Physical AI in practice: Technical foundations that fuel human-machine interactionsArtificial Intelligence In this post, we explore the complete development lifecycle of physical AI—from data collection and model training to edge deployment—and examine how these intelligent systems learn to understand, reason, and interact with the physical world through continuous feedback loops. We illustrate this workflow through Diligent Robotics’ Moxi, a mobile manipulation robot that has completed over 1.2 million deliveries in hospitals, saving nearly 600,000 hours for clinical staff while transforming healthcare logistics and returning valuable time to patient care.
In this post, we explore the complete development lifecycle of physical AI—from data collection and model training to edge deployment—and examine how these intelligent systems learn to understand, reason, and interact with the physical world through continuous feedback loops. We illustrate this workflow through Diligent Robotics’ Moxi, a mobile manipulation robot that has completed over 1.2 million deliveries in hospitals, saving nearly 600,000 hours for clinical staff while transforming healthcare logistics and returning valuable time to patient care. Read More
HyperPod now supports Multi-Instance GPU to maximize GPU utilization for generative AI tasksArtificial Intelligence In this post, we explore how Amazon SageMaker HyperPod now supports NVIDIA Multi-Instance GPU (MIG) technology, enabling you to partition powerful GPUs into multiple isolated instances for running concurrent workloads like inference, research, and interactive development. By maximizing GPU utilization and reducing wasted resources, MIG helps organizations optimize costs while maintaining performance isolation and predictable quality of service across diverse machine learning tasks.
In this post, we explore how Amazon SageMaker HyperPod now supports NVIDIA Multi-Instance GPU (MIG) technology, enabling you to partition powerful GPUs into multiple isolated instances for running concurrent workloads like inference, research, and interactive development. By maximizing GPU utilization and reducing wasted resources, MIG helps organizations optimize costs while maintaining performance isolation and predictable quality of service across diverse machine learning tasks. Read More
Deploy an AI Analyst in Minutes: Connect Any LLM to Any Data Source with Bag of WordsKDnuggets Deploy an AI analyst fast by connecting any LLM to your SQL database with Bag of Words, allowing immediate, trustworthy data insights via natural language queries.
Deploy an AI analyst fast by connecting any LLM to your SQL database with Bag of Words, allowing immediate, trustworthy data insights via natural language queries. Read More
Adversarial learning breakthrough enables real-time AI securityAI News The ability to execute adversarial learning for real-time AI security offers a decisive advantage over static defence mechanisms. The emergence of AI-driven attacks – utilising reinforcement learning (RL) and Large Language Model (LLM) capabilities – has created a class of “vibe hacking” and adaptive threats that mutate faster than human teams can respond. This represents
The post Adversarial learning breakthrough enables real-time AI security appeared first on AI News.
The ability to execute adversarial learning for real-time AI security offers a decisive advantage over static defence mechanisms. The emergence of AI-driven attacks – utilising reinforcement learning (RL) and Large Language Model (LLM) capabilities – has created a class of “vibe hacking” and adaptive threats that mutate faster than human teams can respond. This represents
The post Adversarial learning breakthrough enables real-time AI security appeared first on AI News. Read More
The actor behind the “Contagious Interview” campaign is continuing to refine its tactics and social engineering scams to wrest credentials from macOS users. Read More
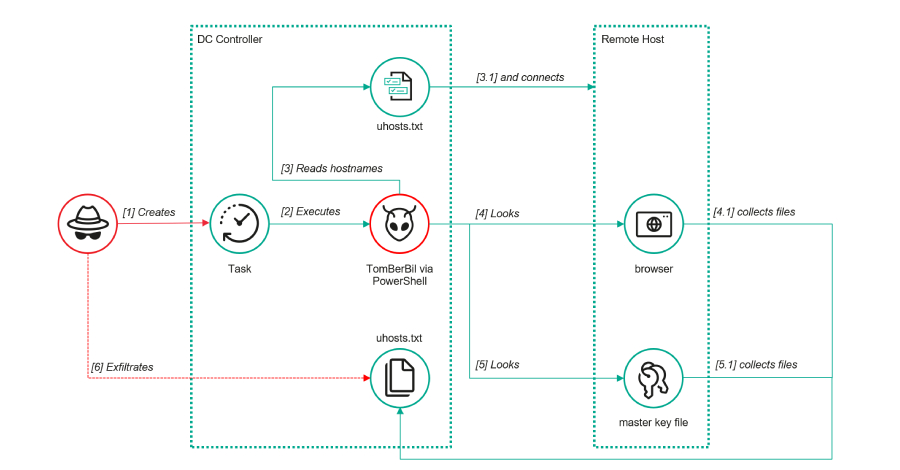
The threat actor known as ToddyCat has been observed adopting new methods to obtain access to corporate email data belonging to target companies, including using a custom tool dubbed TCSectorCopy. “This attack allows them to obtain tokens for the OAuth 2.0 authorization protocol using the user’s browser, which can be used outside the perimeter of […]
Microsoft says it will add a new Teams call handler beginning in January 2026 to reduce launch times and boost call performance for the Windows desktop client. […] Read More
New research reveals that sophisticated phishing attacks consistently bypass traditional enterprise security measures. Read More
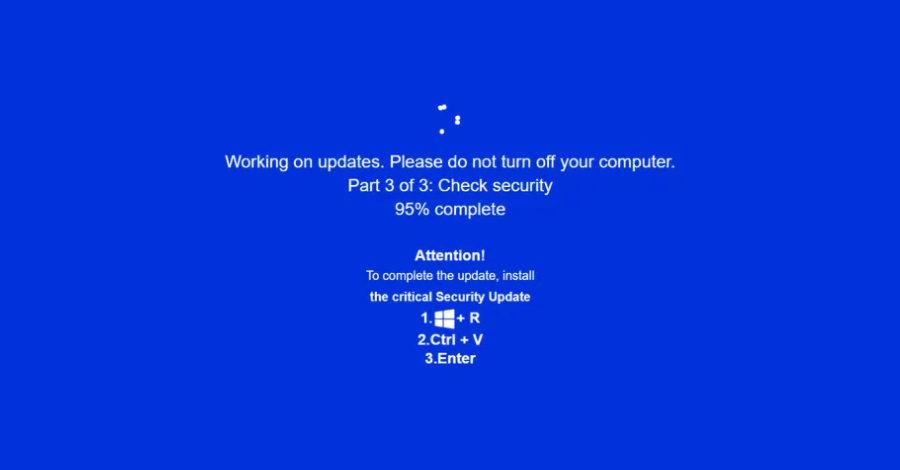
Cybersecurity researchers are calling attention to a new campaign that’s leveraging a combination of ClickFix lures and fake adult websites to deceive users into running malicious commands under the guise of a “critical” Windows security update. “Campaign leverages fake adult websites (xHamster, PornHub clones) as its phishing mechanism, likely distributed via malvertising,” Acronis said in […]
Black Friday 2025 is almost here, and early deals are already live across security software, online courses, system administration tools, antivirus products, and VPN services. These discounts are limited-time offers and vary by provider, so if you see something that fits your needs, it’s best to act while it’s available. […] Read More