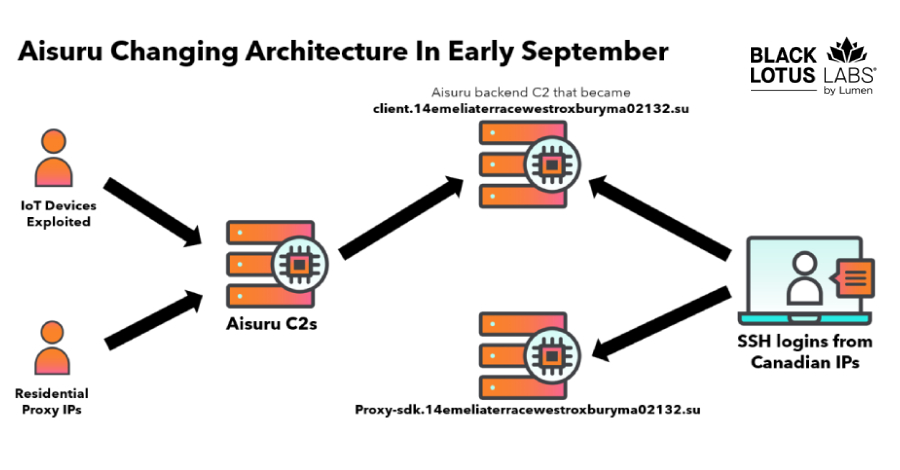
The Black Lotus Labs team at Lumen Technologies said it null-routed traffic to more than 550 command-and-control (C2) nodes associated with the AISURU/Kimwolf botnet since early October 2025. AISURU and its Android counterpart, Kimwolf, have emerged as some of the biggest botnets in recent times, capable of directing enslaved devices to participate in distributed denial-of-service […]
Microsoft confirmed that a recent Windows 365 update is blocking customers from accessing their Microsoft 365 Cloud PC sessions. […] Read More
Fortinet has released updates to fix a critical security flaw impacting FortiSIEM that could allow an unauthenticated attacker to achieve code execution on susceptible instances. The operating system (OS) injection vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-64155, is rated 9.4 out of 10.0 on the CVSS scoring system. “An improper neutralization of special elements used in an OS […]
Microsoft on Tuesday rolled out its first security update for 2026, addressing 114 security flaws, including one vulnerability that it said has been actively exploited in the wild. Of the 114 flaws, eight are rated Critical, and 106 are rated Important in severity. As many as 58 vulnerabilities have been classified as privilege escalation, followed […]
VideoHEDGE: Entropy-Based Hallucination Detection for Video-VLMs via Semantic Clustering and Spatiotemporal Perturbationscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.08557v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Hallucinations in video-capable vision-language models (Video-VLMs) remain frequent and high-confidence, while existing uncertainty metrics often fail to align with correctness. We introduce VideoHEDGE, a modular framework for hallucination detection in video question answering that extends entropy-based reliability estimation from images to temporally structured inputs. Given a video-question pair, VideoHEDGE draws a baseline answer and multiple high-temperature generations from both clean clips and photometrically and spatiotemporally perturbed variants, then clusters the resulting textual outputs into semantic hypotheses using either Natural Language Inference (NLI)-based or embedding-based methods. Cluster-level probability masses yield three reliability scores: Semantic Entropy (SE), RadFlag, and Vision-Amplified Semantic Entropy (VASE). We evaluate VideoHEDGE on the SoccerChat benchmark using an LLM-as-a-judge to obtain binary hallucination labels. Across three 7B Video-VLMs (Qwen2-VL, Qwen2.5-VL, and a SoccerChat-finetuned model), VASE consistently achieves the highest ROC-AUC, especially at larger distortion budgets, while SE and RadFlag often operate near chance. We further show that embedding-based clustering matches NLI-based clustering in detection performance at substantially lower computational cost, and that domain fine-tuning reduces hallucination frequency but yields only modest improvements in calibration. The hedge-bench PyPI library enables reproducible and extensible benchmarking, with full code and experimental resources available at https://github.com/Simula/HEDGE#videohedge .
arXiv:2601.08557v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Hallucinations in video-capable vision-language models (Video-VLMs) remain frequent and high-confidence, while existing uncertainty metrics often fail to align with correctness. We introduce VideoHEDGE, a modular framework for hallucination detection in video question answering that extends entropy-based reliability estimation from images to temporally structured inputs. Given a video-question pair, VideoHEDGE draws a baseline answer and multiple high-temperature generations from both clean clips and photometrically and spatiotemporally perturbed variants, then clusters the resulting textual outputs into semantic hypotheses using either Natural Language Inference (NLI)-based or embedding-based methods. Cluster-level probability masses yield three reliability scores: Semantic Entropy (SE), RadFlag, and Vision-Amplified Semantic Entropy (VASE). We evaluate VideoHEDGE on the SoccerChat benchmark using an LLM-as-a-judge to obtain binary hallucination labels. Across three 7B Video-VLMs (Qwen2-VL, Qwen2.5-VL, and a SoccerChat-finetuned model), VASE consistently achieves the highest ROC-AUC, especially at larger distortion budgets, while SE and RadFlag often operate near chance. We further show that embedding-based clustering matches NLI-based clustering in detection performance at substantially lower computational cost, and that domain fine-tuning reduces hallucination frequency but yields only modest improvements in calibration. The hedge-bench PyPI library enables reproducible and extensible benchmarking, with full code and experimental resources available at https://github.com/Simula/HEDGE#videohedge . Read More
Node.js has released updates to fix what it described as a critical security issue impacting “virtually every production Node.js app” that, if successfully exploited, could trigger a denial-of-service (DoS) condition. “Node.js/V8 makes a best-effort attempt to recover from stack space exhaustion with a catchable error, which frameworks have come to rely on for service availability,” […]
Multiplex Thinking: Reasoning via Token-wise Branch-and-Mergecs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.08808v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Large language models often solve complex reasoning tasks more effectively with Chain-of-Thought (CoT), but at the cost of long, low-bandwidth token sequences. Humans, by contrast, often reason softly by maintaining a distribution over plausible next steps. Motivated by this, we propose Multiplex Thinking, a stochastic soft reasoning mechanism that, at each thinking step, samples K candidate tokens and aggregates their embeddings into a single continuous multiplex token. This preserves the vocabulary embedding prior and the sampling dynamics of standard discrete generation, while inducing a tractable probability distribution over multiplex rollouts. Consequently, multiplex trajectories can be directly optimized with on-policy reinforcement learning (RL). Importantly, Multiplex Thinking is self-adaptive: when the model is confident, the multiplex token is nearly discrete and behaves like standard CoT; when it is uncertain, it compactly represents multiple plausible next steps without increasing sequence length. Across challenging math reasoning benchmarks, Multiplex Thinking consistently outperforms strong discrete CoT and RL baselines from Pass@1 through Pass@1024, while producing shorter sequences. The code and checkpoints are available at https://github.com/GMLR-Penn/Multiplex-Thinking.
arXiv:2601.08808v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Large language models often solve complex reasoning tasks more effectively with Chain-of-Thought (CoT), but at the cost of long, low-bandwidth token sequences. Humans, by contrast, often reason softly by maintaining a distribution over plausible next steps. Motivated by this, we propose Multiplex Thinking, a stochastic soft reasoning mechanism that, at each thinking step, samples K candidate tokens and aggregates their embeddings into a single continuous multiplex token. This preserves the vocabulary embedding prior and the sampling dynamics of standard discrete generation, while inducing a tractable probability distribution over multiplex rollouts. Consequently, multiplex trajectories can be directly optimized with on-policy reinforcement learning (RL). Importantly, Multiplex Thinking is self-adaptive: when the model is confident, the multiplex token is nearly discrete and behaves like standard CoT; when it is uncertain, it compactly represents multiple plausible next steps without increasing sequence length. Across challenging math reasoning benchmarks, Multiplex Thinking consistently outperforms strong discrete CoT and RL baselines from Pass@1 through Pass@1024, while producing shorter sequences. The code and checkpoints are available at https://github.com/GMLR-Penn/Multiplex-Thinking. Read More
Feed-Forward Optimization With Delayed Feedback for Neural Network Trainingcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2304.13372v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Backpropagation has long been criticized for being biologically implausible due to its reliance on concepts that are not viable in natural learning processes. Two core issues are the weight transport and update locking problems caused by the forward-backward dependencies, which limit biological plausibility, computational efficiency, and parallelization. Although several alternatives have been proposed to increase biological plausibility, they often come at the cost of reduced predictive performance. This paper proposes an alternative approach to training feed-forward neural networks addressing these issues by using approximate gradient information. We introduce Feed-Forward with delayed Feedback (F$^3$), which approximates gradients using fixed random feedback paths and delayed error information from the previous epoch to balance biological plausibility with predictive performance. We evaluate F$^3$ across multiple tasks and architectures, including both fully-connected and Transformer networks. Our results demonstrate that, compared to similarly plausible approaches, F$^3$ significantly improves predictive performance, narrowing the gap to backpropagation by up to 56% for classification and 96% for regression. This work is a step towards more biologically plausible learning algorithms while opening up new avenues for energy-efficient and parallelizable neural network training.
arXiv:2304.13372v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Backpropagation has long been criticized for being biologically implausible due to its reliance on concepts that are not viable in natural learning processes. Two core issues are the weight transport and update locking problems caused by the forward-backward dependencies, which limit biological plausibility, computational efficiency, and parallelization. Although several alternatives have been proposed to increase biological plausibility, they often come at the cost of reduced predictive performance. This paper proposes an alternative approach to training feed-forward neural networks addressing these issues by using approximate gradient information. We introduce Feed-Forward with delayed Feedback (F$^3$), which approximates gradients using fixed random feedback paths and delayed error information from the previous epoch to balance biological plausibility with predictive performance. We evaluate F$^3$ across multiple tasks and architectures, including both fully-connected and Transformer networks. Our results demonstrate that, compared to similarly plausible approaches, F$^3$ significantly improves predictive performance, narrowing the gap to backpropagation by up to 56% for classification and 96% for regression. This work is a step towards more biologically plausible learning algorithms while opening up new avenues for energy-efficient and parallelizable neural network training. Read More
Structured Debate Improves Corporate Credit Reasoning in Financial AIcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.17108v4 Announce Type: replace
Abstract: This study investigated LLM-based automation for analyzing non-financial data in corporate credit evaluation. Two systems were developed and compared: a Single-Agent System (SAS), in which one LLM agent infers favorable and adverse repayment signals, and a Popperian Multi-agent Debate System (PMADS), which structures the dual-perspective analysis as adversarial argumentation under the Karl Popper Debate protocol. Evaluation addressed three fronts: (i) work productivity compared with human experts; (ii) perceived report quality and usability, rated by credit risk professionals for system-generated reports; and (iii) reasoning characteristics quantified via reasoning-tree analysis. Both systems drastically reduced task completion time relative to human experts. Professionals rated SAS reports as adequate, while PMADS reports exceeded neutral benchmarks and scored significantly higher in explanatory adequacy, practical applicability, and usability. Reasoning-tree analysis showed PMADS produced deeper, more elaborated structures, whereas SAS yielded single-layered trees. These findings suggest that structured multi-agent debate enhances analytical rigor and perceived usefulness, though at the cost of longer computation time. Overall, the results demonstrate that reasoning-centered automation represents a promising approach for developing useful AI systems in decision-critical financial contexts.
arXiv:2510.17108v4 Announce Type: replace
Abstract: This study investigated LLM-based automation for analyzing non-financial data in corporate credit evaluation. Two systems were developed and compared: a Single-Agent System (SAS), in which one LLM agent infers favorable and adverse repayment signals, and a Popperian Multi-agent Debate System (PMADS), which structures the dual-perspective analysis as adversarial argumentation under the Karl Popper Debate protocol. Evaluation addressed three fronts: (i) work productivity compared with human experts; (ii) perceived report quality and usability, rated by credit risk professionals for system-generated reports; and (iii) reasoning characteristics quantified via reasoning-tree analysis. Both systems drastically reduced task completion time relative to human experts. Professionals rated SAS reports as adequate, while PMADS reports exceeded neutral benchmarks and scored significantly higher in explanatory adequacy, practical applicability, and usability. Reasoning-tree analysis showed PMADS produced deeper, more elaborated structures, whereas SAS yielded single-layered trees. These findings suggest that structured multi-agent debate enhances analytical rigor and perceived usefulness, though at the cost of longer computation time. Overall, the results demonstrate that reasoning-centered automation represents a promising approach for developing useful AI systems in decision-critical financial contexts. Read More
SAC: A Framework for Measuring and Inducing Personality Traits in LLMs with Dynamic Intensity Controlcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2506.20993v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) have gained significant traction across a wide range of fields in recent years. There is also a growing expectation for them to display human-like personalities during interactions. To meet this expectation, numerous studies have proposed methods for modelling LLM personalities through psychometric evaluations. However, most existing models face two major limitations: they rely on the Big Five (OCEAN) framework, which only provides coarse personality dimensions, and they lack mechanisms for controlling trait intensity. In this paper, we address this gap by extending the Machine Personality Inventory (MPI), which originally used the Big Five model, to incorporate the 16 Personality Factor (16PF) model, allowing expressive control over sixteen distinct traits. We also developed a structured framework known as Specific Attribute Control (SAC) for evaluating and dynamically inducing trait intensity in LLMs. Our method introduces adjective-based semantic anchoring to guide trait intensity expression and leverages behavioural questions across five intensity factors: textit{Frequency}, textit{Depth}, textit{Threshold}, textit{Effort}, and textit{Willingness}. Through experimentation, we find that modelling intensity as a continuous spectrum yields substantially more consistent and controllable personality expression compared to binary trait toggling. Moreover, we observe that changes in target trait intensity systematically influence closely related traits in psychologically coherent directions, suggesting that LLMs internalize multi-dimensional personality structures rather than treating traits in isolation. Our work opens new pathways for controlled and nuanced human-machine interactions in domains such as healthcare, education, and interviewing processes, bringing us one step closer to truly human-like social machines.
arXiv:2506.20993v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) have gained significant traction across a wide range of fields in recent years. There is also a growing expectation for them to display human-like personalities during interactions. To meet this expectation, numerous studies have proposed methods for modelling LLM personalities through psychometric evaluations. However, most existing models face two major limitations: they rely on the Big Five (OCEAN) framework, which only provides coarse personality dimensions, and they lack mechanisms for controlling trait intensity. In this paper, we address this gap by extending the Machine Personality Inventory (MPI), which originally used the Big Five model, to incorporate the 16 Personality Factor (16PF) model, allowing expressive control over sixteen distinct traits. We also developed a structured framework known as Specific Attribute Control (SAC) for evaluating and dynamically inducing trait intensity in LLMs. Our method introduces adjective-based semantic anchoring to guide trait intensity expression and leverages behavioural questions across five intensity factors: textit{Frequency}, textit{Depth}, textit{Threshold}, textit{Effort}, and textit{Willingness}. Through experimentation, we find that modelling intensity as a continuous spectrum yields substantially more consistent and controllable personality expression compared to binary trait toggling. Moreover, we observe that changes in target trait intensity systematically influence closely related traits in psychologically coherent directions, suggesting that LLMs internalize multi-dimensional personality structures rather than treating traits in isolation. Our work opens new pathways for controlled and nuanced human-machine interactions in domains such as healthcare, education, and interviewing processes, bringing us one step closer to truly human-like social machines. Read More