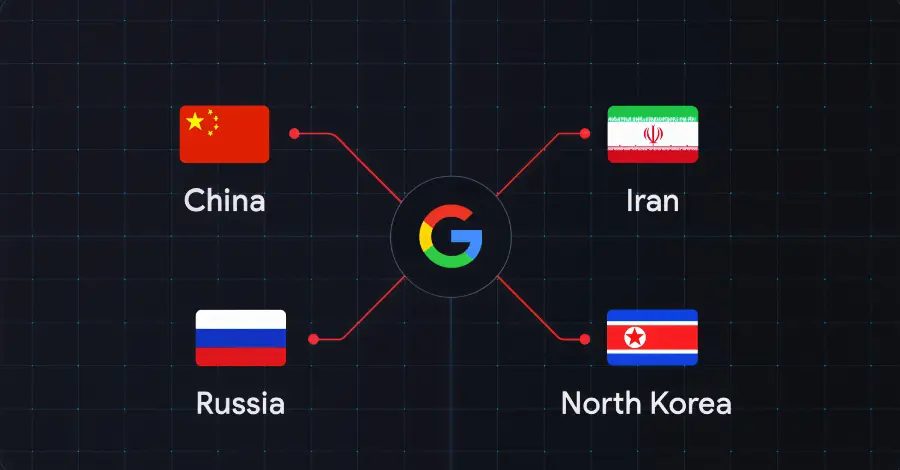
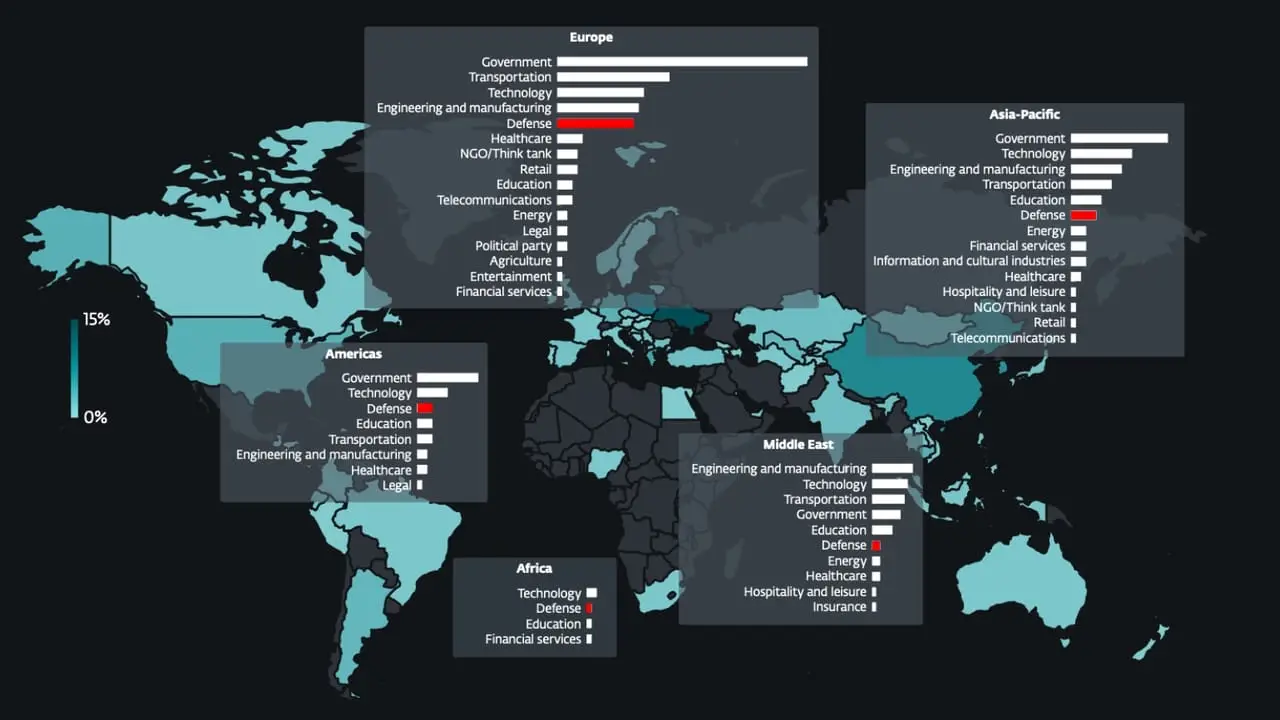
Several state-sponsored actors, hacktivist entities, and criminal groups from China, Iran, North Korea, and Russia have trained their sights on the defense industrial base (DIB) sector, according to findings from Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG). The tech giant’s threat intelligence division said the adversarial targeting of the sector is centered around four key themes: striking […]
A previously unknown threat actor tracked as UAT-9921 has been observed leveraging a new modular framework called VoidLink in its campaigns targeting the technology and financial services sectors, according to findings from Cisco Talos. “This threat actor seems to have been active since 2019, although they have not necessarily used VoidLink over the duration of […]
Threat actors are exploiting security gaps to weaponize Windows drivers and terminate security processes in targeted networks, and there may be no easy fixes in sight. Read More
Espionage groups from China, Russia and other nations burned at least two dozen zero-days in edge devices in attempts to infiltrate defense contractors’ networks. Read More
Customize AI agent browsing with proxies, profiles, and extensions in Amazon Bedrock AgentCore BrowserArtificial Intelligence Today, we are announcing three new capabilities that address these requirements: proxy configuration, browser profiles, and browser extensions. Together, these features give you fine-grained control over how your AI agents interact with the web. This post will walk through each capability with configuration examples and practical use cases to help you get started.
Today, we are announcing three new capabilities that address these requirements: proxy configuration, browser profiles, and browser extensions. Together, these features give you fine-grained control over how your AI agents interact with the web. This post will walk through each capability with configuration examples and practical use cases to help you get started. Read More
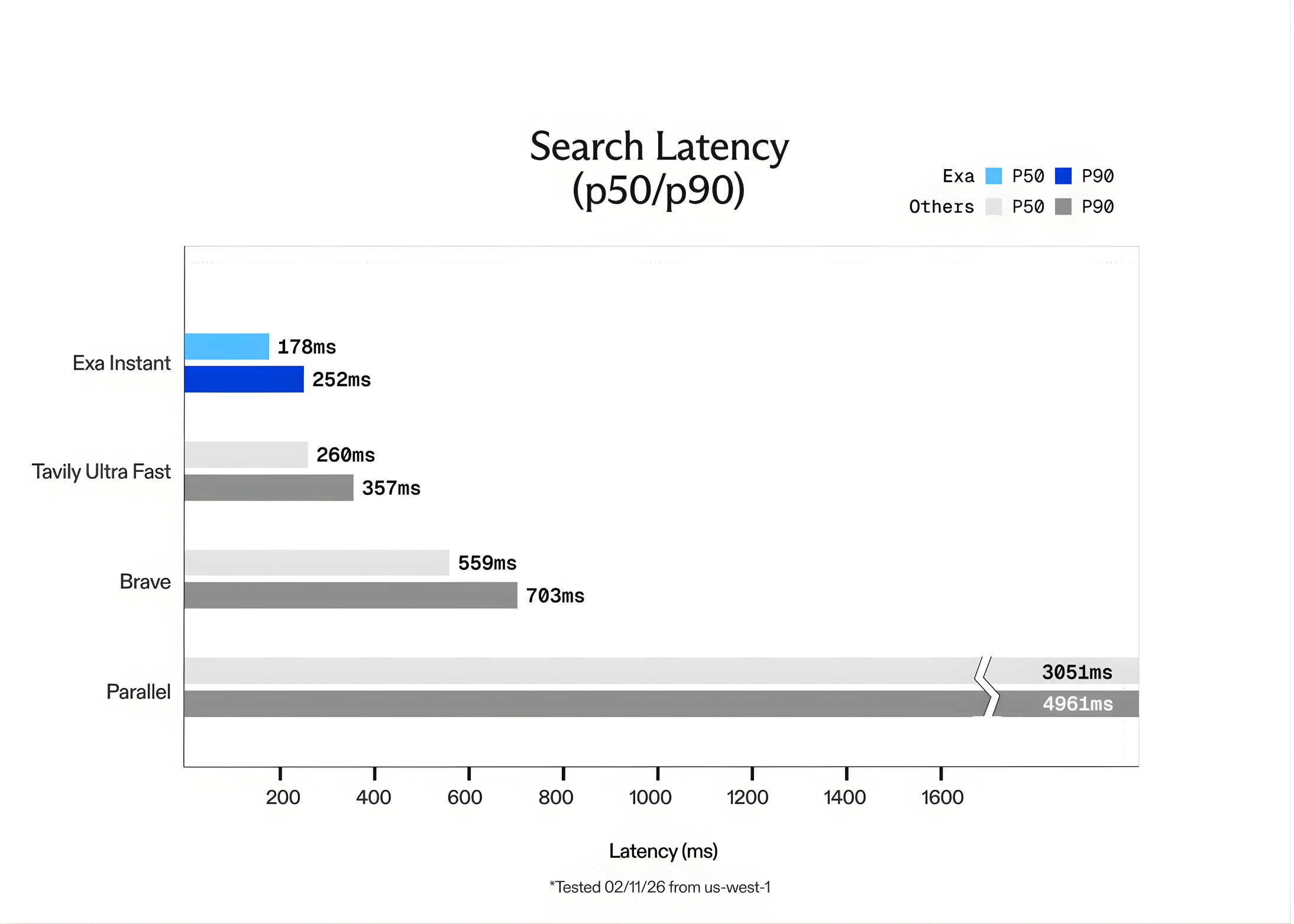
Exa AI Introduces Exa Instant: A Sub-200ms Neural Search Engine Designed to Eliminate Bottlenecks for Real-Time Agentic WorkflowsMarkTechPost In the world of Large Language Models (LLMs), speed is the only feature that matters once accuracy is solved. For a human, waiting 1 second for a search result is fine. For an AI agent performing 10 sequential searches to solve a complex task, a 1-second delay per search creates a 10-second lag. This latency
The post Exa AI Introduces Exa Instant: A Sub-200ms Neural Search Engine Designed to Eliminate Bottlenecks for Real-Time Agentic Workflows appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In the world of Large Language Models (LLMs), speed is the only feature that matters once accuracy is solved. For a human, waiting 1 second for a search result is fine. For an AI agent performing 10 sequential searches to solve a complex task, a 1-second delay per search creates a 10-second lag. This latency
The post Exa AI Introduces Exa Instant: A Sub-200ms Neural Search Engine Designed to Eliminate Bottlenecks for Real-Time Agentic Workflows appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
[In-Depth Guide] The Complete CTGAN + SDV Pipeline for High-Fidelity Synthetic DataMarkTechPost In this tutorial, we build a complete, production-grade synthetic data pipeline using CTGAN and the SDV ecosystem. We start from raw mixed-type tabular data and progressively move toward constrained generation, conditional sampling, statistical validation, and downstream utility testing. Rather than stopping at sample generation, we focus on understanding how well synthetic data preserves structure, distributions,
The post [In-Depth Guide] The Complete CTGAN + SDV Pipeline for High-Fidelity Synthetic Data appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In this tutorial, we build a complete, production-grade synthetic data pipeline using CTGAN and the SDV ecosystem. We start from raw mixed-type tabular data and progressively move toward constrained generation, conditional sampling, statistical validation, and downstream utility testing. Rather than stopping at sample generation, we focus on understanding how well synthetic data preserves structure, distributions,
The post [In-Depth Guide] The Complete CTGAN + SDV Pipeline for High-Fidelity Synthetic Data appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Threat actors are abusing Claude artifacts and Google Ads in ClickFix campaigns that deliver infostealer malware to macOS users searching for specific queries. […] Read More
Remote Sensing Retrieval-Augmented Generation: Bridging Remote Sensing Imagery and Comprehensive Knowledge with a Multi-Modal Dataset and Retrieval-Augmented Generation Modelcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2504.04988v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Recent progress in VLMs has demonstrated impressive capabilities across a variety of tasks in the natural image domain. Motivated by these advancements, the remote sensing community has begun to adopt VLMs for remote sensing vision-language tasks, including scene understanding, image captioning, and visual question answering. However, existing remote sensing VLMs typically rely on closed-set scene understanding and focus on generic scene descriptions, yet lack the ability to incorporate external knowledge. This limitation hinders their capacity for semantic reasoning over complex or context-dependent queries that involve domain-specific or world knowledge. To address these challenges, we first introduced a multimodal Remote Sensing World Knowledge (RSWK) dataset, which comprises high-resolution satellite imagery and detailed textual descriptions for 14,141 well-known landmarks from 175 countries, integrating both remote sensing domain knowledge and broader world knowledge. Building upon this dataset, we proposed a novel Remote Sensing Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RS-RAG) framework, which consists of two key components. The Multi-Modal Knowledge Vector Database Construction module encodes remote sensing imagery and associated textual knowledge into a unified vector space. The Knowledge Retrieval and Response Generation module retrieves and re-ranks relevant knowledge based on image and/or text queries, and incorporates the retrieved content into a knowledge-augmented prompt to guide the VLM in producing contextually grounded responses. We validated the effectiveness of our approach on three representative vision-language tasks, including image captioning, image classification, and visual question answering, where RS-RAG significantly outperformed state-of-the-art baselines.
arXiv:2504.04988v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Recent progress in VLMs has demonstrated impressive capabilities across a variety of tasks in the natural image domain. Motivated by these advancements, the remote sensing community has begun to adopt VLMs for remote sensing vision-language tasks, including scene understanding, image captioning, and visual question answering. However, existing remote sensing VLMs typically rely on closed-set scene understanding and focus on generic scene descriptions, yet lack the ability to incorporate external knowledge. This limitation hinders their capacity for semantic reasoning over complex or context-dependent queries that involve domain-specific or world knowledge. To address these challenges, we first introduced a multimodal Remote Sensing World Knowledge (RSWK) dataset, which comprises high-resolution satellite imagery and detailed textual descriptions for 14,141 well-known landmarks from 175 countries, integrating both remote sensing domain knowledge and broader world knowledge. Building upon this dataset, we proposed a novel Remote Sensing Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RS-RAG) framework, which consists of two key components. The Multi-Modal Knowledge Vector Database Construction module encodes remote sensing imagery and associated textual knowledge into a unified vector space. The Knowledge Retrieval and Response Generation module retrieves and re-ranks relevant knowledge based on image and/or text queries, and incorporates the retrieved content into a knowledge-augmented prompt to guide the VLM in producing contextually grounded responses. We validated the effectiveness of our approach on three representative vision-language tasks, including image captioning, image classification, and visual question answering, where RS-RAG significantly outperformed state-of-the-art baselines. Read More
Test-Time Alignment of LLMs via Sampling-Based Optimal Control in pre-logit spacecs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.26219v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Test-time alignment of large language models (LLMs) attracts attention because fine-tuning LLMs requires high computational costs. In this paper, we propose a new test-time alignment method called adaptive importance sampling on pre-logits (AISP) on the basis of the sampling-based model predictive control with the stochastic control input. AISP applies the Gaussian perturbation into pre-logits, which are outputs of the penultimate layer, so as to maximize expected rewards with respect to the mean of the perturbation. We demonstrate that the optimal mean is obtained by importance sampling with sampled rewards. AISP outperforms best-of-n sampling in terms of rewards over the number of used samples and achieves higher rewards than other reward-based test-time alignment methods.
arXiv:2510.26219v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Test-time alignment of large language models (LLMs) attracts attention because fine-tuning LLMs requires high computational costs. In this paper, we propose a new test-time alignment method called adaptive importance sampling on pre-logits (AISP) on the basis of the sampling-based model predictive control with the stochastic control input. AISP applies the Gaussian perturbation into pre-logits, which are outputs of the penultimate layer, so as to maximize expected rewards with respect to the mean of the perturbation. We demonstrate that the optimal mean is obtained by importance sampling with sampled rewards. AISP outperforms best-of-n sampling in terms of rewards over the number of used samples and achieves higher rewards than other reward-based test-time alignment methods. Read More