A General Incentives-Based Framework for Fairness in Multi-agent Resource Allocationcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.26740v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: We introduce the General Incentives-based Framework for Fairness (GIFF), a novel approach for fair multi-agent resource allocation that infers fair decision-making from standard value functions. In resource-constrained settings, agents optimizing for efficiency often create inequitable outcomes. Our approach leverages the action-value (Q-)function to balance efficiency and fairness without requiring additional training. Specifically, our method computes a local fairness gain for each action and introduces a counterfactual advantage correction term to discourage over-allocation to already well-off agents. This approach is formalized within a centralized control setting, where an arbitrator uses the GIFF-modified Q-values to solve an allocation problem.
Empirical evaluations across diverse domains, including dynamic ridesharing, homelessness prevention, and a complex job allocation task-demonstrate that our framework consistently outperforms strong baselines and can discover far-sighted, equitable policies. The framework’s effectiveness is supported by a theoretical foundation; we prove its fairness surrogate is a principled lower bound on the true fairness improvement and that its trade-off parameter offers monotonic tuning. Our findings establish GIFF as a robust and principled framework for leveraging standard reinforcement learning components to achieve more equitable outcomes in complex multi-agent systems.
arXiv:2510.26740v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: We introduce the General Incentives-based Framework for Fairness (GIFF), a novel approach for fair multi-agent resource allocation that infers fair decision-making from standard value functions. In resource-constrained settings, agents optimizing for efficiency often create inequitable outcomes. Our approach leverages the action-value (Q-)function to balance efficiency and fairness without requiring additional training. Specifically, our method computes a local fairness gain for each action and introduces a counterfactual advantage correction term to discourage over-allocation to already well-off agents. This approach is formalized within a centralized control setting, where an arbitrator uses the GIFF-modified Q-values to solve an allocation problem.
Empirical evaluations across diverse domains, including dynamic ridesharing, homelessness prevention, and a complex job allocation task-demonstrate that our framework consistently outperforms strong baselines and can discover far-sighted, equitable policies. The framework’s effectiveness is supported by a theoretical foundation; we prove its fairness surrogate is a principled lower bound on the true fairness improvement and that its trade-off parameter offers monotonic tuning. Our findings establish GIFF as a robust and principled framework for leveraging standard reinforcement learning components to achieve more equitable outcomes in complex multi-agent systems. Read More
Approximating Human Preferences Using a Multi-Judge Learned Systemcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.25884v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Aligning LLM-based judges with human preferences is a significant challenge, as they are difficult to calibrate and often suffer from rubric sensitivity, bias, and instability. Overcoming this challenge advances key applications, such as creating reliable reward models for Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) and building effective routing systems that select the best-suited model for a given user query. In this work, we propose a framework for modeling diverse, persona-based preferences by learning to aggregate outputs from multiple rubric-conditioned judges. We investigate the performance of this approach against naive baselines and assess its robustness through case studies on both human and LLM-judges biases. Our primary contributions include a persona-based method for synthesizing preference labels at scale and two distinct implementations of our aggregator: Generalized Additive Model (GAM) and a Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP).
arXiv:2510.25884v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Aligning LLM-based judges with human preferences is a significant challenge, as they are difficult to calibrate and often suffer from rubric sensitivity, bias, and instability. Overcoming this challenge advances key applications, such as creating reliable reward models for Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) and building effective routing systems that select the best-suited model for a given user query. In this work, we propose a framework for modeling diverse, persona-based preferences by learning to aggregate outputs from multiple rubric-conditioned judges. We investigate the performance of this approach against naive baselines and assess its robustness through case studies on both human and LLM-judges biases. Our primary contributions include a persona-based method for synthesizing preference labels at scale and two distinct implementations of our aggregator: Generalized Additive Model (GAM) and a Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP). Read More
SciTrust 2.0: A Comprehensive Framework for Evaluating Trustworthiness of Large Language Models in Scientific Applicationscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.25908v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated transformative potential in scientific research, yet their deployment in high-stakes contexts raises significant trustworthiness concerns. Here, we introduce SciTrust 2.0, a comprehensive framework for evaluating LLM trustworthiness in scientific applications across four dimensions: truthfulness, adversarial robustness, scientific safety, and scientific ethics. Our framework incorporates novel, open-ended truthfulness benchmarks developed through a verified reflection-tuning pipeline and expert validation, alongside a novel ethics benchmark for scientific research contexts covering eight subcategories including dual-use research and bias. We evaluated seven prominent LLMs, including four science-specialized models and three general-purpose industry models, using multiple evaluation metrics including accuracy, semantic similarity measures, and LLM-based scoring. General-purpose industry models overall outperformed science-specialized models across each trustworthiness dimension, with GPT-o4-mini demonstrating superior performance in truthfulness assessments and adversarial robustness. Science-specialized models showed significant deficiencies in logical and ethical reasoning capabilities, along with concerning vulnerabilities in safety evaluations, particularly in high-risk domains such as biosecurity and chemical weapons. By open-sourcing our framework, we provide a foundation for developing more trustworthy AI systems and advancing research on model safety and ethics in scientific contexts.
arXiv:2510.25908v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated transformative potential in scientific research, yet their deployment in high-stakes contexts raises significant trustworthiness concerns. Here, we introduce SciTrust 2.0, a comprehensive framework for evaluating LLM trustworthiness in scientific applications across four dimensions: truthfulness, adversarial robustness, scientific safety, and scientific ethics. Our framework incorporates novel, open-ended truthfulness benchmarks developed through a verified reflection-tuning pipeline and expert validation, alongside a novel ethics benchmark for scientific research contexts covering eight subcategories including dual-use research and bias. We evaluated seven prominent LLMs, including four science-specialized models and three general-purpose industry models, using multiple evaluation metrics including accuracy, semantic similarity measures, and LLM-based scoring. General-purpose industry models overall outperformed science-specialized models across each trustworthiness dimension, with GPT-o4-mini demonstrating superior performance in truthfulness assessments and adversarial robustness. Science-specialized models showed significant deficiencies in logical and ethical reasoning capabilities, along with concerning vulnerabilities in safety evaluations, particularly in high-risk domains such as biosecurity and chemical weapons. By open-sourcing our framework, we provide a foundation for developing more trustworthy AI systems and advancing research on model safety and ethics in scientific contexts. Read More
The Information-Theoretic Imperative: Compression and the Epistemic Foundations of Intelligencecs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.25883v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Existing frameworks converge on the centrality of compression to intelligence but leave underspecified why this process enforces the discovery of causal structure rather than superficial statistical patterns. We introduce a two-level framework to address this gap. The Information-Theoretic Imperative (ITI) establishes that any system persisting in uncertain environments must minimize epistemic entropy through predictive compression: this is the evolutionary “why” linking survival pressure to information-processing demands. The Compression Efficiency Principle (CEP) specifies how efficient compression mechanically selects for generative, causal models through exception-accumulation dynamics, making reality alignment a consequence rather than a contingent achievement. Together, ITI and CEP define a causal chain: from survival pressure to prediction necessity, compression requirement, efficiency optimization, generative structure discovery, and ultimately reality alignment. Each link follows from physical, information-theoretic, or evolutionary constraints, implying that intelligence is the mechanically necessary outcome of persistence in structured environments. This framework yields empirically testable predictions: compression efficiency, measured as approach to the rate-distortion frontier, correlates with out-of-distribution generalization; exception-accumulation rates differentiate causal from correlational models; hierarchical systems exhibit increasing efficiency across abstraction layers; and biological systems demonstrate metabolic costs that track representational complexity. ITI and CEP thereby provide a unified account of convergence across biological, artificial, and multi-scale systems, addressing the epistemic and functional dimensions of intelligence without invoking assumptions about consciousness or subjective experience.
arXiv:2510.25883v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Existing frameworks converge on the centrality of compression to intelligence but leave underspecified why this process enforces the discovery of causal structure rather than superficial statistical patterns. We introduce a two-level framework to address this gap. The Information-Theoretic Imperative (ITI) establishes that any system persisting in uncertain environments must minimize epistemic entropy through predictive compression: this is the evolutionary “why” linking survival pressure to information-processing demands. The Compression Efficiency Principle (CEP) specifies how efficient compression mechanically selects for generative, causal models through exception-accumulation dynamics, making reality alignment a consequence rather than a contingent achievement. Together, ITI and CEP define a causal chain: from survival pressure to prediction necessity, compression requirement, efficiency optimization, generative structure discovery, and ultimately reality alignment. Each link follows from physical, information-theoretic, or evolutionary constraints, implying that intelligence is the mechanically necessary outcome of persistence in structured environments. This framework yields empirically testable predictions: compression efficiency, measured as approach to the rate-distortion frontier, correlates with out-of-distribution generalization; exception-accumulation rates differentiate causal from correlational models; hierarchical systems exhibit increasing efficiency across abstraction layers; and biological systems demonstrate metabolic costs that track representational complexity. ITI and CEP thereby provide a unified account of convergence across biological, artificial, and multi-scale systems, addressing the epistemic and functional dimensions of intelligence without invoking assumptions about consciousness or subjective experience. Read More
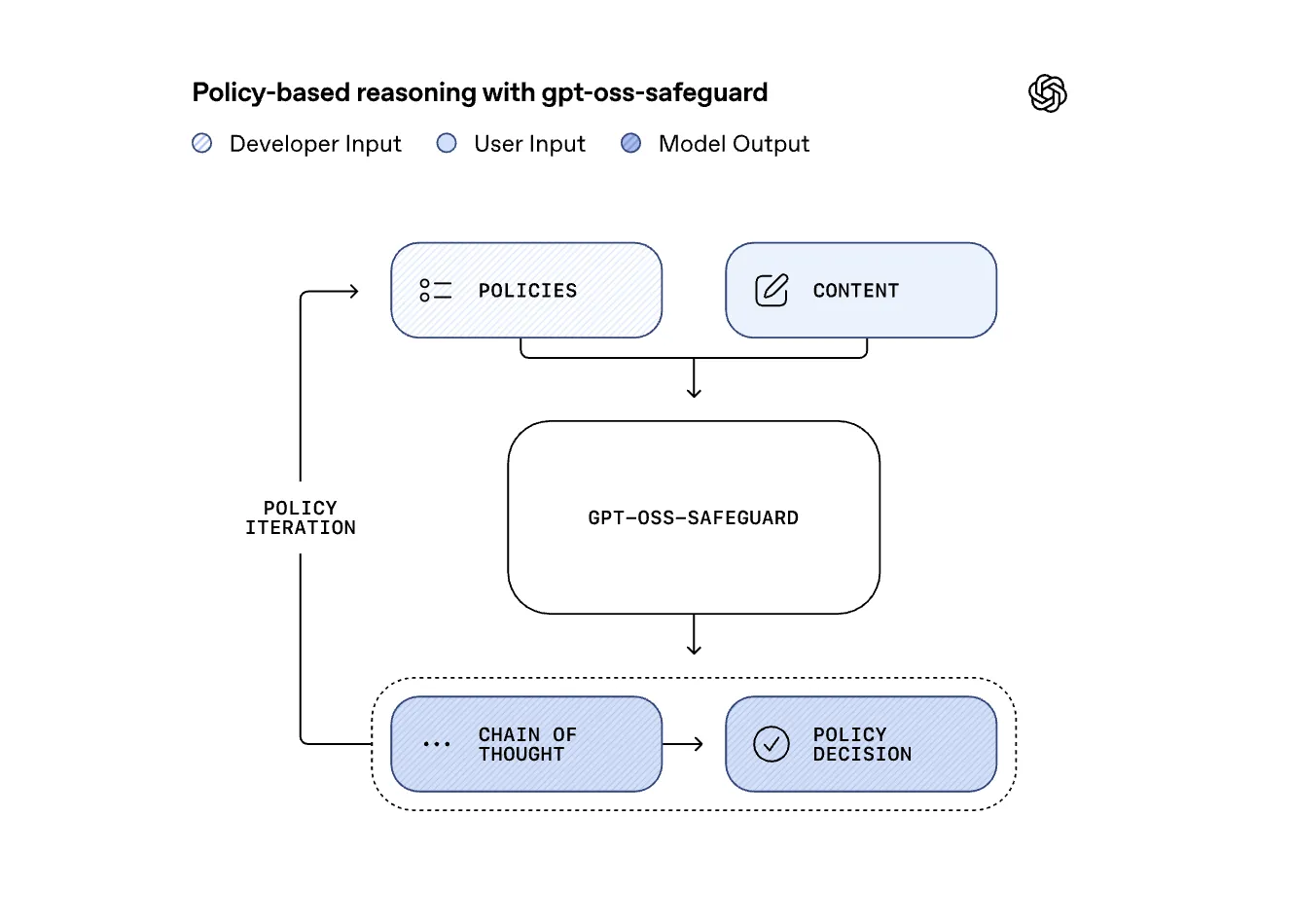
OpenAI Releases Research Preview of ‘gpt-oss-safeguard’: Two Open-Weight Reasoning Models for Safety Classification TasksMarkTechPost OpenAI has released a research preview of gpt-oss-safeguard, two open weight safety reasoning models that let developers apply custom safety policies at inference time. The models come in two sizes, gpt-oss-safeguard-120b and gpt-oss-safeguard-20b, both fine tuned from gpt-oss, both licensed under Apache 2.0, and both available on Hugging Face for local use. Why Policy-Conditioned Safety
The post OpenAI Releases Research Preview of ‘gpt-oss-safeguard’: Two Open-Weight Reasoning Models for Safety Classification Tasks appeared first on MarkTechPost.
OpenAI has released a research preview of gpt-oss-safeguard, two open weight safety reasoning models that let developers apply custom safety policies at inference time. The models come in two sizes, gpt-oss-safeguard-120b and gpt-oss-safeguard-20b, both fine tuned from gpt-oss, both licensed under Apache 2.0, and both available on Hugging Face for local use. Why Policy-Conditioned Safety
The post OpenAI Releases Research Preview of ‘gpt-oss-safeguard’: Two Open-Weight Reasoning Models for Safety Classification Tasks appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Unravelling the Mechanisms of Manipulating Numbers in Language Modelscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.26285v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Recent work has shown that different large language models (LLMs) converge to similar and accurate input embedding representations for numbers. These findings conflict with the documented propensity of LLMs to produce erroneous outputs when dealing with numeric information. In this work, we aim to explain this conflict by exploring how language models manipulate numbers and quantify the lower bounds of accuracy of these mechanisms. We find that despite surfacing errors, different language models learn interchangeable representations of numbers that are systematic, highly accurate and universal across their hidden states and the types of input contexts. This allows us to create universal probes for each LLM and to trace information — including the causes of output errors — to specific layers. Our results lay a fundamental understanding of how pre-trained LLMs manipulate numbers and outline the potential of more accurate probing techniques in addressed refinements of LLMs’ architectures.
arXiv:2510.26285v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Recent work has shown that different large language models (LLMs) converge to similar and accurate input embedding representations for numbers. These findings conflict with the documented propensity of LLMs to produce erroneous outputs when dealing with numeric information. In this work, we aim to explain this conflict by exploring how language models manipulate numbers and quantify the lower bounds of accuracy of these mechanisms. We find that despite surfacing errors, different language models learn interchangeable representations of numbers that are systematic, highly accurate and universal across their hidden states and the types of input contexts. This allows us to create universal probes for each LLM and to trace information — including the causes of output errors — to specific layers. Our results lay a fundamental understanding of how pre-trained LLMs manipulate numbers and outline the potential of more accurate probing techniques in addressed refinements of LLMs’ architectures. Read More
MisSynth: Improving MISSCI Logical Fallacies Classification with Synthetic Datacs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.26345v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Health-related misinformation is very prevalent and potentially harmful. It is difficult to identify, especially when claims distort or misinterpret scientific findings. We investigate the impact of synthetic data generation and lightweight fine-tuning techniques on the ability of large language models (LLMs) to recognize fallacious arguments using the MISSCI dataset and framework. In this work, we propose MisSynth, a pipeline that applies retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to produce synthetic fallacy samples, which are then used to fine-tune an LLM model. Our results show substantial accuracy gains with fine-tuned models compared to vanilla baselines. For instance, the LLaMA 3.1 8B fine-tuned model achieved an over 35% F1-score absolute improvement on the MISSCI test split over its vanilla baseline. We demonstrate that introducing synthetic fallacy data to augment limited annotated resources can significantly enhance zero-shot LLM classification performance on real-world scientific misinformation tasks, even with limited computational resources. The code and synthetic dataset are available on https://github.com/mxpoliakov/MisSynth.
arXiv:2510.26345v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Health-related misinformation is very prevalent and potentially harmful. It is difficult to identify, especially when claims distort or misinterpret scientific findings. We investigate the impact of synthetic data generation and lightweight fine-tuning techniques on the ability of large language models (LLMs) to recognize fallacious arguments using the MISSCI dataset and framework. In this work, we propose MisSynth, a pipeline that applies retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to produce synthetic fallacy samples, which are then used to fine-tune an LLM model. Our results show substantial accuracy gains with fine-tuned models compared to vanilla baselines. For instance, the LLaMA 3.1 8B fine-tuned model achieved an over 35% F1-score absolute improvement on the MISSCI test split over its vanilla baseline. We demonstrate that introducing synthetic fallacy data to augment limited annotated resources can significantly enhance zero-shot LLM classification performance on real-world scientific misinformation tasks, even with limited computational resources. The code and synthetic dataset are available on https://github.com/mxpoliakov/MisSynth. Read More
Robust Graph Condensation via Classification Complexity Mitigationcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.26451v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Graph condensation (GC) has gained significant attention for its ability to synthesize smaller yet informative graphs. However, existing studies often overlook the robustness of GC in scenarios where the original graph is corrupted. In such cases, we observe that the performance of GC deteriorates significantly, while existing robust graph learning technologies offer only limited effectiveness. Through both empirical investigation and theoretical analysis, we reveal that GC is inherently an intrinsic-dimension-reducing process, synthesizing a condensed graph with lower classification complexity. Although this property is critical for effective GC performance, it remains highly vulnerable to adversarial perturbations. To tackle this vulnerability and improve GC robustness, we adopt the geometry perspective of graph data manifold and propose a novel Manifold-constrained Robust Graph Condensation framework named MRGC. Specifically, we introduce three graph data manifold learning modules that guide the condensed graph to lie within a smooth, low-dimensional manifold with minimal class ambiguity, thereby preserving the classification complexity reduction capability of GC and ensuring robust performance under universal adversarial attacks. Extensive experiments demonstrate the robustness of ModelName across diverse attack scenarios.
arXiv:2510.26451v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Graph condensation (GC) has gained significant attention for its ability to synthesize smaller yet informative graphs. However, existing studies often overlook the robustness of GC in scenarios where the original graph is corrupted. In such cases, we observe that the performance of GC deteriorates significantly, while existing robust graph learning technologies offer only limited effectiveness. Through both empirical investigation and theoretical analysis, we reveal that GC is inherently an intrinsic-dimension-reducing process, synthesizing a condensed graph with lower classification complexity. Although this property is critical for effective GC performance, it remains highly vulnerable to adversarial perturbations. To tackle this vulnerability and improve GC robustness, we adopt the geometry perspective of graph data manifold and propose a novel Manifold-constrained Robust Graph Condensation framework named MRGC. Specifically, we introduce three graph data manifold learning modules that guide the condensed graph to lie within a smooth, low-dimensional manifold with minimal class ambiguity, thereby preserving the classification complexity reduction capability of GC and ensuring robust performance under universal adversarial attacks. Extensive experiments demonstrate the robustness of ModelName across diverse attack scenarios. Read More
How to Design an Autonomous Multi-Agent Data and Infrastructure Strategy System Using Lightweight Qwen Models for Efficient Pipeline Intelligence?MarkTechPost In this tutorial, we build an Agentic Data and Infrastructure Strategy system using the lightweight Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct model for efficient execution. We begin by creating a flexible LLM agent framework and then develop specialized agents that handle different layers of data management, from ingestion and quality analysis to infrastructure optimization. We integrate these agents into an
The post How to Design an Autonomous Multi-Agent Data and Infrastructure Strategy System Using Lightweight Qwen Models for Efficient Pipeline Intelligence? appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In this tutorial, we build an Agentic Data and Infrastructure Strategy system using the lightweight Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct model for efficient execution. We begin by creating a flexible LLM agent framework and then develop specialized agents that handle different layers of data management, from ingestion and quality analysis to infrastructure optimization. We integrate these agents into an
The post How to Design an Autonomous Multi-Agent Data and Infrastructure Strategy System Using Lightweight Qwen Models for Efficient Pipeline Intelligence? appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Build LLM Agents Faster with Datapizza AITowards Data Science Intro Organizations are increasingly investing in AI as these new tools are adopted in everyday operations more and more. This continuous wave of innovation is fueling the demand for more efficient and reliable frameworks. Following this trend, Datapizza (the startup behind Italy’s tech community) just released an open-source framework for GenAI with Python, called Datapizza
The post Build LLM Agents Faster with Datapizza AI appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Intro Organizations are increasingly investing in AI as these new tools are adopted in everyday operations more and more. This continuous wave of innovation is fueling the demand for more efficient and reliable frameworks. Following this trend, Datapizza (the startup behind Italy’s tech community) just released an open-source framework for GenAI with Python, called Datapizza
The post Build LLM Agents Faster with Datapizza AI appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More