Integrating Knowledge Distillation Methods: A Sequential Multi-Stage Frameworkcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.15657v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Knowledge distillation (KD) transfers knowledge from large teacher models to compact student models, enabling efficient deployment on resource constrained devices. While diverse KD methods, including response based, feature based, and relation based approaches, capture different aspects of teacher knowledge, integrating multiple methods or knowledge sources is promising but often hampered by complex implementation, inflexible combinations, and catastrophic forgetting, which limits practical effectiveness.
This work proposes SMSKD (Sequential Multi Stage Knowledge Distillation), a flexible framework that sequentially integrates heterogeneous KD methods. At each stage, the student is trained with a specific distillation method, while a frozen reference model from the previous stage anchors learned knowledge to mitigate forgetting. In addition, we introduce an adaptive weighting mechanism based on the teacher true class probability (TCP) that dynamically adjusts the reference loss per sample to balance knowledge retention and integration.
By design, SMSKD supports arbitrary method combinations and stage counts with negligible computational overhead. Extensive experiments show that SMSKD consistently improves student accuracy across diverse teacher student architectures and method combinations, outperforming existing baselines. Ablation studies confirm that stage wise distillation and reference model supervision are primary contributors to performance gains, with TCP based adaptive weighting providing complementary benefits. Overall, SMSKD is a practical and resource efficient solution for integrating heterogeneous KD methods.
arXiv:2601.15657v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Knowledge distillation (KD) transfers knowledge from large teacher models to compact student models, enabling efficient deployment on resource constrained devices. While diverse KD methods, including response based, feature based, and relation based approaches, capture different aspects of teacher knowledge, integrating multiple methods or knowledge sources is promising but often hampered by complex implementation, inflexible combinations, and catastrophic forgetting, which limits practical effectiveness.
This work proposes SMSKD (Sequential Multi Stage Knowledge Distillation), a flexible framework that sequentially integrates heterogeneous KD methods. At each stage, the student is trained with a specific distillation method, while a frozen reference model from the previous stage anchors learned knowledge to mitigate forgetting. In addition, we introduce an adaptive weighting mechanism based on the teacher true class probability (TCP) that dynamically adjusts the reference loss per sample to balance knowledge retention and integration.
By design, SMSKD supports arbitrary method combinations and stage counts with negligible computational overhead. Extensive experiments show that SMSKD consistently improves student accuracy across diverse teacher student architectures and method combinations, outperforming existing baselines. Ablation studies confirm that stage wise distillation and reference model supervision are primary contributors to performance gains, with TCP based adaptive weighting providing complementary benefits. Overall, SMSKD is a practical and resource efficient solution for integrating heterogeneous KD methods. Read More
Prometheus Mind: Retrofitting Memory to Frozen Language Modelscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.15324v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Adding memory to pretrained language models typically requires architectural changes or weight modification. We present Prometheus Mind, which retrofits memory to a frozen Qwen3-4B using 11 modular adapters (530MB, 7% overhead) — fully reversible by removing the adapters. Building this system required solving four problems: (1) Extraction — we develop Contrastive Direction Discovery (CDD), which finds semantic directions via minimal pairs without labeled data. (2) Training — end-to-end optimization collapses; stage-wise training of each adapter on simple proxy tasks succeeds. (3) Injection — learned encoders fail to generalize; we find that lm_head.weight rows already provide the mapping we need, requiring no training. (4) Hidden state collapse — transformers make “wife” and “brother” 0.98+ similar; we train projections to recover distinction (0.98 $rightarrow$ 0.09). On PrometheusExtract-132 (132 cases), the system achieves 94.4% retrieval on clean inputs (n=54, 95% CI: [84.9%, 98.1%]), degrading to 19.4% on informal inputs with ellipsis, filler words, or implicit subjects (n=36). The primary bottleneck is relation classification (47.3% accuracy), responsible for most extraction errors.
arXiv:2601.15324v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Adding memory to pretrained language models typically requires architectural changes or weight modification. We present Prometheus Mind, which retrofits memory to a frozen Qwen3-4B using 11 modular adapters (530MB, 7% overhead) — fully reversible by removing the adapters. Building this system required solving four problems: (1) Extraction — we develop Contrastive Direction Discovery (CDD), which finds semantic directions via minimal pairs without labeled data. (2) Training — end-to-end optimization collapses; stage-wise training of each adapter on simple proxy tasks succeeds. (3) Injection — learned encoders fail to generalize; we find that lm_head.weight rows already provide the mapping we need, requiring no training. (4) Hidden state collapse — transformers make “wife” and “brother” 0.98+ similar; we train projections to recover distinction (0.98 $rightarrow$ 0.09). On PrometheusExtract-132 (132 cases), the system achieves 94.4% retrieval on clean inputs (n=54, 95% CI: [84.9%, 98.1%]), degrading to 19.4% on informal inputs with ellipsis, filler words, or implicit subjects (n=36). The primary bottleneck is relation classification (47.3% accuracy), responsible for most extraction errors. Read More
Defensive AI and how machine learning strengthens cyber defenseAI News Cyber threats don’t follow predictable patterns, forcing security teams to rethink how protection works at scale. Defensive AI is emerging as a practical response, combining machine learning with human oversight. Cybersecurity rarely fails because teams lack tools. It fails because threats move faster than detection can keep pace. As digital systems expand, attackers adapt in
The post Defensive AI and how machine learning strengthens cyber defense appeared first on AI News.
Cyber threats don’t follow predictable patterns, forcing security teams to rethink how protection works at scale. Defensive AI is emerging as a practical response, combining machine learning with human oversight. Cybersecurity rarely fails because teams lack tools. It fails because threats move faster than detection can keep pace. As digital systems expand, attackers adapt in
The post Defensive AI and how machine learning strengthens cyber defense appeared first on AI News. Read More
From Transactions to Trends: Predict When a Customer Is About to Stop BuyingTowards Data Science Customer churn is usually a gradual process, not a sudden event. In this post, we analyze monthly transaction trends and convert regression slopes into degrees to clearly identify declining purchase behavior. A small negative slope today can prevent a big revenue loss tomorrow.
The post From Transactions to Trends: Predict When a Customer Is About to Stop Buying appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Customer churn is usually a gradual process, not a sudden event. In this post, we analyze monthly transaction trends and convert regression slopes into degrees to clearly identify declining purchase behavior. A small negative slope today can prevent a big revenue loss tomorrow.
The post From Transactions to Trends: Predict When a Customer Is About to Stop Buying appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
Top 5 Self Hosting Platform Alternative to Vercel, Heroku & NetlifyKDnuggets The best self hosting platforms that help developers deploy, scale, and turn their projects into production ready applications while avoiding the complexity of becoming a full time DevOps engineer.
The best self hosting platforms that help developers deploy, scale, and turn their projects into production ready applications while avoiding the complexity of becoming a full time DevOps engineer. Read More
Why the Sophistication of Your Prompt Correlates Almost Perfectly with the Sophistication of the Response, as Research by Anthropic FoundTowards Data Science How prompt engineering has evolved, examined scientifically; and implications for the future of conversational AI tools
The post Why the Sophistication of Your Prompt Correlates Almost Perfectly with the Sophistication of the Response, as Research by Anthropic Found appeared first on Towards Data Science.
How prompt engineering has evolved, examined scientifically; and implications for the future of conversational AI tools
The post Why the Sophistication of Your Prompt Correlates Almost Perfectly with the Sophistication of the Response, as Research by Anthropic Found appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
Delayed Assignments in Online Non-Centroid Clustering with Stochastic Arrivalscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.16091v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Clustering is a fundamental problem, aiming to partition a set of elements, like agents or data points, into clusters such that elements in the same cluster are closer to each other than to those in other clusters. In this paper, we present a new framework for studying online non-centroid clustering with delays, where elements, that arrive one at a time as points in a finite metric space, should be assigned to clusters, but assignments need not be immediate. Specifically, upon arrival, each point’s location is revealed, and an online algorithm has to irrevocably assign it to an existing cluster or create a new one containing, at this moment, only this point. However, we allow decisions to be postponed at a delay cost, instead of following the more common assumption of immediate decisions upon arrival. This poses a critical challenge: the goal is to minimize both the total distance costs between points in each cluster and the overall delay costs incurred by postponing assignments. In the classic worst-case arrival model, where points arrive in an arbitrary order, no algorithm has a competitive ratio better than sublogarithmic in the number of points. To overcome this strong impossibility, we focus on a stochastic arrival model, where points’ locations are drawn independently across time from an unknown and fixed probability distribution over the finite metric space. We offer hope for beyond worst-case adversaries: we devise an algorithm that is constant competitive in the sense that, as the number of points grows, the ratio between the expected overall costs of the output clustering and an optimal offline clustering is bounded by a constant.
arXiv:2601.16091v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Clustering is a fundamental problem, aiming to partition a set of elements, like agents or data points, into clusters such that elements in the same cluster are closer to each other than to those in other clusters. In this paper, we present a new framework for studying online non-centroid clustering with delays, where elements, that arrive one at a time as points in a finite metric space, should be assigned to clusters, but assignments need not be immediate. Specifically, upon arrival, each point’s location is revealed, and an online algorithm has to irrevocably assign it to an existing cluster or create a new one containing, at this moment, only this point. However, we allow decisions to be postponed at a delay cost, instead of following the more common assumption of immediate decisions upon arrival. This poses a critical challenge: the goal is to minimize both the total distance costs between points in each cluster and the overall delay costs incurred by postponing assignments. In the classic worst-case arrival model, where points arrive in an arbitrary order, no algorithm has a competitive ratio better than sublogarithmic in the number of points. To overcome this strong impossibility, we focus on a stochastic arrival model, where points’ locations are drawn independently across time from an unknown and fixed probability distribution over the finite metric space. We offer hope for beyond worst-case adversaries: we devise an algorithm that is constant competitive in the sense that, as the number of points grows, the ratio between the expected overall costs of the output clustering and an optimal offline clustering is bounded by a constant. Read More
Do You Feel Comfortable? Detecting Hidden Conversational Escalation in AI Chatbotscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.06193v4 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Large Language Models (LLM) are increasingly integrated into everyday interactions, serving not only as information assistants but also as emotional companions. Even in the absence of explicit toxicity, repeated emotional reinforcement or affective drift can gradually escalate distress in a form of textit{implicit harm} that traditional toxicity filters fail to detect. Existing guardrail mechanisms often rely on external classifiers or clinical rubrics that may lag behind the nuanced, real-time dynamics of a developing conversation. To address this gap, we propose GAUGE (Guarding Affective Utterance Generation Escalation), logit-based framework for the real-time detection of hidden conversational escalation. GAUGE measures how an LLM’s output probabilistically shifts the affective state of a dialogue.
arXiv:2512.06193v4 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Large Language Models (LLM) are increasingly integrated into everyday interactions, serving not only as information assistants but also as emotional companions. Even in the absence of explicit toxicity, repeated emotional reinforcement or affective drift can gradually escalate distress in a form of textit{implicit harm} that traditional toxicity filters fail to detect. Existing guardrail mechanisms often rely on external classifiers or clinical rubrics that may lag behind the nuanced, real-time dynamics of a developing conversation. To address this gap, we propose GAUGE (Guarding Affective Utterance Generation Escalation), logit-based framework for the real-time detection of hidden conversational escalation. GAUGE measures how an LLM’s output probabilistically shifts the affective state of a dialogue. Read More
Knowing When to Abstain: Medical LLMs Under Clinical Uncertaintycs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.12471v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Current evaluation of large language models (LLMs) overwhelmingly prioritizes accuracy; however, in real-world and safety-critical applications, the ability to abstain when uncertain is equally vital for trustworthy deployment. We introduce MedAbstain, a unified benchmark and evaluation protocol for abstention in medical multiple-choice question answering (MCQA) — a discrete-choice setting that generalizes to agentic action selection — integrating conformal prediction, adversarial question perturbations, and explicit abstention options. Our systematic evaluation of both open- and closed-source LLMs reveals that even state-of-the-art, high-accuracy models often fail to abstain with uncertain. Notably, providing explicit abstention options consistently increases model uncertainty and safer abstention, far more than input perturbations, while scaling model size or advanced prompting brings little improvement. These findings highlight the central role of abstention mechanisms for trustworthy LLM deployment and offer practical guidance for improving safety in high-stakes applications.
arXiv:2601.12471v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Current evaluation of large language models (LLMs) overwhelmingly prioritizes accuracy; however, in real-world and safety-critical applications, the ability to abstain when uncertain is equally vital for trustworthy deployment. We introduce MedAbstain, a unified benchmark and evaluation protocol for abstention in medical multiple-choice question answering (MCQA) — a discrete-choice setting that generalizes to agentic action selection — integrating conformal prediction, adversarial question perturbations, and explicit abstention options. Our systematic evaluation of both open- and closed-source LLMs reveals that even state-of-the-art, high-accuracy models often fail to abstain with uncertain. Notably, providing explicit abstention options consistently increases model uncertainty and safer abstention, far more than input perturbations, while scaling model size or advanced prompting brings little improvement. These findings highlight the central role of abstention mechanisms for trustworthy LLM deployment and offer practical guidance for improving safety in high-stakes applications. Read More
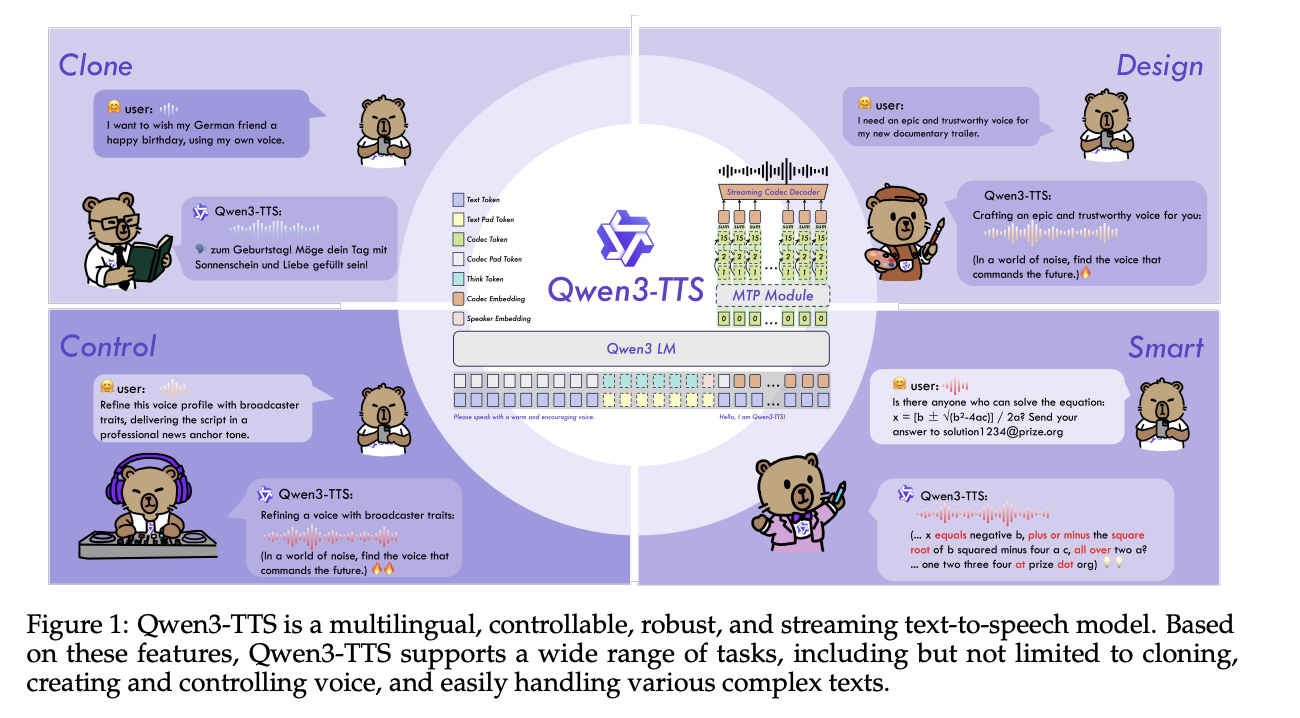
Qwen Researchers Release Qwen3-TTS: an Open Multilingual TTS Suite with Real-Time Latency and Fine-Grained Voice ControlMarkTechPost Alibaba Cloud’s Qwen team has open-sourced Qwen3-TTS, a family of multilingual text-to-speech models that target three core tasks in one stack, voice clone, voice design, and high quality speech generation. Model family and capabilities Qwen3-TTS uses a 12Hz speech tokenizer and 2 language model sizes, 0.6B and 1.7B, packaged into 3 main tasks. The open
The post Qwen Researchers Release Qwen3-TTS: an Open Multilingual TTS Suite with Real-Time Latency and Fine-Grained Voice Control appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Alibaba Cloud’s Qwen team has open-sourced Qwen3-TTS, a family of multilingual text-to-speech models that target three core tasks in one stack, voice clone, voice design, and high quality speech generation. Model family and capabilities Qwen3-TTS uses a 12Hz speech tokenizer and 2 language model sizes, 0.6B and 1.7B, packaged into 3 main tasks. The open
The post Qwen Researchers Release Qwen3-TTS: an Open Multilingual TTS Suite with Real-Time Latency and Fine-Grained Voice Control appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More