Inverse Entropic Optimal Transport Solves Semi-supervised Learning via Data Likelihood Maximizationcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2410.02628v4 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Learning conditional distributions $pi^*(cdot|x)$ is a central problem in machine learning, which is typically approached via supervised methods with paired data $(x,y) sim pi^*$. However, acquiring paired data samples is often challenging, especially in problems such as domain translation. This necessitates the development of $textit{semi-supervised}$ models that utilize both limited paired data and additional unpaired i.i.d. samples $x sim pi^*_x$ and $y sim pi^*_y$ from the marginal distributions. The usage of such combined data is complex and often relies on heuristic approaches. To tackle this issue, we propose a new learning paradigm that integrates both paired and unpaired data $textbf{seamlessly}$ using the data likelihood maximization techniques. We demonstrate that our approach also connects intriguingly with inverse entropic optimal transport (OT). This finding allows us to apply recent advances in computational OT to establish an $textbf{end-to-end}$ learning algorithm to get $pi^*(cdot|x)$. In addition, we derive the universal approximation property, demonstrating that our approach can theoretically recover true conditional distributions with arbitrarily small error. Furthermore, we demonstrate through empirical tests that our method effectively learns conditional distributions using paired and unpaired data simultaneously.
arXiv:2410.02628v4 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Learning conditional distributions $pi^*(cdot|x)$ is a central problem in machine learning, which is typically approached via supervised methods with paired data $(x,y) sim pi^*$. However, acquiring paired data samples is often challenging, especially in problems such as domain translation. This necessitates the development of $textit{semi-supervised}$ models that utilize both limited paired data and additional unpaired i.i.d. samples $x sim pi^*_x$ and $y sim pi^*_y$ from the marginal distributions. The usage of such combined data is complex and often relies on heuristic approaches. To tackle this issue, we propose a new learning paradigm that integrates both paired and unpaired data $textbf{seamlessly}$ using the data likelihood maximization techniques. We demonstrate that our approach also connects intriguingly with inverse entropic optimal transport (OT). This finding allows us to apply recent advances in computational OT to establish an $textbf{end-to-end}$ learning algorithm to get $pi^*(cdot|x)$. In addition, we derive the universal approximation property, demonstrating that our approach can theoretically recover true conditional distributions with arbitrarily small error. Furthermore, we demonstrate through empirical tests that our method effectively learns conditional distributions using paired and unpaired data simultaneously. Read More
Traversal Verification for Speculative Tree Decodingcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2505.12398v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Speculative decoding is a promising approach for accelerating large language models. The primary idea is to use a lightweight draft model to speculate the output of the target model for multiple subsequent timesteps, and then verify them in parallel to determine whether the drafted tokens should be accepted or rejected. To enhance acceptance rates, existing frameworks typically construct token trees containing multiple candidates in each timestep. However, their reliance on token-level verification mechanisms introduces two critical limitations: First, the probability distribution of a sequence differs from that of individual tokens, leading to suboptimal acceptance length. Second, current verification schemes begin from the root node and proceed layer by layer in a top-down manner. Once a parent node is rejected, all its child nodes should be discarded, resulting in inefficient utilization of speculative candidates. This paper introduces Traversal Verification, a novel speculative decoding algorithm that fundamentally rethinks the verification paradigm through leaf-to-root traversal. Our approach considers the acceptance of the entire token sequence from the current node to the root, and preserves potentially valid subsequences that would be prematurely discarded by existing methods. We theoretically prove that the probability distribution obtained through Traversal Verification is identical to that of the target model, guaranteeing lossless inference while achieving substantial acceleration gains. Experimental results across different large language models and multiple tasks show that our method consistently improves acceptance length and throughput over existing methods.
arXiv:2505.12398v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Speculative decoding is a promising approach for accelerating large language models. The primary idea is to use a lightweight draft model to speculate the output of the target model for multiple subsequent timesteps, and then verify them in parallel to determine whether the drafted tokens should be accepted or rejected. To enhance acceptance rates, existing frameworks typically construct token trees containing multiple candidates in each timestep. However, their reliance on token-level verification mechanisms introduces two critical limitations: First, the probability distribution of a sequence differs from that of individual tokens, leading to suboptimal acceptance length. Second, current verification schemes begin from the root node and proceed layer by layer in a top-down manner. Once a parent node is rejected, all its child nodes should be discarded, resulting in inefficient utilization of speculative candidates. This paper introduces Traversal Verification, a novel speculative decoding algorithm that fundamentally rethinks the verification paradigm through leaf-to-root traversal. Our approach considers the acceptance of the entire token sequence from the current node to the root, and preserves potentially valid subsequences that would be prematurely discarded by existing methods. We theoretically prove that the probability distribution obtained through Traversal Verification is identical to that of the target model, guaranteeing lossless inference while achieving substantial acceleration gains. Experimental results across different large language models and multiple tasks show that our method consistently improves acceptance length and throughput over existing methods. Read More
Using Multi-modal Large Language Model to Boost Fireworks Algorithm’s Ability in Settling Challenging Optimization Taskscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.03137v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: As optimization problems grow increasingly complex and diverse, advancements in optimization techniques and paradigm innovations hold significant importance. The challenges posed by optimization problems are primarily manifested in their non-convexity, high-dimensionality, black-box nature, and other unfavorable characteristics. Traditional zero-order or first-order methods, which are often characterized by low efficiency, inaccurate gradient information, and insufficient utilization of optimization information, are ill-equipped to address these challenges effectively. In recent years, the rapid development of large language models (LLM) has led to substantial improvements in their language understanding and code generation capabilities. Consequently, the design of optimization algorithms leveraging large language models has garnered increasing attention from researchers. In this study, we choose the fireworks algorithm(FWA) as the basic optimizer and propose a novel approach to assist the design of the FWA by incorporating multi-modal large language model(MLLM). To put it simply, we propose the concept of Critical Part(CP), which extends FWA to complex high-dimensional tasks, and further utilizes the information in the optimization process with the help of the multi-modal characteristics of large language models. We focus on two specific tasks: the textit{traveling salesman problem }(TSP) and textit{electronic design automation problem} (EDA). The experimental results show that FWAs generated under our new framework have achieved or surpassed SOTA results on many problem instances.
arXiv:2511.03137v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: As optimization problems grow increasingly complex and diverse, advancements in optimization techniques and paradigm innovations hold significant importance. The challenges posed by optimization problems are primarily manifested in their non-convexity, high-dimensionality, black-box nature, and other unfavorable characteristics. Traditional zero-order or first-order methods, which are often characterized by low efficiency, inaccurate gradient information, and insufficient utilization of optimization information, are ill-equipped to address these challenges effectively. In recent years, the rapid development of large language models (LLM) has led to substantial improvements in their language understanding and code generation capabilities. Consequently, the design of optimization algorithms leveraging large language models has garnered increasing attention from researchers. In this study, we choose the fireworks algorithm(FWA) as the basic optimizer and propose a novel approach to assist the design of the FWA by incorporating multi-modal large language model(MLLM). To put it simply, we propose the concept of Critical Part(CP), which extends FWA to complex high-dimensional tasks, and further utilizes the information in the optimization process with the help of the multi-modal characteristics of large language models. We focus on two specific tasks: the textit{traveling salesman problem }(TSP) and textit{electronic design automation problem} (EDA). The experimental results show that FWAs generated under our new framework have achieved or surpassed SOTA results on many problem instances. Read More
A Proprietary Model-Based Safety Response Framework for AI Agentscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.03138v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: With the widespread application of Large Language Models (LLMs), their associated security issues have become increasingly prominent, severely constraining their trustworthy deployment in critical domains. This paper proposes a novel safety response framework designed to systematically safeguard LLMs at both the input and output levels. At the input level, the framework employs a supervised fine-tuning-based safety classification model. Through a fine-grained four-tier taxonomy (Safe, Unsafe, Conditionally Safe, Focused Attention), it performs precise risk identification and differentiated handling of user queries, significantly enhancing risk coverage and business scenario adaptability, and achieving a risk recall rate of 99.3%. At the output level, the framework integrates Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with a specifically fine-tuned interpretation model, ensuring all responses are grounded in a real-time, trustworthy knowledge base. This approach eliminates information fabrication and enables result traceability. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed safety control model achieves a significantly higher safety score on public safety evaluation benchmarks compared to the baseline model, TinyR1-Safety-8B. Furthermore, on our proprietary high-risk test set, the framework’s components attained a perfect 100% safety score, validating their exceptional protective capabilities in complex risk scenarios. This research provides an effective engineering pathway for building high-security, high-trust LLM applications.
arXiv:2511.03138v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: With the widespread application of Large Language Models (LLMs), their associated security issues have become increasingly prominent, severely constraining their trustworthy deployment in critical domains. This paper proposes a novel safety response framework designed to systematically safeguard LLMs at both the input and output levels. At the input level, the framework employs a supervised fine-tuning-based safety classification model. Through a fine-grained four-tier taxonomy (Safe, Unsafe, Conditionally Safe, Focused Attention), it performs precise risk identification and differentiated handling of user queries, significantly enhancing risk coverage and business scenario adaptability, and achieving a risk recall rate of 99.3%. At the output level, the framework integrates Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with a specifically fine-tuned interpretation model, ensuring all responses are grounded in a real-time, trustworthy knowledge base. This approach eliminates information fabrication and enables result traceability. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed safety control model achieves a significantly higher safety score on public safety evaluation benchmarks compared to the baseline model, TinyR1-Safety-8B. Furthermore, on our proprietary high-risk test set, the framework’s components attained a perfect 100% safety score, validating their exceptional protective capabilities in complex risk scenarios. This research provides an effective engineering pathway for building high-security, high-trust LLM applications. Read More
Apple plans big Siri update with help from Google AIAI News Apple is planning to use a custom version of Google’s Gemini model to support a major upgrade to Siri, according to Bloomberg’s Mark Gurman. The company may pay Google about $1 billion each year for access to technology that can create summaries and handle planning tasks. Bloomberg says Apple will run the custom model on
The post Apple plans big Siri update with help from Google AI appeared first on AI News.
Apple is planning to use a custom version of Google’s Gemini model to support a major upgrade to Siri, according to Bloomberg’s Mark Gurman. The company may pay Google about $1 billion each year for access to technology that can create summaries and handle planning tasks. Bloomberg says Apple will run the custom model on
The post Apple plans big Siri update with help from Google AI appeared first on AI News. Read More
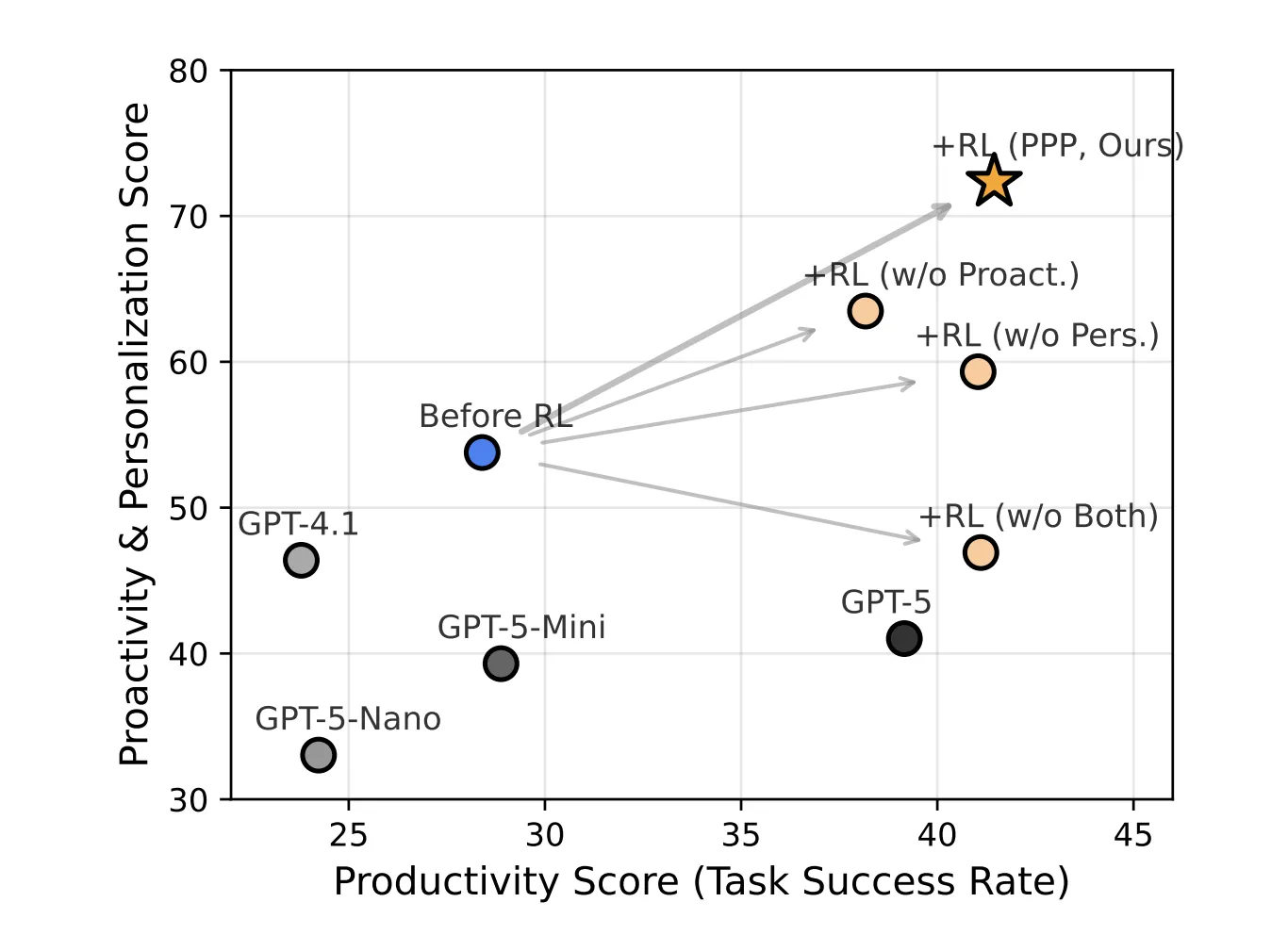
CMU Researchers Introduce PPP and UserVille To Train Proactive And Personalized LLM AgentsMarkTechPost Most LLM agents are tuned to maximize task success. They resolve GitHub issues or answer deep research queries, but they do not reason carefully about when to ask the user questions or how to respect different interaction preferences. How can we design LLM agents that know when to ask better questions and adapt their behavior
The post CMU Researchers Introduce PPP and UserVille To Train Proactive And Personalized LLM Agents appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Most LLM agents are tuned to maximize task success. They resolve GitHub issues or answer deep research queries, but they do not reason carefully about when to ask the user questions or how to respect different interaction preferences. How can we design LLM agents that know when to ask better questions and adapt their behavior
The post CMU Researchers Introduce PPP and UserVille To Train Proactive And Personalized LLM Agents appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
LiveTradeBench: Seeking Real-World Alpha with Large Language Modelscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.03628v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) achieve strong performance across benchmarks–from knowledge quizzes and math reasoning to web-agent tasks–but these tests occur in static settings, lacking real dynamics and uncertainty. Consequently, they evaluate isolated reasoning or problem-solving rather than decision-making under uncertainty. To address this, we introduce LiveTradeBench, a live trading environment for evaluating LLM agents in realistic and evolving markets. LiveTradeBench follows three design principles: (i) Live data streaming of market prices and news, eliminating dependence on offline backtesting and preventing information leakage while capturing real-time uncertainty; (ii) a portfolio-management abstraction that extends control from single-asset actions to multi-asset allocation, integrating risk management and cross-asset reasoning; and (iii) multi-market evaluation across structurally distinct environments–U.S. stocks and Polymarket prediction markets–differing in volatility, liquidity, and information flow. At each step, an agent observes prices, news, and its portfolio, then outputs percentage allocations that balance risk and return. Using LiveTradeBench, we run 50-day live evaluations of 21 LLMs across families. Results show that (1) high LMArena scores do not imply superior trading outcomes; (2) models display distinct portfolio styles reflecting risk appetite and reasoning dynamics; and (3) some LLMs effectively leverage live signals to adapt decisions. These findings expose a gap between static evaluation and real-world competence, motivating benchmarks that test sequential decision making and consistency under live uncertainty.
arXiv:2511.03628v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) achieve strong performance across benchmarks–from knowledge quizzes and math reasoning to web-agent tasks–but these tests occur in static settings, lacking real dynamics and uncertainty. Consequently, they evaluate isolated reasoning or problem-solving rather than decision-making under uncertainty. To address this, we introduce LiveTradeBench, a live trading environment for evaluating LLM agents in realistic and evolving markets. LiveTradeBench follows three design principles: (i) Live data streaming of market prices and news, eliminating dependence on offline backtesting and preventing information leakage while capturing real-time uncertainty; (ii) a portfolio-management abstraction that extends control from single-asset actions to multi-asset allocation, integrating risk management and cross-asset reasoning; and (iii) multi-market evaluation across structurally distinct environments–U.S. stocks and Polymarket prediction markets–differing in volatility, liquidity, and information flow. At each step, an agent observes prices, news, and its portfolio, then outputs percentage allocations that balance risk and return. Using LiveTradeBench, we run 50-day live evaluations of 21 LLMs across families. Results show that (1) high LMArena scores do not imply superior trading outcomes; (2) models display distinct portfolio styles reflecting risk appetite and reasoning dynamics; and (3) some LLMs effectively leverage live signals to adapt decisions. These findings expose a gap between static evaluation and real-world competence, motivating benchmarks that test sequential decision making and consistency under live uncertainty. Read More
RefAgent: A Multi-agent LLM-based Framework for Automatic Software Refactoringcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.03153v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Large Language Models (LLMs) have substantially influenced various software engineering tasks. Indeed, in the case of software refactoring, traditional LLMs have shown the ability to reduce development time and enhance code quality. However, these LLMs often rely on static, detailed instructions for specific tasks. In contrast, LLM-based agents can dynamically adapt to evolving contexts and autonomously make decisions by interacting with software tools and executing workflows. In this paper, we explore the potential of LLM-based agents in supporting refactoring activities. Specifically, we introduce RefAgent, a multi-agent LLM-based framework for end-to-end software refactoring. RefAgent consists of specialized agents responsible for planning, executing, testing, and iteratively refining refactorings using self-reflection and tool-calling capabilities. We evaluate RefAgent on eight open-source Java projects, comparing its effectiveness against a single-agent approach, a search-based refactoring tool, and historical developer refactorings. Our assessment focuses on: (1) the impact of generated refactorings on software quality, (2) the ability to identify refactoring opportunities, and (3) the contribution of each LLM agent through an ablation study. Our results show that RefAgent achieves a median unit test pass rate of 90%, reduces code smells by a median of 52.5%, and improves key quality attributes (e.g., reusability) by a median of 8.6%. Additionally, it closely aligns with developer refactorings and the search-based tool in identifying refactoring opportunities, attaining a median F1-score of 79.15% and 72.7%, respectively. Compared to single-agent approaches, RefAgent improves the median unit test pass rate by 64.7% and the median compilation success rate by 40.1%. These findings highlight the promise of multi-agent architectures in advancing automated software refactoring.
arXiv:2511.03153v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Large Language Models (LLMs) have substantially influenced various software engineering tasks. Indeed, in the case of software refactoring, traditional LLMs have shown the ability to reduce development time and enhance code quality. However, these LLMs often rely on static, detailed instructions for specific tasks. In contrast, LLM-based agents can dynamically adapt to evolving contexts and autonomously make decisions by interacting with software tools and executing workflows. In this paper, we explore the potential of LLM-based agents in supporting refactoring activities. Specifically, we introduce RefAgent, a multi-agent LLM-based framework for end-to-end software refactoring. RefAgent consists of specialized agents responsible for planning, executing, testing, and iteratively refining refactorings using self-reflection and tool-calling capabilities. We evaluate RefAgent on eight open-source Java projects, comparing its effectiveness against a single-agent approach, a search-based refactoring tool, and historical developer refactorings. Our assessment focuses on: (1) the impact of generated refactorings on software quality, (2) the ability to identify refactoring opportunities, and (3) the contribution of each LLM agent through an ablation study. Our results show that RefAgent achieves a median unit test pass rate of 90%, reduces code smells by a median of 52.5%, and improves key quality attributes (e.g., reusability) by a median of 8.6%. Additionally, it closely aligns with developer refactorings and the search-based tool in identifying refactoring opportunities, attaining a median F1-score of 79.15% and 72.7%, respectively. Compared to single-agent approaches, RefAgent improves the median unit test pass rate by 64.7% and the median compilation success rate by 40.1%. These findings highlight the promise of multi-agent architectures in advancing automated software refactoring. Read More
Deploying Rapid Damage Assessments from sUAS Imagery for Disaster Responsecs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.03132v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: This paper presents the first AI/ML system for automating building damage assessment in uncrewed aerial systems (sUAS) imagery to be deployed operationally during federally declared disasters (Hurricanes Debby and Helene). In response to major disasters, sUAS teams are dispatched to collect imagery of the affected areas to assess damage; however, at recent disasters, teams collectively delivered between 47GB and 369GB of imagery per day, representing more imagery than can reasonably be transmitted or interpreted by subject matter experts in the disaster scene, thus delaying response efforts. To alleviate this data avalanche encountered in practice, computer vision and machine learning techniques are necessary. While prior work has been deployed to automatically assess damage in satellite imagery, there is no current state of practice for sUAS-based damage assessment systems, as all known work has been confined to academic settings. This work establishes the state of practice via the development and deployment of models for building damage assessment with sUAS imagery. The model development involved training on the largest known dataset of post-disaster sUAS aerial imagery, containing 21,716 building damage labels, and the operational training of 91 disaster practitioners. The best performing model was deployed during the responses to Hurricanes Debby and Helene, where it assessed a combined 415 buildings in approximately 18 minutes. This work contributes documentation of the actual use of AI/ML for damage assessment during a disaster and lessons learned to the benefit of the AI/ML research and user communities.
arXiv:2511.03132v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: This paper presents the first AI/ML system for automating building damage assessment in uncrewed aerial systems (sUAS) imagery to be deployed operationally during federally declared disasters (Hurricanes Debby and Helene). In response to major disasters, sUAS teams are dispatched to collect imagery of the affected areas to assess damage; however, at recent disasters, teams collectively delivered between 47GB and 369GB of imagery per day, representing more imagery than can reasonably be transmitted or interpreted by subject matter experts in the disaster scene, thus delaying response efforts. To alleviate this data avalanche encountered in practice, computer vision and machine learning techniques are necessary. While prior work has been deployed to automatically assess damage in satellite imagery, there is no current state of practice for sUAS-based damage assessment systems, as all known work has been confined to academic settings. This work establishes the state of practice via the development and deployment of models for building damage assessment with sUAS imagery. The model development involved training on the largest known dataset of post-disaster sUAS aerial imagery, containing 21,716 building damage labels, and the operational training of 91 disaster practitioners. The best performing model was deployed during the responses to Hurricanes Debby and Helene, where it assessed a combined 415 buildings in approximately 18 minutes. This work contributes documentation of the actual use of AI/ML for damage assessment during a disaster and lessons learned to the benefit of the AI/ML research and user communities. Read More
Benchmarking the Thinking Mode of Multimodal Large Language Models in Clinical Taskscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.03328v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: A recent advancement in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) research is the emergence of “reasoning MLLMs” that offer explicit control over their internal thinking processes (normally referred as the “thinking mode”) alongside the standard “non-thinking mode”. This capability allows these models to engage in a step-by-step process of internal deliberation before generating a final response. With the rapid transition to and adoption of these “dual-state” MLLMs, this work rigorously evaluated how the enhanced reasoning processes of these MLLMs impact model performance and reliability in clinical tasks. This paper evaluates the active “thinking mode” capabilities of two leading MLLMs, Seed1.5-VL and Gemini-2.5-Flash, for medical applications. We assessed their performance on four visual medical tasks using VQA-RAD and ROCOv2 datasets. Our findings reveal that the improvement from activating the thinking mode remains marginal compared to the standard non-thinking mode for the majority of the tasks. Their performance on complex medical tasks such as open-ended VQA and medical image interpretation remains suboptimal, highlighting the need for domain-specific medical data and more advanced methods for medical knowledge integration.
arXiv:2511.03328v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: A recent advancement in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) research is the emergence of “reasoning MLLMs” that offer explicit control over their internal thinking processes (normally referred as the “thinking mode”) alongside the standard “non-thinking mode”. This capability allows these models to engage in a step-by-step process of internal deliberation before generating a final response. With the rapid transition to and adoption of these “dual-state” MLLMs, this work rigorously evaluated how the enhanced reasoning processes of these MLLMs impact model performance and reliability in clinical tasks. This paper evaluates the active “thinking mode” capabilities of two leading MLLMs, Seed1.5-VL and Gemini-2.5-Flash, for medical applications. We assessed their performance on four visual medical tasks using VQA-RAD and ROCOv2 datasets. Our findings reveal that the improvement from activating the thinking mode remains marginal compared to the standard non-thinking mode for the majority of the tasks. Their performance on complex medical tasks such as open-ended VQA and medical image interpretation remains suboptimal, highlighting the need for domain-specific medical data and more advanced methods for medical knowledge integration. Read More