How to Build a Self-Organizing Agent Memory System for Long-Term AI Reasoning MarkTechPost In this tutorial, we build a self-organizing memory system for an agent that goes beyond storing raw conversation history and instead structures interactions into persistent, meaningful knowledge units. We design the system so that reasoning and memory management are clearly separated, allowing a dedicated component to extract, compress, and organize information. At the same time,
The post How to Build a Self-Organizing Agent Memory System for Long-Term AI Reasoning appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In this tutorial, we build a self-organizing memory system for an agent that goes beyond storing raw conversation history and instead structures interactions into persistent, meaningful knowledge units. We design the system so that reasoning and memory management are clearly separated, allowing a dedicated component to extract, compress, and organize information. At the same time,
The post How to Build a Self-Organizing Agent Memory System for Long-Term AI Reasoning appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Your First 90 Days as a Data ScientistTowards Data Science A practical onboarding checklist for building trust, business fluency, and data intuition
The post Your First 90 Days as a Data Scientist appeared first on Towards Data Science.
A practical onboarding checklist for building trust, business fluency, and data intuition
The post Your First 90 Days as a Data Scientist appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
AI forecasting model targets healthcare resource efficiencyAI News An operational AI forecasting model developed by Hertfordshire University researchers aims to improve resource efficiency within healthcare. Public sector organisations often hold large archives of historical data that do not inform forward-looking decisions. A partnership between the University of Hertfordshire and regional NHS health bodies addresses this issue by applying machine learning to operational planning.
The post AI forecasting model targets healthcare resource efficiency appeared first on AI News.
An operational AI forecasting model developed by Hertfordshire University researchers aims to improve resource efficiency within healthcare. Public sector organisations often hold large archives of historical data that do not inform forward-looking decisions. A partnership between the University of Hertfordshire and regional NHS health bodies addresses this issue by applying machine learning to operational planning.
The post AI forecasting model targets healthcare resource efficiency appeared first on AI News. Read More
GPT-5.2 derives a new result in theoretical physicsOpenAI News A new preprint shows GPT-5.2 proposing a new formula for a gluon amplitude, later formally proved and verified by OpenAI and academic collaborators.
A new preprint shows GPT-5.2 proposing a new formula for a gluon amplitude, later formally proved and verified by OpenAI and academic collaborators. Read More
[In-Depth Guide] The Complete CTGAN + SDV Pipeline for High-Fidelity Synthetic DataMarkTechPost In this tutorial, we build a complete, production-grade synthetic data pipeline using CTGAN and the SDV ecosystem. We start from raw mixed-type tabular data and progressively move toward constrained generation, conditional sampling, statistical validation, and downstream utility testing. Rather than stopping at sample generation, we focus on understanding how well synthetic data preserves structure, distributions,
The post [In-Depth Guide] The Complete CTGAN + SDV Pipeline for High-Fidelity Synthetic Data appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In this tutorial, we build a complete, production-grade synthetic data pipeline using CTGAN and the SDV ecosystem. We start from raw mixed-type tabular data and progressively move toward constrained generation, conditional sampling, statistical validation, and downstream utility testing. Rather than stopping at sample generation, we focus on understanding how well synthetic data preserves structure, distributions,
The post [In-Depth Guide] The Complete CTGAN + SDV Pipeline for High-Fidelity Synthetic Data appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Customize AI agent browsing with proxies, profiles, and extensions in Amazon Bedrock AgentCore BrowserArtificial Intelligence Today, we are announcing three new capabilities that address these requirements: proxy configuration, browser profiles, and browser extensions. Together, these features give you fine-grained control over how your AI agents interact with the web. This post will walk through each capability with configuration examples and practical use cases to help you get started.
Today, we are announcing three new capabilities that address these requirements: proxy configuration, browser profiles, and browser extensions. Together, these features give you fine-grained control over how your AI agents interact with the web. This post will walk through each capability with configuration examples and practical use cases to help you get started. Read More
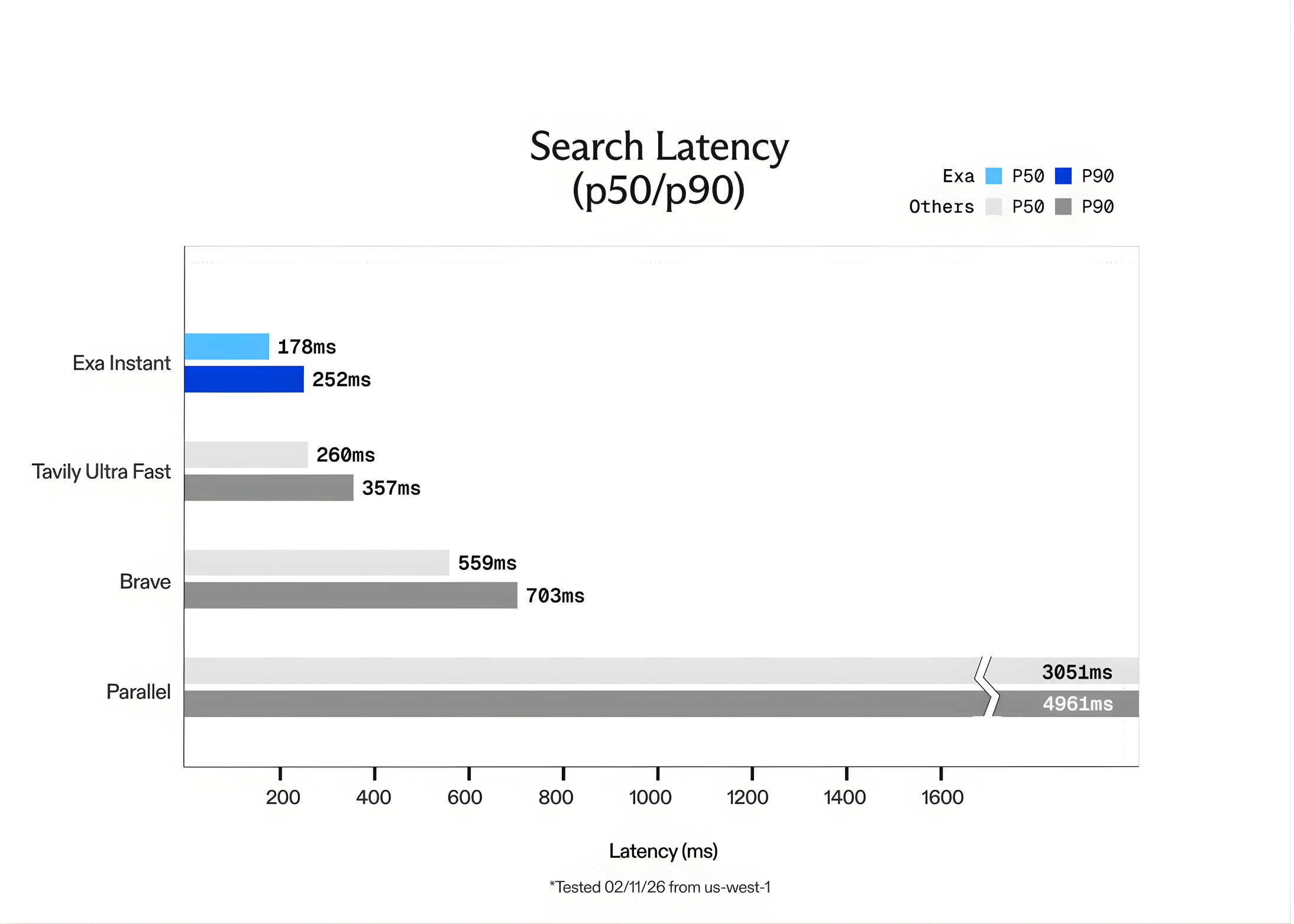
Exa AI Introduces Exa Instant: A Sub-200ms Neural Search Engine Designed to Eliminate Bottlenecks for Real-Time Agentic WorkflowsMarkTechPost In the world of Large Language Models (LLMs), speed is the only feature that matters once accuracy is solved. For a human, waiting 1 second for a search result is fine. For an AI agent performing 10 sequential searches to solve a complex task, a 1-second delay per search creates a 10-second lag. This latency
The post Exa AI Introduces Exa Instant: A Sub-200ms Neural Search Engine Designed to Eliminate Bottlenecks for Real-Time Agentic Workflows appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In the world of Large Language Models (LLMs), speed is the only feature that matters once accuracy is solved. For a human, waiting 1 second for a search result is fine. For an AI agent performing 10 sequential searches to solve a complex task, a 1-second delay per search creates a 10-second lag. This latency
The post Exa AI Introduces Exa Instant: A Sub-200ms Neural Search Engine Designed to Eliminate Bottlenecks for Real-Time Agentic Workflows appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Remote Sensing Retrieval-Augmented Generation: Bridging Remote Sensing Imagery and Comprehensive Knowledge with a Multi-Modal Dataset and Retrieval-Augmented Generation Modelcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2504.04988v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Recent progress in VLMs has demonstrated impressive capabilities across a variety of tasks in the natural image domain. Motivated by these advancements, the remote sensing community has begun to adopt VLMs for remote sensing vision-language tasks, including scene understanding, image captioning, and visual question answering. However, existing remote sensing VLMs typically rely on closed-set scene understanding and focus on generic scene descriptions, yet lack the ability to incorporate external knowledge. This limitation hinders their capacity for semantic reasoning over complex or context-dependent queries that involve domain-specific or world knowledge. To address these challenges, we first introduced a multimodal Remote Sensing World Knowledge (RSWK) dataset, which comprises high-resolution satellite imagery and detailed textual descriptions for 14,141 well-known landmarks from 175 countries, integrating both remote sensing domain knowledge and broader world knowledge. Building upon this dataset, we proposed a novel Remote Sensing Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RS-RAG) framework, which consists of two key components. The Multi-Modal Knowledge Vector Database Construction module encodes remote sensing imagery and associated textual knowledge into a unified vector space. The Knowledge Retrieval and Response Generation module retrieves and re-ranks relevant knowledge based on image and/or text queries, and incorporates the retrieved content into a knowledge-augmented prompt to guide the VLM in producing contextually grounded responses. We validated the effectiveness of our approach on three representative vision-language tasks, including image captioning, image classification, and visual question answering, where RS-RAG significantly outperformed state-of-the-art baselines.
arXiv:2504.04988v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Recent progress in VLMs has demonstrated impressive capabilities across a variety of tasks in the natural image domain. Motivated by these advancements, the remote sensing community has begun to adopt VLMs for remote sensing vision-language tasks, including scene understanding, image captioning, and visual question answering. However, existing remote sensing VLMs typically rely on closed-set scene understanding and focus on generic scene descriptions, yet lack the ability to incorporate external knowledge. This limitation hinders their capacity for semantic reasoning over complex or context-dependent queries that involve domain-specific or world knowledge. To address these challenges, we first introduced a multimodal Remote Sensing World Knowledge (RSWK) dataset, which comprises high-resolution satellite imagery and detailed textual descriptions for 14,141 well-known landmarks from 175 countries, integrating both remote sensing domain knowledge and broader world knowledge. Building upon this dataset, we proposed a novel Remote Sensing Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RS-RAG) framework, which consists of two key components. The Multi-Modal Knowledge Vector Database Construction module encodes remote sensing imagery and associated textual knowledge into a unified vector space. The Knowledge Retrieval and Response Generation module retrieves and re-ranks relevant knowledge based on image and/or text queries, and incorporates the retrieved content into a knowledge-augmented prompt to guide the VLM in producing contextually grounded responses. We validated the effectiveness of our approach on three representative vision-language tasks, including image captioning, image classification, and visual question answering, where RS-RAG significantly outperformed state-of-the-art baselines. Read More
Test-Time Alignment of LLMs via Sampling-Based Optimal Control in pre-logit spacecs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.26219v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Test-time alignment of large language models (LLMs) attracts attention because fine-tuning LLMs requires high computational costs. In this paper, we propose a new test-time alignment method called adaptive importance sampling on pre-logits (AISP) on the basis of the sampling-based model predictive control with the stochastic control input. AISP applies the Gaussian perturbation into pre-logits, which are outputs of the penultimate layer, so as to maximize expected rewards with respect to the mean of the perturbation. We demonstrate that the optimal mean is obtained by importance sampling with sampled rewards. AISP outperforms best-of-n sampling in terms of rewards over the number of used samples and achieves higher rewards than other reward-based test-time alignment methods.
arXiv:2510.26219v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Test-time alignment of large language models (LLMs) attracts attention because fine-tuning LLMs requires high computational costs. In this paper, we propose a new test-time alignment method called adaptive importance sampling on pre-logits (AISP) on the basis of the sampling-based model predictive control with the stochastic control input. AISP applies the Gaussian perturbation into pre-logits, which are outputs of the penultimate layer, so as to maximize expected rewards with respect to the mean of the perturbation. We demonstrate that the optimal mean is obtained by importance sampling with sampled rewards. AISP outperforms best-of-n sampling in terms of rewards over the number of used samples and achieves higher rewards than other reward-based test-time alignment methods. Read More
AgentNoiseBench: Benchmarking Robustness of Tool-Using LLM Agents Under Noisy Conditioncs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2602.11348v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Recent advances in large language models have enabled LLM-based agents to achieve strong performance on a variety of benchmarks. However, their performance in real-world deployments often that observed on benchmark settings, especially in complex and imperfect environments. This discrepancy largely arises because prevailing training and evaluation paradigms are typically built on idealized assumptions, overlooking the inherent stochasticity and noise present in real-world interactions. To bridge this gap, we introduce AgentNoiseBench, a framework for systematically evaluating the robustness of agentic models under noisy environments. We first conduct an in-depth analysis of biases and uncertainties in real-world scenarios and categorize environmental noise into two primary types: user-noise and tool-noise. Building on this analysis, we develop an automated pipeline that injects controllable noise into existing agent-centric benchmarks while preserving task solvability. Leveraging this pipeline, we perform extensive evaluations across a wide range of models with diverse architectures and parameter scales. Our results reveal consistent performance variations under different noise conditions, highlighting the sensitivity of current agentic models to realistic environmental perturbations.
arXiv:2602.11348v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Recent advances in large language models have enabled LLM-based agents to achieve strong performance on a variety of benchmarks. However, their performance in real-world deployments often that observed on benchmark settings, especially in complex and imperfect environments. This discrepancy largely arises because prevailing training and evaluation paradigms are typically built on idealized assumptions, overlooking the inherent stochasticity and noise present in real-world interactions. To bridge this gap, we introduce AgentNoiseBench, a framework for systematically evaluating the robustness of agentic models under noisy environments. We first conduct an in-depth analysis of biases and uncertainties in real-world scenarios and categorize environmental noise into two primary types: user-noise and tool-noise. Building on this analysis, we develop an automated pipeline that injects controllable noise into existing agent-centric benchmarks while preserving task solvability. Leveraging this pipeline, we perform extensive evaluations across a wide range of models with diverse architectures and parameter scales. Our results reveal consistent performance variations under different noise conditions, highlighting the sensitivity of current agentic models to realistic environmental perturbations. Read More