Learning Fourier shapes to probe the geometric world of deep neural networks AI updates on arXiv.org
Learning Fourier shapes to probe the geometric world of deep neural networkscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.04970v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: While both shape and texture are fundamental to visual recognition, research on deep neural networks (DNNs) has predominantly focused on the latter, leaving their geometric understanding poorly probed. Here, we show: first, that optimized shapes can act as potent semantic carriers, generating high-confidence classifications from inputs defined purely by their geometry; second, that they are high-fidelity interpretability tools that precisely isolate a model’s salient regions; and third, that they constitute a new, generalizable adversarial paradigm capable of deceiving downstream visual tasks. This is achieved through an end-to-end differentiable framework that unifies a powerful Fourier series to parameterize arbitrary shapes, a winding number-based mapping to translate them into the pixel grid required by DNNs, and signal energy constraints that enhance optimization efficiency while ensuring physically plausible shapes. Our work provides a versatile framework for probing the geometric world of DNNs and opens new frontiers for challenging and understanding machine perception.
arXiv:2511.04970v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: While both shape and texture are fundamental to visual recognition, research on deep neural networks (DNNs) has predominantly focused on the latter, leaving their geometric understanding poorly probed. Here, we show: first, that optimized shapes can act as potent semantic carriers, generating high-confidence classifications from inputs defined purely by their geometry; second, that they are high-fidelity interpretability tools that precisely isolate a model’s salient regions; and third, that they constitute a new, generalizable adversarial paradigm capable of deceiving downstream visual tasks. This is achieved through an end-to-end differentiable framework that unifies a powerful Fourier series to parameterize arbitrary shapes, a winding number-based mapping to translate them into the pixel grid required by DNNs, and signal energy constraints that enhance optimization efficiency while ensuring physically plausible shapes. Our work provides a versatile framework for probing the geometric world of DNNs and opens new frontiers for challenging and understanding machine perception. Read More
Monitor-Generate-Verify (MGV): Formalising Metacognitive Theory for Language Model Reasoningcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.04341v2 Announce Type: replace
Abstract: Test-time reasoning architectures such as those following the Generate-Verify paradigm — where a model iteratively refines or verifies its own generated outputs — prioritise generation and verification but exclude the monitoring processes that determine when and how reasoning should begin. This omission may contribute to the prefix dominance trap, in which models commit early to suboptimal reasoning paths and seldom recover, yielding roughly 20% accuracy loss. We address this architectural gap by formalising Flavell’s and Nelson and Narens’ metacognitive theories into computational specifications, proposing the Monitor-Generate-Verify (MGV) framework. MGV extends the Generate-Verify paradigm by adding explicit monitoring that captures metacognitive experiences (from difficulty assessments to confidence judgements) before generation begins and refines future monitoring through verification feedback. Though we present no empirical validation, this work provides the first systematic computational translation of foundational metacognitive theories, offering a principled vocabulary for understanding reasoning system failures and suggesting specific architectural interventions for future test-time reasoning designs.
arXiv:2511.04341v2 Announce Type: replace
Abstract: Test-time reasoning architectures such as those following the Generate-Verify paradigm — where a model iteratively refines or verifies its own generated outputs — prioritise generation and verification but exclude the monitoring processes that determine when and how reasoning should begin. This omission may contribute to the prefix dominance trap, in which models commit early to suboptimal reasoning paths and seldom recover, yielding roughly 20% accuracy loss. We address this architectural gap by formalising Flavell’s and Nelson and Narens’ metacognitive theories into computational specifications, proposing the Monitor-Generate-Verify (MGV) framework. MGV extends the Generate-Verify paradigm by adding explicit monitoring that captures metacognitive experiences (from difficulty assessments to confidence judgements) before generation begins and refines future monitoring through verification feedback. Though we present no empirical validation, this work provides the first systematic computational translation of foundational metacognitive theories, offering a principled vocabulary for understanding reasoning system failures and suggesting specific architectural interventions for future test-time reasoning designs. Read More
Reimagining cybersecurity in the era of AI and quantumMIT Technology Review AI and quantum technologies are dramatically reconfiguring how cybersecurity functions, redefining the speed and scale with which digital defenders and their adversaries can operate. The weaponization of AI tools for cyberattacks is already proving a worthy opponent to current defenses. From reconnaissance to ransomware, cybercriminals can automate attacks faster than ever before with AI. This…
AI and quantum technologies are dramatically reconfiguring how cybersecurity functions, redefining the speed and scale with which digital defenders and their adversaries can operate. The weaponization of AI tools for cyberattacks is already proving a worthy opponent to current defenses. From reconnaissance to ransomware, cybercriminals can automate attacks faster than ever before with AI. This… Read More
LLM-Powered Time-Series AnalysisTowards Data Science Part 2: Prompts for Advanced Model Development
The post LLM-Powered Time-Series Analysis appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Part 2: Prompts for Advanced Model Development
The post LLM-Powered Time-Series Analysis appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
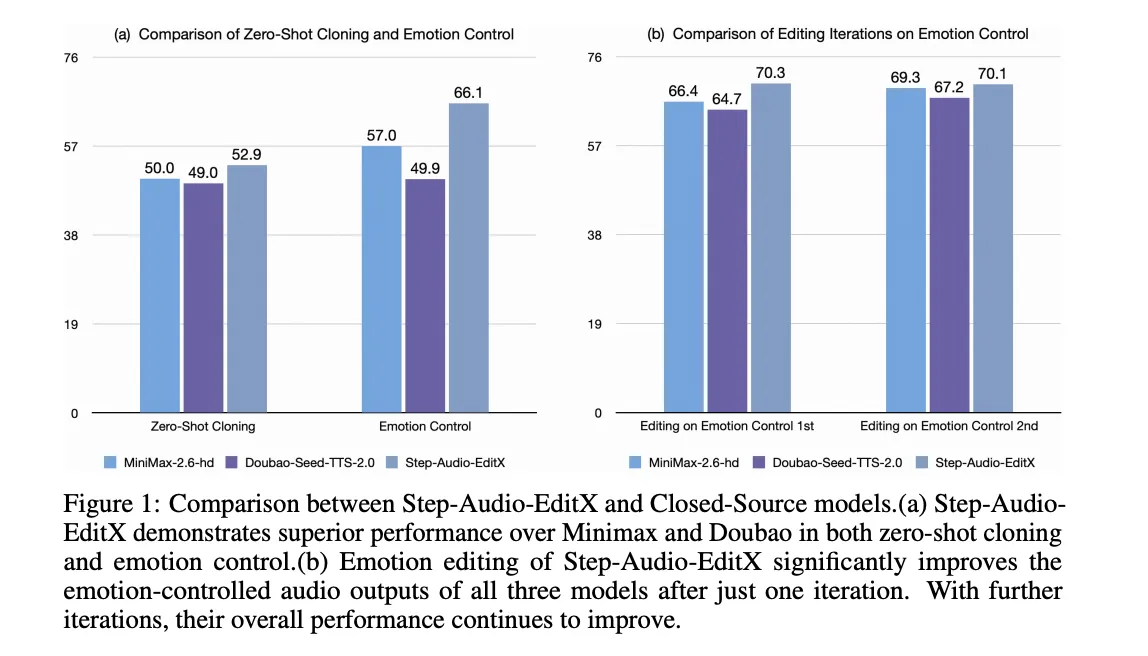
StepFun AI Releases Step-Audio-EditX: A New Open-Source 3B LLM-Grade Audio Editing Model Excelling at Expressive and Iterative Audio EditingMarkTechPost How can speech editing become as direct and controllable as simply rewriting a line of text? StepFun AI has open sourced Step-Audio-EditX, a 3B parameter LLM based audio model that turns expressive speech editing into a token level text like operation, instead of a waveform level signal processing task. Why developers care about controllable TTS?
The post StepFun AI Releases Step-Audio-EditX: A New Open-Source 3B LLM-Grade Audio Editing Model Excelling at Expressive and Iterative Audio Editing appeared first on MarkTechPost.
How can speech editing become as direct and controllable as simply rewriting a line of text? StepFun AI has open sourced Step-Audio-EditX, a 3B parameter LLM based audio model that turns expressive speech editing into a token level text like operation, instead of a waveform level signal processing task. Why developers care about controllable TTS?
The post StepFun AI Releases Step-Audio-EditX: A New Open-Source 3B LLM-Grade Audio Editing Model Excelling at Expressive and Iterative Audio Editing appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
How to Build Your Own Agentic AI System Using CrewAITowards Data Science This article demonstrates how to develop your own Agentic AI system using CrewAI framework. By orchestrating specialized agents with distinct roles and tools, we implement a multi-agent team that is capable of generating optimized content for different social media platforms.
The post How to Build Your Own Agentic AI System Using CrewAI appeared first on Towards Data Science.
This article demonstrates how to develop your own Agentic AI system using CrewAI framework. By orchestrating specialized agents with distinct roles and tools, we implement a multi-agent team that is capable of generating optimized content for different social media platforms.
The post How to Build Your Own Agentic AI System Using CrewAI appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
Nested Learning: A New Machine Learning Approach for Continual Learning that Views Models as Nested Optimization Problems to Enhance Long Context ProcessingMarkTechPost How can we build AI systems that keep learning new information over time without forgetting what they learned before or retraining from scratch? Google Researchers has introduced Nested Learning, a machine learning approach that treats a model as a collection of smaller nested optimization problems, instead of a single network trained by one outer loop.
The post Nested Learning: A New Machine Learning Approach for Continual Learning that Views Models as Nested Optimization Problems to Enhance Long Context Processing appeared first on MarkTechPost.
How can we build AI systems that keep learning new information over time without forgetting what they learned before or retraining from scratch? Google Researchers has introduced Nested Learning, a machine learning approach that treats a model as a collection of smaller nested optimization problems, instead of a single network trained by one outer loop.
The post Nested Learning: A New Machine Learning Approach for Continual Learning that Views Models as Nested Optimization Problems to Enhance Long Context Processing appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
How to Build an Agentic Voice AI Assistant that Understands, Reasons, Plans, and Responds through Autonomous Multi-Step IntelligenceMarkTechPost In this tutorial, we explore how to build an Agentic Voice AI Assistant capable of understanding, reasoning, and responding through natural speech in real time. We begin by setting up a self-contained voice intelligence pipeline that integrates speech recognition, intent detection, multi-step reasoning, and text-to-speech synthesis. Along the way, we design an agent that listens
The post How to Build an Agentic Voice AI Assistant that Understands, Reasons, Plans, and Responds through Autonomous Multi-Step Intelligence appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In this tutorial, we explore how to build an Agentic Voice AI Assistant capable of understanding, reasoning, and responding through natural speech in real time. We begin by setting up a self-contained voice intelligence pipeline that integrates speech recognition, intent detection, multi-step reasoning, and text-to-speech synthesis. Along the way, we design an agent that listens
The post How to Build an Agentic Voice AI Assistant that Understands, Reasons, Plans, and Responds through Autonomous Multi-Step Intelligence appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
How to Build an Advanced Multi-Page Reflex Web Application with Real-Time Database, Dynamic State Management, and Reactive UIMarkTechPost In this tutorial, we build an advanced Reflex web application entirely in Python that runs seamlessly inside Colab. We design the app to demonstrate how Reflex enables full-stack development with no JavaScript, just reactive Python code. We create a complete notes-management dashboard featuring two pages, real-time database interactions, filtering, sorting, analytics, and user personalization. We
The post How to Build an Advanced Multi-Page Reflex Web Application with Real-Time Database, Dynamic State Management, and Reactive UI appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In this tutorial, we build an advanced Reflex web application entirely in Python that runs seamlessly inside Colab. We design the app to demonstrate how Reflex enables full-stack development with no JavaScript, just reactive Python code. We create a complete notes-management dashboard featuring two pages, real-time database interactions, filtering, sorting, analytics, and user personalization. We
The post How to Build an Advanced Multi-Page Reflex Web Application with Real-Time Database, Dynamic State Management, and Reactive UI appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Anthropic Turns MCP Agents Into Code First Systems With ‘Code Execution With MCP’ ApproachMarkTechPost Agents that use the Model Context Protocol MCP have a scaling problem. Every tool definition and every intermediate result is pushed through the context window, which means large workflows burn tokens and hit latency and cost limits fast. Anthropic’s new ‘code execution with MCP’ pattern restructures this pipeline by turning MCP tools into code level
The post Anthropic Turns MCP Agents Into Code First Systems With ‘Code Execution With MCP’ Approach appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Agents that use the Model Context Protocol MCP have a scaling problem. Every tool definition and every intermediate result is pushed through the context window, which means large workflows burn tokens and hit latency and cost limits fast. Anthropic’s new ‘code execution with MCP’ pattern restructures this pipeline by turning MCP tools into code level
The post Anthropic Turns MCP Agents Into Code First Systems With ‘Code Execution With MCP’ Approach appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More