ORCHID: Orchestrated Retrieval-Augmented Classification with Human-in-the-Loop Intelligent Decision-Making for High-Risk Propertycs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.04956v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: High-Risk Property (HRP) classification is critical at U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) sites, where inventories include sensitive and often dual-use equipment. Compliance must track evolving rules designated by various export control policies to make transparent and auditable decisions. Traditional expert-only workflows are time-consuming, backlog-prone, and struggle to keep pace with shifting regulatory boundaries. We demo ORCHID, a modular agentic system for HRP classification that pairs retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) with human oversight to produce policy-based outputs that can be audited. Small cooperating agents, retrieval, description refiner, classifier, validator, and feedback logger, coordinate via agent-to-agent messaging and invoke tools through the Model Context Protocol (MCP) for model-agnostic on-premise operation. The interface follows an Item to Evidence to Decision loop with step-by-step reasoning, on-policy citations, and append-only audit bundles (run-cards, prompts, evidence). In preliminary tests on real HRP cases, ORCHID improves accuracy and traceability over a non-agentic baseline while deferring uncertain items to Subject Matter Experts (SMEs). The demonstration shows single item submission, grounded citations, SME feedback capture, and exportable audit artifacts, illustrating a practical path to trustworthy LLM assistance in sensitive DOE compliance workflows.
arXiv:2511.04956v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: High-Risk Property (HRP) classification is critical at U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) sites, where inventories include sensitive and often dual-use equipment. Compliance must track evolving rules designated by various export control policies to make transparent and auditable decisions. Traditional expert-only workflows are time-consuming, backlog-prone, and struggle to keep pace with shifting regulatory boundaries. We demo ORCHID, a modular agentic system for HRP classification that pairs retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) with human oversight to produce policy-based outputs that can be audited. Small cooperating agents, retrieval, description refiner, classifier, validator, and feedback logger, coordinate via agent-to-agent messaging and invoke tools through the Model Context Protocol (MCP) for model-agnostic on-premise operation. The interface follows an Item to Evidence to Decision loop with step-by-step reasoning, on-policy citations, and append-only audit bundles (run-cards, prompts, evidence). In preliminary tests on real HRP cases, ORCHID improves accuracy and traceability over a non-agentic baseline while deferring uncertain items to Subject Matter Experts (SMEs). The demonstration shows single item submission, grounded citations, SME feedback capture, and exportable audit artifacts, illustrating a practical path to trustworthy LLM assistance in sensitive DOE compliance workflows. Read More
10% of Nvidia’s cost: Why Tesla-Intel chip partnership demands attentionAI News The potential Tesla-Intel chip partnership could deliver AI chips at just 10% of Nvidia’s cost – a claim that represents a significant development in AI infrastructure that enterprise technology leaders cannot afford to ignore. On November 6, 2025, Tesla CEO Elon Musk stated publicly at the company’s annual shareholder meeting that the electric vehicle manufacturer
The post 10% of Nvidia’s cost: Why Tesla-Intel chip partnership demands attention appeared first on AI News.
The potential Tesla-Intel chip partnership could deliver AI chips at just 10% of Nvidia’s cost – a claim that represents a significant development in AI infrastructure that enterprise technology leaders cannot afford to ignore. On November 6, 2025, Tesla CEO Elon Musk stated publicly at the company’s annual shareholder meeting that the electric vehicle manufacturer
The post 10% of Nvidia’s cost: Why Tesla-Intel chip partnership demands attention appeared first on AI News. Read More
What Is ISO 42001 Clause 6: The Strategic Core of AI Governance Your organization mapped its AI landscape in Clause 4 and secured leadership commitment in Clause 5. Clause 6 is where ISO/IEC 42001:2023 gets operational: systematic planning for AI risk management. This is where you establish formal methodologies for identifying AI system risks and […]
A benchmark multimodal oro-dental dataset for large vision-language modelscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.04948v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: The advancement of artificial intelligence in oral healthcare relies on the availability of large-scale multimodal datasets that capture the complexity of clinical practice. In this paper, we present a comprehensive multimodal dataset, comprising 8775 dental checkups from 4800 patients collected over eight years (2018-2025), with patients ranging from 10 to 90 years of age. The dataset includes 50000 intraoral images, 8056 radiographs, and detailed textual records, including diagnoses, treatment plans, and follow-up notes. The data were collected under standard ethical guidelines and annotated for benchmarking. To demonstrate its utility, we fine-tuned state-of-the-art large vision-language models, Qwen-VL 3B and 7B, and evaluated them on two tasks: classification of six oro-dental anomalies and generation of complete diagnostic reports from multimodal inputs. We compared the fine-tuned models with their base counterparts and GPT-4o. The fine-tuned models achieved substantial gains over these baselines, validating the dataset and underscoring its effectiveness in advancing AI-driven oro-dental healthcare solutions. The dataset is publicly available, providing an essential resource for future research in AI dentistry.
arXiv:2511.04948v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: The advancement of artificial intelligence in oral healthcare relies on the availability of large-scale multimodal datasets that capture the complexity of clinical practice. In this paper, we present a comprehensive multimodal dataset, comprising 8775 dental checkups from 4800 patients collected over eight years (2018-2025), with patients ranging from 10 to 90 years of age. The dataset includes 50000 intraoral images, 8056 radiographs, and detailed textual records, including diagnoses, treatment plans, and follow-up notes. The data were collected under standard ethical guidelines and annotated for benchmarking. To demonstrate its utility, we fine-tuned state-of-the-art large vision-language models, Qwen-VL 3B and 7B, and evaluated them on two tasks: classification of six oro-dental anomalies and generation of complete diagnostic reports from multimodal inputs. We compared the fine-tuned models with their base counterparts and GPT-4o. The fine-tuned models achieved substantial gains over these baselines, validating the dataset and underscoring its effectiveness in advancing AI-driven oro-dental healthcare solutions. The dataset is publicly available, providing an essential resource for future research in AI dentistry. Read More
PECL: A Heterogeneous Parallel Multi-Domain Network for Radar-Based Human Activity Recognitioncs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.05039v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Radar systems are increasingly favored for medical applications because they provide non-intrusive monitoring with high privacy and robustness to lighting conditions. However, existing research typically relies on single-domain radar signals and overlooks the temporal dependencies inherent in human activity, which complicates the classification of similar actions. To address this issue, we designed the Parallel-EfficientNet-CBAM-LSTM (PECL) network to process data in three complementary domains: Range-Time, Doppler-Time, and Range-Doppler. PECL combines a channel-spatial attention module and temporal units to capture more features and dynamic dependencies during action sequences, improving both accuracy and robustness. The experimental results show that PECL achieves an accuracy of 96.16% on the same dataset, outperforming existing methods by at least 4.78%. PECL also performs best in distinguishing between easily confused actions. Despite its strong performance, PECL maintains moderate model complexity, with 23.42M parameters and 1324.82M FLOPs. Its parameter-efficient design further reduces computational cost.
arXiv:2511.05039v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Radar systems are increasingly favored for medical applications because they provide non-intrusive monitoring with high privacy and robustness to lighting conditions. However, existing research typically relies on single-domain radar signals and overlooks the temporal dependencies inherent in human activity, which complicates the classification of similar actions. To address this issue, we designed the Parallel-EfficientNet-CBAM-LSTM (PECL) network to process data in three complementary domains: Range-Time, Doppler-Time, and Range-Doppler. PECL combines a channel-spatial attention module and temporal units to capture more features and dynamic dependencies during action sequences, improving both accuracy and robustness. The experimental results show that PECL achieves an accuracy of 96.16% on the same dataset, outperforming existing methods by at least 4.78%. PECL also performs best in distinguishing between easily confused actions. Despite its strong performance, PECL maintains moderate model complexity, with 23.42M parameters and 1324.82M FLOPs. Its parameter-efficient design further reduces computational cost. Read More
Pluralistic Behavior Suite: Stress-Testing Multi-Turn Adherence to Custom Behavioral Policiescs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.05018v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) are typically aligned to a universal set of safety and usage principles intended for broad public acceptability. Yet, real-world applications of LLMs often take place within organizational ecosystems shaped by distinctive corporate policies, regulatory requirements, use cases, brand guidelines, and ethical commitments. This reality highlights the need for rigorous and comprehensive evaluation of LLMs with pluralistic alignment goals, an alignment paradigm that emphasizes adaptability to diverse user values and needs. In this work, we present PLURALISTIC BEHAVIOR SUITE (PBSUITE), a dynamic evaluation suite designed to systematically assess LLMs’ capacity to adhere to pluralistic alignment specifications in multi-turn, interactive conversations. PBSUITE consists of (1) a diverse dataset of 300 realistic LLM behavioral policies, grounded in 30 industries; and (2) a dynamic evaluation framework for stress-testing model compliance with custom behavioral specifications under adversarial conditions. Using PBSUITE, We find that leading open- and closed-source LLMs maintain robust adherence to behavioral policies in single-turn settings (less than 4% failure rates), but their compliance weakens substantially in multi-turn adversarial interactions (up to 84% failure rates). These findings highlight that existing model alignment and safety moderation methods fall short in coherently enforcing pluralistic behavioral policies in real-world LLM interactions. Our work contributes both the dataset and analytical framework to support future research toward robust and context-aware pluralistic alignment techniques.
arXiv:2511.05018v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) are typically aligned to a universal set of safety and usage principles intended for broad public acceptability. Yet, real-world applications of LLMs often take place within organizational ecosystems shaped by distinctive corporate policies, regulatory requirements, use cases, brand guidelines, and ethical commitments. This reality highlights the need for rigorous and comprehensive evaluation of LLMs with pluralistic alignment goals, an alignment paradigm that emphasizes adaptability to diverse user values and needs. In this work, we present PLURALISTIC BEHAVIOR SUITE (PBSUITE), a dynamic evaluation suite designed to systematically assess LLMs’ capacity to adhere to pluralistic alignment specifications in multi-turn, interactive conversations. PBSUITE consists of (1) a diverse dataset of 300 realistic LLM behavioral policies, grounded in 30 industries; and (2) a dynamic evaluation framework for stress-testing model compliance with custom behavioral specifications under adversarial conditions. Using PBSUITE, We find that leading open- and closed-source LLMs maintain robust adherence to behavioral policies in single-turn settings (less than 4% failure rates), but their compliance weakens substantially in multi-turn adversarial interactions (up to 84% failure rates). These findings highlight that existing model alignment and safety moderation methods fall short in coherently enforcing pluralistic behavioral policies in real-world LLM interactions. Our work contributes both the dataset and analytical framework to support future research toward robust and context-aware pluralistic alignment techniques. Read More
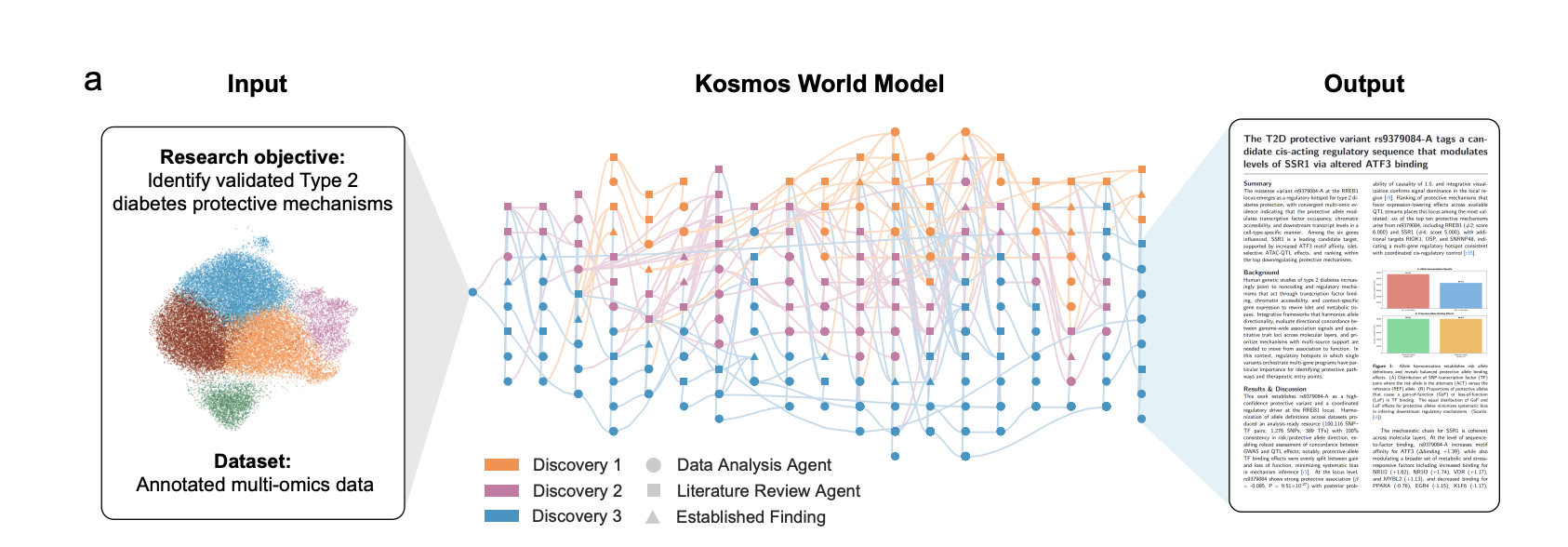
Meet Kosmos: An AI Scientist that Automates Data-Driven DiscoveryMarkTechPost Kosmos, built by Edison Scientific, is an autonomous discovery system that runs long research campaigns on a single goal. Given a dataset and an open ended natural language objective, it performs repeated cycles of data analysis, literature search, and hypothesis generation, then synthesizes the results into a fully cited scientific report. A typical run lasts
The post Meet Kosmos: An AI Scientist that Automates Data-Driven Discovery appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Kosmos, built by Edison Scientific, is an autonomous discovery system that runs long research campaigns on a single goal. Given a dataset and an open ended natural language objective, it performs repeated cycles of data analysis, literature search, and hypothesis generation, then synthesizes the results into a fully cited scientific report. A typical run lasts
The post Meet Kosmos: An AI Scientist that Automates Data-Driven Discovery appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Comparing Memory Systems for LLM Agents: Vector, Graph, and Event LogsMarkTechPost Reliable multi-agent systems are mostly a memory design problem. Once agents call tools, collaborate, and run long workflows, you need explicit mechanisms for what gets stored, how it is retrieved, and how the system behaves when memory is wrong or missing. This article compares 6 memory system patterns commonly used in agent stacks, grouped into
The post Comparing Memory Systems for LLM Agents: Vector, Graph, and Event Logs appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Reliable multi-agent systems are mostly a memory design problem. Once agents call tools, collaborate, and run long workflows, you need explicit mechanisms for what gets stored, how it is retrieved, and how the system behaves when memory is wrong or missing. This article compares 6 memory system patterns commonly used in agent stacks, grouped into
The post Comparing Memory Systems for LLM Agents: Vector, Graph, and Event Logs appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
APP: Accelerated Path Patching with Task-Specific Pruningcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.05442v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Circuit discovery is a key step in many mechanistic interpretability pipelines. Current methods, such as Path Patching, are computationally expensive and have limited in-depth circuit analysis for smaller models. In this study, we propose Accelerated Path Patching (APP), a hybrid approach leveraging our novel contrastive attention head pruning method to drastically reduce the search space of circuit discovery methods. Our Contrastive-FLAP pruning algorithm uses techniques from causal mediation analysis to assign higher pruning scores to task-specific attention heads, leading to higher performing sparse models compared to traditional pruning techniques. Although Contrastive-FLAP is successful at preserving task-specific heads that existing pruning algorithms remove at low sparsity ratios, the circuits found by Contrastive-FLAP alone are too large to satisfy the minimality constraint required in circuit analysis. APP first applies Contrastive-FLAP to reduce the search space on required for circuit discovery algorithms by, on average, 56%. Next, APP, applies traditional Path Patching on the remaining attention heads, leading to a speed up of 59.63%-93.27% compared to Path Patching applied to the dense model. Despite the substantial computational saving that APP provides, circuits obtained from APP exhibit substantial overlap and similar performance to previously established Path Patching circuits
arXiv:2511.05442v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Circuit discovery is a key step in many mechanistic interpretability pipelines. Current methods, such as Path Patching, are computationally expensive and have limited in-depth circuit analysis for smaller models. In this study, we propose Accelerated Path Patching (APP), a hybrid approach leveraging our novel contrastive attention head pruning method to drastically reduce the search space of circuit discovery methods. Our Contrastive-FLAP pruning algorithm uses techniques from causal mediation analysis to assign higher pruning scores to task-specific attention heads, leading to higher performing sparse models compared to traditional pruning techniques. Although Contrastive-FLAP is successful at preserving task-specific heads that existing pruning algorithms remove at low sparsity ratios, the circuits found by Contrastive-FLAP alone are too large to satisfy the minimality constraint required in circuit analysis. APP first applies Contrastive-FLAP to reduce the search space on required for circuit discovery algorithms by, on average, 56%. Next, APP, applies traditional Path Patching on the remaining attention heads, leading to a speed up of 59.63%-93.27% compared to Path Patching applied to the dense model. Despite the substantial computational saving that APP provides, circuits obtained from APP exhibit substantial overlap and similar performance to previously established Path Patching circuits Read More
Rethinking Metrics and Diffusion Architecture for 3D Point Cloud Generationcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.05308v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: As 3D point clouds become a cornerstone of modern technology, the need for sophisticated generative models and reliable evaluation metrics has grown exponentially. In this work, we first expose that some commonly used metrics for evaluating generated point clouds, particularly those based on Chamfer Distance (CD), lack robustness against defects and fail to capture geometric fidelity and local shape consistency when used as quality indicators. We further show that introducing samples alignment prior to distance calculation and replacing CD with Density-Aware Chamfer Distance (DCD) are simple yet essential steps to ensure the consistency and robustness of point cloud generative model evaluation metrics. While existing metrics primarily focus on directly comparing 3D Euclidean coordinates, we present a novel metric, named Surface Normal Concordance (SNC), which approximates surface similarity by comparing estimated point normals. This new metric, when combined with traditional ones, provides a more comprehensive evaluation of the quality of generated samples. Finally, leveraging recent advancements in transformer-based models for point cloud analysis, such as serialized patch attention , we propose a new architecture for generating high-fidelity 3D structures, the Diffusion Point Transformer. We perform extensive experiments and comparisons on the ShapeNet dataset, showing that our model outperforms previous solutions, particularly in terms of quality of generated point clouds, achieving new state-of-the-art. Code available at https://github.com/matteo-bastico/DiffusionPointTransformer.
arXiv:2511.05308v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: As 3D point clouds become a cornerstone of modern technology, the need for sophisticated generative models and reliable evaluation metrics has grown exponentially. In this work, we first expose that some commonly used metrics for evaluating generated point clouds, particularly those based on Chamfer Distance (CD), lack robustness against defects and fail to capture geometric fidelity and local shape consistency when used as quality indicators. We further show that introducing samples alignment prior to distance calculation and replacing CD with Density-Aware Chamfer Distance (DCD) are simple yet essential steps to ensure the consistency and robustness of point cloud generative model evaluation metrics. While existing metrics primarily focus on directly comparing 3D Euclidean coordinates, we present a novel metric, named Surface Normal Concordance (SNC), which approximates surface similarity by comparing estimated point normals. This new metric, when combined with traditional ones, provides a more comprehensive evaluation of the quality of generated samples. Finally, leveraging recent advancements in transformer-based models for point cloud analysis, such as serialized patch attention , we propose a new architecture for generating high-fidelity 3D structures, the Diffusion Point Transformer. We perform extensive experiments and comparisons on the ShapeNet dataset, showing that our model outperforms previous solutions, particularly in terms of quality of generated point clouds, achieving new state-of-the-art. Code available at https://github.com/matteo-bastico/DiffusionPointTransformer. Read More