Chinese state-sponsored threat actors were likely behind the hijacking of Notepad++ update traffic last year that lasted for almost half a year, the developer states in an official announcement today. […] Read More
The data breach notification service Have I Been Pwned says that a data breach at the U.S. food chain Panera Bread affected 5.1 million accounts, not 14 million customers as previously reported. […] Read More
Fake high-yield investment platforms are surging worldwide, promising “guaranteed” returns that mask classic Ponzi schemes.CTM360 explains how HYIP scams scale through social media, recycled templates, and referral abuse. […] Read More
Semi-Autonomous Mathematics Discovery with Gemini: A Case Study on the ErdH{o}s Problemscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.22401v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: We present a case study in semi-autonomous mathematics discovery, using Gemini to systematically evaluate 700 conjectures labeled ‘Open’ in Bloom’s ErdH{o}s Problems database. We employ a hybrid methodology: AI-driven natural language verification to narrow the search space, followed by human expert evaluation to gauge correctness and novelty. We address 13 problems that were marked ‘Open’ in the database: 5 through seemingly novel autonomous solutions, and 8 through identification of previous solutions in the existing literature. Our findings suggest that the ‘Open’ status of the problems was through obscurity rather than difficulty. We also identify and discuss issues arising in applying AI to math conjectures at scale, highlighting the difficulty of literature identification and the risk of ”subconscious plagiarism” by AI. We reflect on the takeaways from AI-assisted efforts on the ErdH{o}s Problems.
arXiv:2601.22401v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: We present a case study in semi-autonomous mathematics discovery, using Gemini to systematically evaluate 700 conjectures labeled ‘Open’ in Bloom’s ErdH{o}s Problems database. We employ a hybrid methodology: AI-driven natural language verification to narrow the search space, followed by human expert evaluation to gauge correctness and novelty. We address 13 problems that were marked ‘Open’ in the database: 5 through seemingly novel autonomous solutions, and 8 through identification of previous solutions in the existing literature. Our findings suggest that the ‘Open’ status of the problems was through obscurity rather than difficulty. We also identify and discuss issues arising in applying AI to math conjectures at scale, highlighting the difficulty of literature identification and the risk of ”subconscious plagiarism” by AI. We reflect on the takeaways from AI-assisted efforts on the ErdH{o}s Problems. Read More
FraudShield: Knowledge Graph Empowered Defense for LLMs against Fraud Attackscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.22485v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) have been widely integrated into critical automated workflows, including contract review and job application processes. However, LLMs are susceptible to manipulation by fraudulent information, which can lead to harmful outcomes. Although advanced defense methods have been developed to address this issue, they often exhibit limitations in effectiveness, interpretability, and generalizability, particularly when applied to LLM-based applications. To address these challenges, we introduce FraudShield, a novel framework designed to protect LLMs from fraudulent content by leveraging a comprehensive analysis of fraud tactics. Specifically, FraudShield constructs and refines a fraud tactic-keyword knowledge graph to capture high-confidence associations between suspicious text and fraud techniques. The structured knowledge graph augments the original input by highlighting keywords and providing supporting evidence, guiding the LLM toward more secure responses. Extensive experiments show that FraudShield consistently outperforms state-of-the-art defenses across four mainstream LLMs and five representative fraud types, while also offering interpretable clues for the model’s generations.
arXiv:2601.22485v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) have been widely integrated into critical automated workflows, including contract review and job application processes. However, LLMs are susceptible to manipulation by fraudulent information, which can lead to harmful outcomes. Although advanced defense methods have been developed to address this issue, they often exhibit limitations in effectiveness, interpretability, and generalizability, particularly when applied to LLM-based applications. To address these challenges, we introduce FraudShield, a novel framework designed to protect LLMs from fraudulent content by leveraging a comprehensive analysis of fraud tactics. Specifically, FraudShield constructs and refines a fraud tactic-keyword knowledge graph to capture high-confidence associations between suspicious text and fraud techniques. The structured knowledge graph augments the original input by highlighting keywords and providing supporting evidence, guiding the LLM toward more secure responses. Extensive experiments show that FraudShield consistently outperforms state-of-the-art defenses across four mainstream LLMs and five representative fraud types, while also offering interpretable clues for the model’s generations. Read More
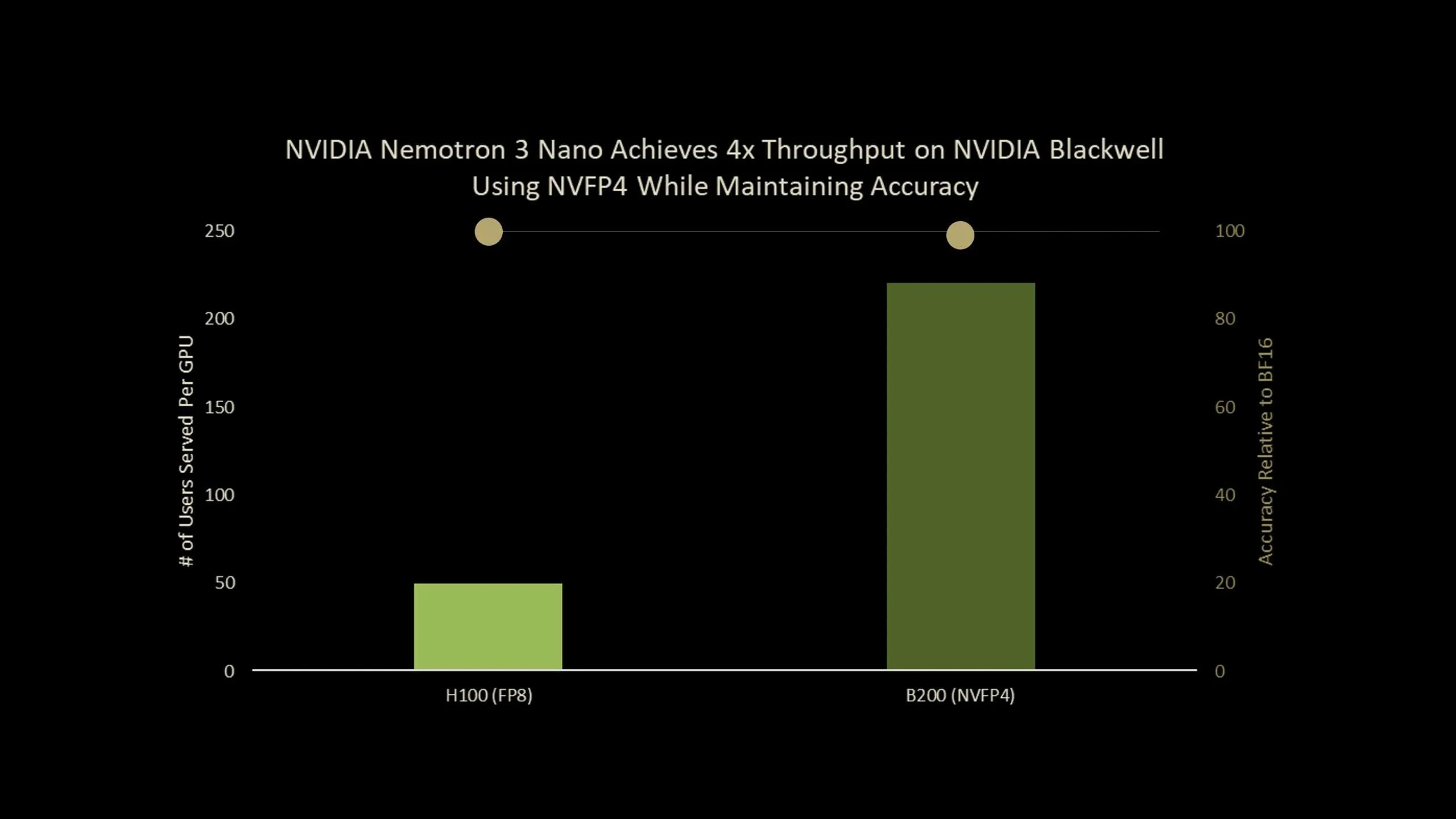
NVIDIA AI Brings Nemotron-3-Nano-30B to NVFP4 with Quantization Aware Distillation (QAD) for Efficient Reasoning InferenceMarkTechPost NVIDIA has released Nemotron-Nano-3-30B-A3B-NVFP4, a production checkpoint that runs a 30B parameter reasoning model in 4 bit NVFP4 format while keeping accuracy close to its BF16 baseline. The model combines a hybrid Mamba2 Transformer Mixture of Experts architecture with a Quantization Aware Distillation (QAD) recipe designed specifically for NVFP4 deployment. Overall, it is an ultra-efficient
The post NVIDIA AI Brings Nemotron-3-Nano-30B to NVFP4 with Quantization Aware Distillation (QAD) for Efficient Reasoning Inference appeared first on MarkTechPost.
NVIDIA has released Nemotron-Nano-3-30B-A3B-NVFP4, a production checkpoint that runs a 30B parameter reasoning model in 4 bit NVFP4 format while keeping accuracy close to its BF16 baseline. The model combines a hybrid Mamba2 Transformer Mixture of Experts architecture with a Quantization Aware Distillation (QAD) recipe designed specifically for NVFP4 deployment. Overall, it is an ultra-efficient
The post NVIDIA AI Brings Nemotron-3-Nano-30B to NVFP4 with Quantization Aware Distillation (QAD) for Efficient Reasoning Inference appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
“Existential risk” – Why scientists are racing to define consciousnessArtificial Intelligence News — ScienceDaily Scientists warn that rapid advances in AI and neurotechnology are outpacing our understanding of consciousness, creating serious ethical risks. New research argues that developing scientific tests for awareness could transform medicine, animal welfare, law, and AI development. But identifying consciousness in machines, brain organoids, or patients could also force society to rethink responsibility, rights, and moral boundaries. The question of what it means to be conscious has never been more urgent—or more unsettling.
Scientists warn that rapid advances in AI and neurotechnology are outpacing our understanding of consciousness, creating serious ethical risks. New research argues that developing scientific tests for awareness could transform medicine, animal welfare, law, and AI development. But identifying consciousness in machines, brain organoids, or patients could also force society to rethink responsibility, rights, and moral boundaries. The question of what it means to be conscious has never been more urgent—or more unsettling. Read More
A threat actor is targeting exposed MongoDB instances in automated data extortion attacks demanding low ransoms from owners to restore the data. […] Read More
Apple is introducing a new privacy feature that lets users limit the precision of location data shared with cellular networks on some iPhone and iPad models. […] Read More
A U.S. federal jury has convicted Linwei Ding, a former software engineer at Google, for stealing AI supercomputer data from his employer and secretly sharing it with Chinese tech firms. […] Read More