams catch them (missing NIST MANAGE 4.1)
Air Canada’s chatbot provided incorrect information for an extended period before a customer complaint surfaced it publicly.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What’s the difference between MEASURE and NIST MANAGE? MEASURE quantifies risks through testing. NIST MANAGE implements responses to those measured risks.
Q: Can NIST MANAGE activities be automated? Monitoring can be. Accountability cannot. You remain responsible for AI systems you deploy.
Q: What if we can’t eliminate a residual risk? Document it explicitly. NIST MANAGE 1.4 requires communicating residual risks to downstream users.
From Understanding to Implementation
This article introduces what NIST MANAGE is and why it matters. For detailed implementation guidance, NIST publishes a companion resource: the AI RMF Playbook. The Playbook provides suggested actions for each subcategory and is designed to be used selectively based on your organization’s needs.
A deeper dive (including templates and checklists) is covered in our forthcoming “How to Implement NIST AI RMF MANAGE” guide.
Next Steps
New to AI governance? Start with the GOVERN function. GOVERN establishes organizational policies and accountability. Without it, NIST MANAGE activities lack foundation.
Compliance professional? Use the RACI matrix to identify stakeholders. Document your first AI system using NIST MANAGE 1.1 (go/no-go decision) as your starting point. The NIST Playbook contains specific suggested actions for each subcategory.
Executive? Run through the five questions above with your AI teams this week. Document which questions they can’t answer. Those gaps are your priorities.
Article based on NIST AI 100-1 (Artificial Intelligence Risk Management Framework) and supporting documentation from the NIST Trustworthy and Responsible AI Resource Center. Case reference: Moffatt v. Air Canada, 2024 BCCRT 149 (CanLII).