PlotChain: Deterministic Checkpointed Evaluation of Multimodal LLMs on Engineering Plot Readingcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2602.13232v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: We present PlotChain, a deterministic, generator-based benchmark for evaluating multimodal large language models (MLLMs) on engineering plot reading-recovering quantitative values from classic plots (e.g., Bode/FFT, step response, stress-strain, pump curves) rather than OCR-only extraction or free-form captioning. PlotChain contains 15 plot families with 450 rendered plots (30 per family), where every item is produced from known parameters and paired with exact ground truth computed directly from the generating process. A central contribution is checkpoint-based diagnostic evaluation: in addition to final targets, each item includes intermediate ‘cp_’ fields that isolate sub-skills (e.g., reading cutoff frequency or peak magnitude) and enable failure localization within a plot family. We evaluate four state-of-the-art MLLMs under a standardized, deterministic protocol (temperature = 0 and a strict JSON-only numeric output schema) and score predictions using per-field tolerances designed to reflect human plot-reading precision. Under the ‘plotread’ tolerance policy, the top models achieve 80.42% (Gemini 2.5 Pro), 79.84% (GPT-4.1), and 78.21% (Claude Sonnet 4.5) overall field-level pass rates, while GPT-4o trails at 61.59%. Despite strong performance on many families, frequency-domain tasks remain brittle: bandpass response stays low (<= 23%), and FFT spectrum remains challenging. We release the generator, dataset, raw model outputs, scoring code, and manifests with checksums to support fully reproducible runs and retrospective rescoring under alternative tolerance policies.
arXiv:2602.13232v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: We present PlotChain, a deterministic, generator-based benchmark for evaluating multimodal large language models (MLLMs) on engineering plot reading-recovering quantitative values from classic plots (e.g., Bode/FFT, step response, stress-strain, pump curves) rather than OCR-only extraction or free-form captioning. PlotChain contains 15 plot families with 450 rendered plots (30 per family), where every item is produced from known parameters and paired with exact ground truth computed directly from the generating process. A central contribution is checkpoint-based diagnostic evaluation: in addition to final targets, each item includes intermediate ‘cp_’ fields that isolate sub-skills (e.g., reading cutoff frequency or peak magnitude) and enable failure localization within a plot family. We evaluate four state-of-the-art MLLMs under a standardized, deterministic protocol (temperature = 0 and a strict JSON-only numeric output schema) and score predictions using per-field tolerances designed to reflect human plot-reading precision. Under the ‘plotread’ tolerance policy, the top models achieve 80.42% (Gemini 2.5 Pro), 79.84% (GPT-4.1), and 78.21% (Claude Sonnet 4.5) overall field-level pass rates, while GPT-4o trails at 61.59%. Despite strong performance on many families, frequency-domain tasks remain brittle: bandpass response stays low (<= 23%), and FFT spectrum remains challenging. We release the generator, dataset, raw model outputs, scoring code, and manifests with checksums to support fully reproducible runs and retrospective rescoring under alternative tolerance policies. Read More
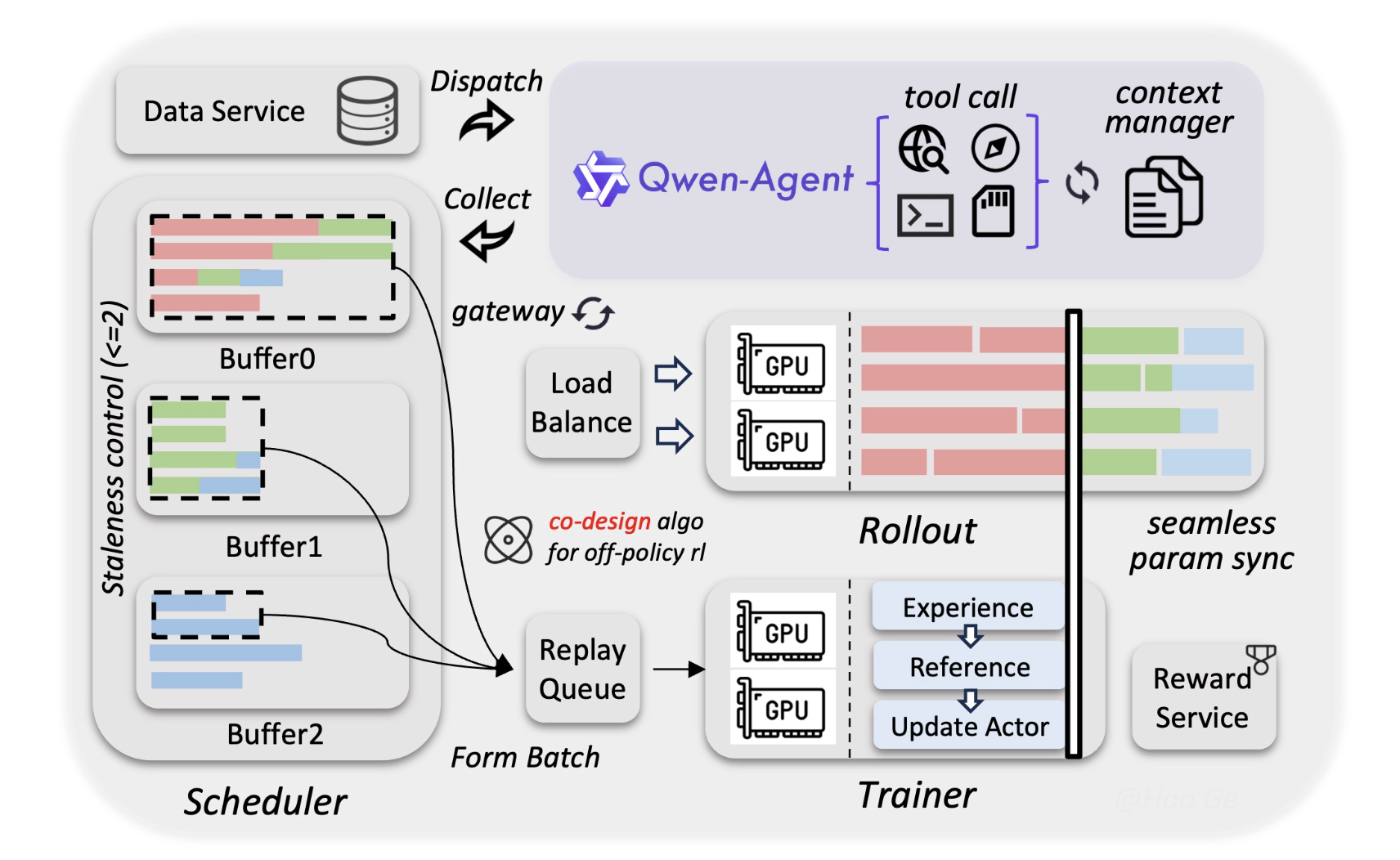
Alibaba Qwen Team Releases Qwen3.5-397B MoE Model with 17B Active Parameters and 1M Token Context for AI agentsMarkTechPost Alibaba Cloud just updated the open-source landscape. Today, the Qwen team released Qwen3.5, the newest generation of their large language model (LLM) family. The most powerful version is Qwen3.5-397B-A17B. This model is a sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) system. It combines massive reasoning power with high efficiency. Qwen3.5 is a native vision-language model. It is designed specifically
The post Alibaba Qwen Team Releases Qwen3.5-397B MoE Model with 17B Active Parameters and 1M Token Context for AI agents appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Alibaba Cloud just updated the open-source landscape. Today, the Qwen team released Qwen3.5, the newest generation of their large language model (LLM) family. The most powerful version is Qwen3.5-397B-A17B. This model is a sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) system. It combines massive reasoning power with high efficiency. Qwen3.5 is a native vision-language model. It is designed specifically
The post Alibaba Qwen Team Releases Qwen3.5-397B MoE Model with 17B Active Parameters and 1M Token Context for AI agents appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Learn Python, SQL and PowerBI to Become a Certified Data Analyst for FREE This WeekKDnuggets From February 16–22, DataCamp’s entire curriculum is 100% free.
From February 16–22, DataCamp’s entire curriculum is 100% free. Read More
How to Build Human-in-the-Loop Plan-and-Execute AI Agents with Explicit User Approval Using LangGraph and StreamlitMarkTechPost In this tutorial, we build a human-in-the-loop travel booking agent that treats the user as a teammate rather than a passive observer. We design the system so the agent first reasons openly by drafting a structured travel plan, then deliberately pauses before taking any action. We expose this proposed plan in a live interface where
The post How to Build Human-in-the-Loop Plan-and-Execute AI Agents with Explicit User Approval Using LangGraph and Streamlit appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In this tutorial, we build a human-in-the-loop travel booking agent that treats the user as a teammate rather than a passive observer. We design the system so the agent first reasons openly by drafting a structured travel plan, then deliberately pauses before taking any action. We expose this proposed plan in a live interface where
The post How to Build Human-in-the-Loop Plan-and-Execute AI Agents with Explicit User Approval Using LangGraph and Streamlit appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
The Strangest Bottleneck in Modern LLMsTowards Data Science Why insanely fast GPUs still can’t make LLMs feel instant
The post The Strangest Bottleneck in Modern LLMs appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Why insanely fast GPUs still can’t make LLMs feel instant
The post The Strangest Bottleneck in Modern LLMs appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
URBN tests agentic AI to automate retail reportingAI News Retail decisions often depend on weekly performance reports, but compiling those reports can take hours of manual work. Urban Outfitters Inc. (URBN) is testing a new approach by using agentic AI systems to generate those reports automatically, changing routine analysis from staff to software. The retailer runs brands like Urban Outfitters, Anthropologie, and Free People,
The post URBN tests agentic AI to automate retail reporting appeared first on AI News.
Retail decisions often depend on weekly performance reports, but compiling those reports can take hours of manual work. Urban Outfitters Inc. (URBN) is testing a new approach by using agentic AI systems to generate those reports automatically, changing routine analysis from staff to software. The retailer runs brands like Urban Outfitters, Anthropologie, and Free People,
The post URBN tests agentic AI to automate retail reporting appeared first on AI News. Read More
CoPE-VideoLM: Codec Primitives For Efficient Video Language Modelscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2602.13191v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Video Language Models (VideoLMs) empower AI systems to understand temporal dynamics in videos. To fit to the maximum context window constraint, current methods use keyframe sampling which can miss both macro-level events and micro-level details due to the sparse temporal coverage. Furthermore, processing full images and their tokens for each frame incurs substantial computational overhead. To address these limitations, we propose to leverage video codec primitives (specifically motion vectors and residuals) which natively encode video redundancy and sparsity without requiring expensive full-image encoding for most frames. To this end, we introduce lightweight transformer-based encoders that aggregate codec primitives and align their representations with image encoder embeddings through a pre-training strategy that accelerates convergence during end-to-end fine-tuning. Our approach reduces the time-to-first-token by up to $86%$ and token usage by up to $93%$ compared to standard VideoLMs. Moreover, by varying the keyframe and codec primitive densities we are able to maintain or exceed performance on $14$ diverse video understanding benchmarks spanning general question answering, temporal reasoning, long-form understanding, and spatial scene understanding.
arXiv:2602.13191v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Video Language Models (VideoLMs) empower AI systems to understand temporal dynamics in videos. To fit to the maximum context window constraint, current methods use keyframe sampling which can miss both macro-level events and micro-level details due to the sparse temporal coverage. Furthermore, processing full images and their tokens for each frame incurs substantial computational overhead. To address these limitations, we propose to leverage video codec primitives (specifically motion vectors and residuals) which natively encode video redundancy and sparsity without requiring expensive full-image encoding for most frames. To this end, we introduce lightweight transformer-based encoders that aggregate codec primitives and align their representations with image encoder embeddings through a pre-training strategy that accelerates convergence during end-to-end fine-tuning. Our approach reduces the time-to-first-token by up to $86%$ and token usage by up to $93%$ compared to standard VideoLMs. Moreover, by varying the keyframe and codec primitive densities we are able to maintain or exceed performance on $14$ diverse video understanding benchmarks spanning general question answering, temporal reasoning, long-form understanding, and spatial scene understanding. Read More
Self-Hosted AI: A Complete Roadmap for BeginnersKDnuggets Build your own private AI hub with Docker, Ollama, and n8n. A beginner’s guide to self-hosted, local automation with no cloud fees.
Build your own private AI hub with Docker, Ollama, and n8n. A beginner’s guide to self-hosted, local automation with no cloud fees. Read More
Top 5 Super Fast LLM API ProvidersKDnuggets Fast providers offering open source LLMs are breaking past previous speed limits, delivering low latency and strong performance that make them suitable for real time interaction, long running coding tasks, and production SaaS applications.
Fast providers offering open source LLMs are breaking past previous speed limits, delivering low latency and strong performance that make them suitable for real time interaction, long running coding tasks, and production SaaS applications. Read More
Banking AI in multiple business functions at NatWestAI News NatWest Group has expanded the use of artificial intelligence in several areas of its operations, citing customer service, document management in its wealth management division, and software development. According to a blog post by its chief information officer, Scott Marcar, 2025 was the first year in which these systems were deployed at scale. The aim
The post Banking AI in multiple business functions at NatWest appeared first on AI News.
NatWest Group has expanded the use of artificial intelligence in several areas of its operations, citing customer service, document management in its wealth management division, and software development. According to a blog post by its chief information officer, Scott Marcar, 2025 was the first year in which these systems were deployed at scale. The aim
The post Banking AI in multiple business functions at NatWest appeared first on AI News. Read More