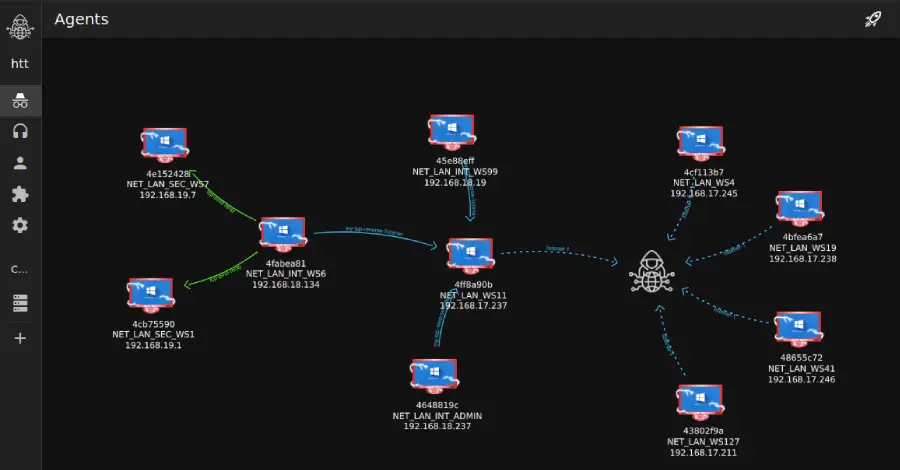
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed details of a cyber attack targeting a major U.S.-based real-estate company that involved the use of a nascent command-and-control (C2) and red teaming framework known as Tuoni. “The campaign leveraged the emerging Tuoni C2 framework, a relatively new, command-and-control (C2) tool (with a free license) that delivers stealthy, in-memory payloads,” Read More
Suspected espionage-driven threat actors from Iran have been observed deploying backdoors like TWOSTROKE and DEEPROOT as part of continued attacks aimed at aerospace, aviation, and defense industries in the Middle East. The activity has been attributed by Google-owned Mandiant to a threat cluster tracked as UNC1549 (aka Nimbus Manticore or Subtle Snail), which was first […]
Identity security fabric (ISF) is a unified architectural framework that brings together disparate identity capabilities. Through ISF, identity governance and administration (IGA), access management (AM), privileged access management (PAM), and identity threat detection and response (ITDR) are all integrated into a single, cohesive control plane. Building on Gartner’s definition of “identity Read More
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a set of seven npm packages published by a single threat actor that leverages a cloaking service called Adspect to differentiate between real victims and security researchers to ultimately redirect them to sketchy crypto-themed sites. The malicious npm packages, published by a threat actor named “dino_reborn” between September and November 2025, […]
Google has released an emergency security update to fix the seventh Chrome zero-day vulnerability exploited in attacks this year. […] Read More
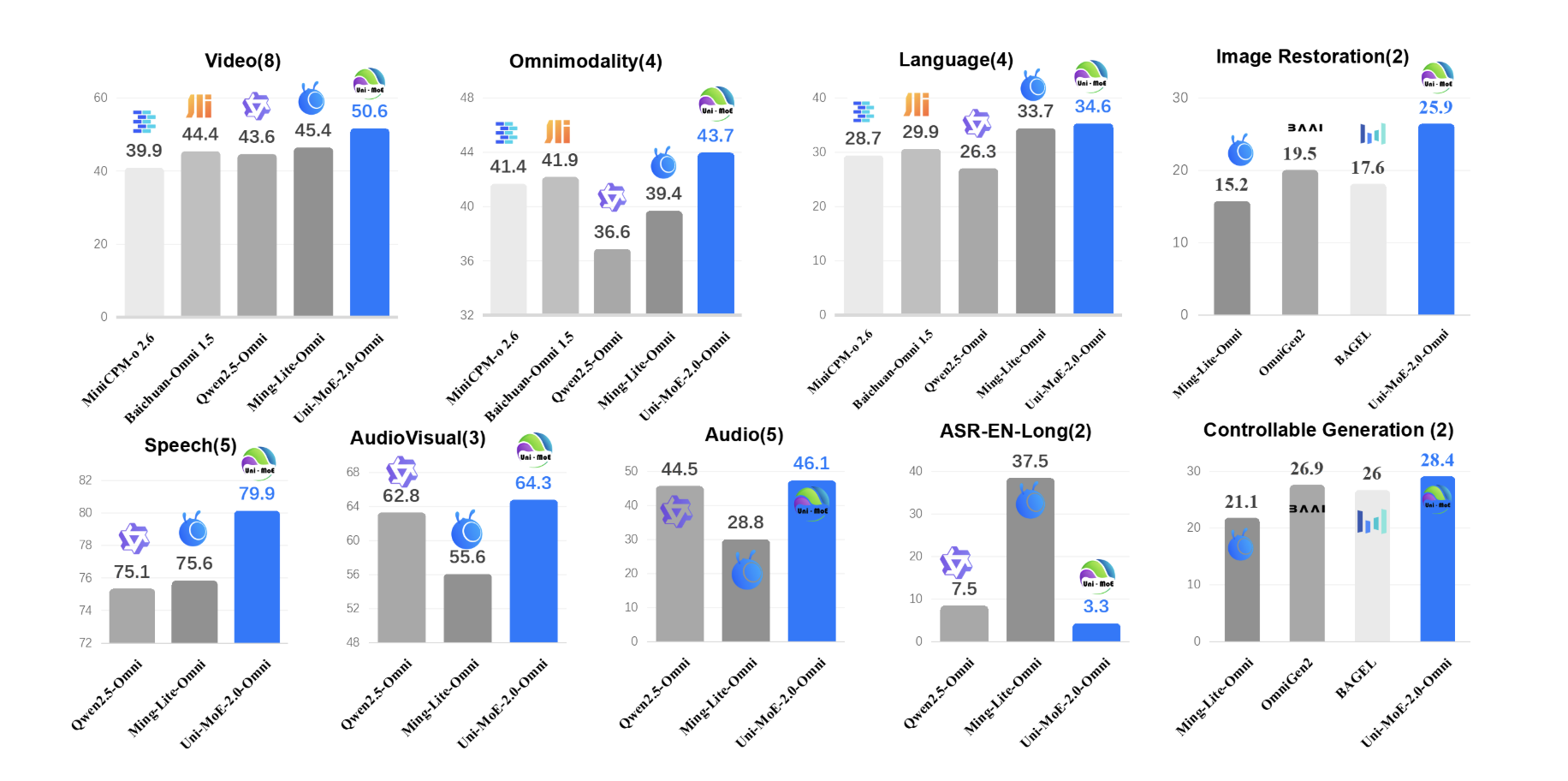
Uni-MoE-2.0-Omni: An Open Qwen2.5-7B Based Omnimodal MoE for Text, Image, Audio and Video UnderstandingMarkTechPost How do you build one open model that can reliably understand text, images, audio and video while still running efficiently? A team of researchers from Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen introduced Uni-MoE-2.0-Omni, a fully open omnimodal large model that pushes Lychee’s Uni-MoE line toward language centric multimodal reasoning. The system is trained from scratch on
The post Uni-MoE-2.0-Omni: An Open Qwen2.5-7B Based Omnimodal MoE for Text, Image, Audio and Video Understanding appeared first on MarkTechPost.
How do you build one open model that can reliably understand text, images, audio and video while still running efficiently? A team of researchers from Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen introduced Uni-MoE-2.0-Omni, a fully open omnimodal large model that pushes Lychee’s Uni-MoE line toward language centric multimodal reasoning. The system is trained from scratch on
The post Uni-MoE-2.0-Omni: An Open Qwen2.5-7B Based Omnimodal MoE for Text, Image, Audio and Video Understanding appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
SC25 showcases the next phase of Dell and NVIDIA’s AI partnershipAI News At SC25, Dell Technologies and NVIDIA introduced new updates to their joint AI platform, aiming to make it easier for organisations to run a wider range of AI workloads, from older models to newer agent-style systems. As more companies scale their AI plans, many run into the same issues. They need to manage a growing
The post SC25 showcases the next phase of Dell and NVIDIA’s AI partnership appeared first on AI News.
At SC25, Dell Technologies and NVIDIA introduced new updates to their joint AI platform, aiming to make it easier for organisations to run a wider range of AI workloads, from older models to newer agent-style systems. As more companies scale their AI plans, many run into the same issues. They need to manage a growing
The post SC25 showcases the next phase of Dell and NVIDIA’s AI partnership appeared first on AI News. Read More
Refine and Align: Confidence Calibration through Multi-Agent Interaction in VQAcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.11169v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: In the context of Visual Question Answering (VQA) and Agentic AI, calibration refers to how closely an AI system’s confidence in its answers reflects their actual correctness. This aspect becomes especially important when such systems operate autonomously and must make decisions under visual uncertainty. While modern VQA systems, powered by advanced vision-language models (VLMs), are increasingly used in high-stakes domains like medical diagnostics and autonomous navigation due to their improved accuracy, the reliability of their confidence estimates remains under-examined. Particularly, these systems often produce overconfident responses. To address this, we introduce AlignVQA, a debate-based multi-agent framework, in which diverse specialized VLM — each following distinct prompting strategies — generate candidate answers and then engage in two-stage interaction: generalist agents critique, refine and aggregate these proposals. This debate process yields confidence estimates that more accurately reflect the model’s true predictive performance. We find that more calibrated specialized agents produce better aligned confidences. Furthermore, we introduce a novel differentiable calibration-aware loss function called aligncal designed to fine-tune the specialized agents by minimizing an upper bound on the calibration error. This objective explicitly improves the fidelity of each agent’s confidence estimates. Empirical results across multiple benchmark VQA datasets substantiate the efficacy of our approach, demonstrating substantial reductions in calibration discrepancies. Furthermore, we propose a novel differentiable calibration-aware loss to fine-tune the specialized agents and improve the quality of their individual confidence estimates based on minimising upper bound calibration error.
arXiv:2511.11169v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: In the context of Visual Question Answering (VQA) and Agentic AI, calibration refers to how closely an AI system’s confidence in its answers reflects their actual correctness. This aspect becomes especially important when such systems operate autonomously and must make decisions under visual uncertainty. While modern VQA systems, powered by advanced vision-language models (VLMs), are increasingly used in high-stakes domains like medical diagnostics and autonomous navigation due to their improved accuracy, the reliability of their confidence estimates remains under-examined. Particularly, these systems often produce overconfident responses. To address this, we introduce AlignVQA, a debate-based multi-agent framework, in which diverse specialized VLM — each following distinct prompting strategies — generate candidate answers and then engage in two-stage interaction: generalist agents critique, refine and aggregate these proposals. This debate process yields confidence estimates that more accurately reflect the model’s true predictive performance. We find that more calibrated specialized agents produce better aligned confidences. Furthermore, we introduce a novel differentiable calibration-aware loss function called aligncal designed to fine-tune the specialized agents by minimizing an upper bound on the calibration error. This objective explicitly improves the fidelity of each agent’s confidence estimates. Empirical results across multiple benchmark VQA datasets substantiate the efficacy of our approach, demonstrating substantial reductions in calibration discrepancies. Furthermore, we propose a novel differentiable calibration-aware loss to fine-tune the specialized agents and improve the quality of their individual confidence estimates based on minimising upper bound calibration error. Read More
Introducing Google’s File Search ToolTowards Data Science The search giant fires its latest salvo against traditional RAG processing.
The post Introducing Google’s File Search Tool appeared first on Towards Data Science.
The search giant fires its latest salvo against traditional RAG processing.
The post Introducing Google’s File Search Tool appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
AI web search risks: Mitigating business data accuracy threatsAI News Over half of us now use AI to search the web, yet the stubbornly low data accuracy of common tools creates new business risks. While generative AI (GenAI) offers undeniable efficiency gains, a new investigation highlights a disparity between user trust and technical accuracy that poses specific risks to corporate compliance, legal standing, and financial
The post AI web search risks: Mitigating business data accuracy threats appeared first on AI News.
Over half of us now use AI to search the web, yet the stubbornly low data accuracy of common tools creates new business risks. While generative AI (GenAI) offers undeniable efficiency gains, a new investigation highlights a disparity between user trust and technical accuracy that poses specific risks to corporate compliance, legal standing, and financial
The post AI web search risks: Mitigating business data accuracy threats appeared first on AI News. Read More