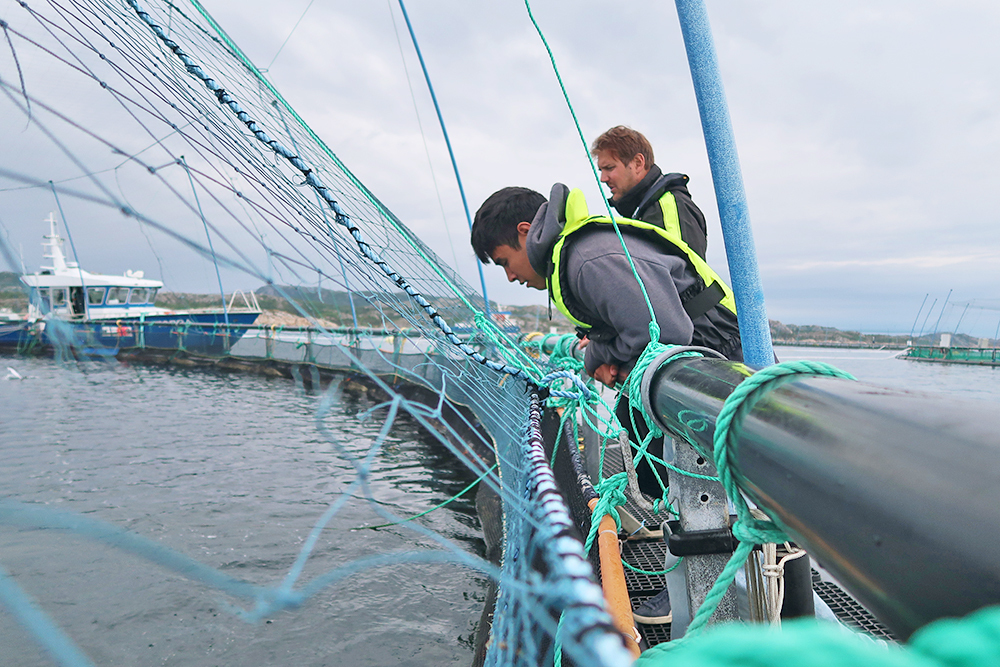
MIT Sea Grant students explore the intersection of technology and offshore aquaculture in NorwayMIT News – Machine learning AquaCulture Shock program, in collaboration with MIT-Scandinavia MISTI, offers international internships for AI and autonomy in aquaculture
AquaCulture Shock program, in collaboration with MIT-Scandinavia MISTI, offers international internships for AI and autonomy in aquaculture Read More
The Machine Learning Lessons I’ve Learned This MonthTowards Data Science Christmas connections, Copilot’s costs, careful (no-)choices
The post The Machine Learning Lessons I’ve Learned This Month appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Christmas connections, Copilot’s costs, careful (no-)choices
The post The Machine Learning Lessons I’ve Learned This Month appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
The Machine Learning “Advent Calendar” Day 1: k-NN Regressor in ExcelTowards Data Science This first day of the Advent Calendar introduces the k-NN regressor, the simplest distance-based model. Using Excel, we explore how predictions rely entirely on the closest observations, why feature scaling matters, and how heterogeneous variables can make distances meaningless. Through examples with continuous and categorical features, including the California Housing and Diamonds datasets, we see the strengths and limitations of k-NN, and why defining the right distance is essential to reflect real-world structure.
The post The Machine Learning “Advent Calendar” Day 1: k-NN Regressor in Excel appeared first on Towards Data Science.
This first day of the Advent Calendar introduces the k-NN regressor, the simplest distance-based model. Using Excel, we explore how predictions rely entirely on the closest observations, why feature scaling matters, and how heterogeneous variables can make distances meaningless. Through examples with continuous and categorical features, including the California Housing and Diamonds datasets, we see the strengths and limitations of k-NN, and why defining the right distance is essential to reflect real-world structure.
The post The Machine Learning “Advent Calendar” Day 1: k-NN Regressor in Excel appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
The Problem with AI Browsers: Security Flaws and the End of PrivacyTowards Data Science How Atlas and most current AI-powered browsers fail on three aspects: privacy, security, and censorship
The post The Problem with AI Browsers: Security Flaws and the End of Privacy appeared first on Towards Data Science.
How Atlas and most current AI-powered browsers fail on three aspects: privacy, security, and censorship
The post The Problem with AI Browsers: Security Flaws and the End of Privacy appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
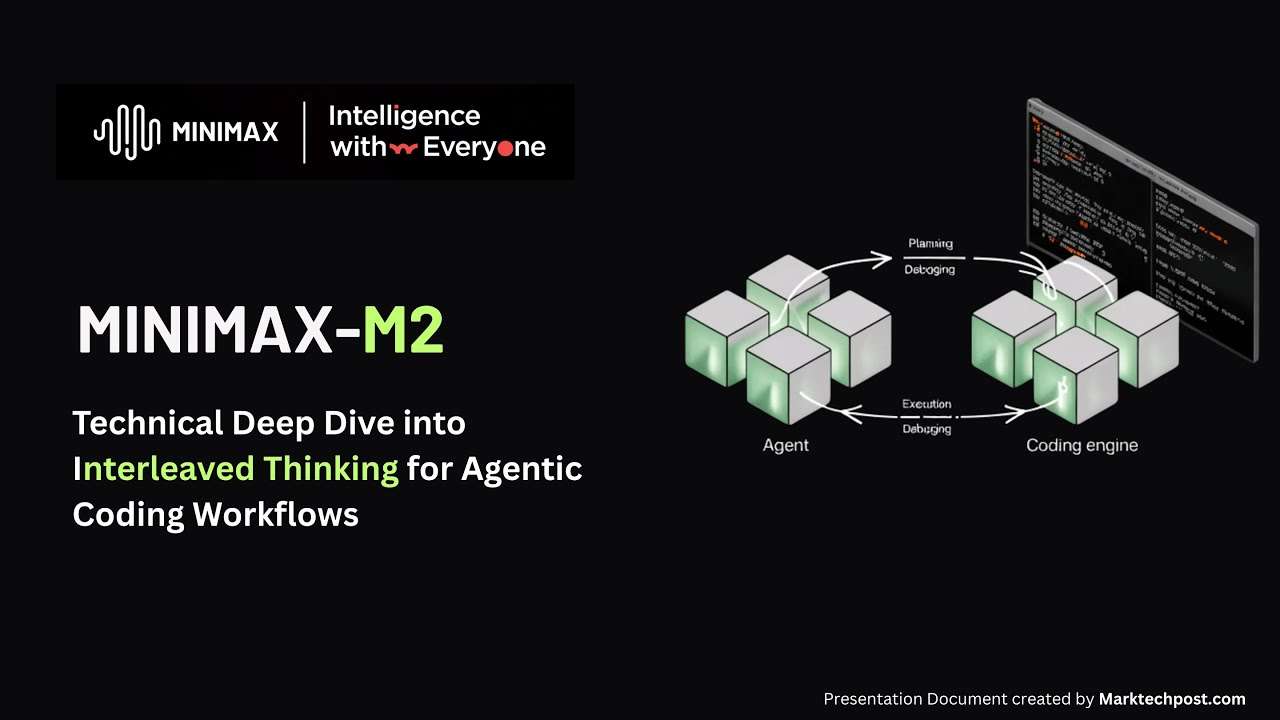
MiniMax-M2: Technical Deep Dive into Interleaved Thinking for Agentic Coding WorkflowsMarkTechPost The AI coding landscape just got a massive shake-up. If you’ve been relying on Claude 3.5 Sonnet or GPT-4o for your dev workflows, you know the pain: great performance often comes with a bill that makes your wallet weep, or latency that breaks your flow.This article provides a technical overview of MiniMax-M2, focusing on its
The post MiniMax-M2: Technical Deep Dive into Interleaved Thinking for Agentic Coding Workflows appeared first on MarkTechPost.
The AI coding landscape just got a massive shake-up. If you’ve been relying on Claude 3.5 Sonnet or GPT-4o for your dev workflows, you know the pain: great performance often comes with a bill that makes your wallet weep, or latency that breaks your flow.This article provides a technical overview of MiniMax-M2, focusing on its
The post MiniMax-M2: Technical Deep Dive into Interleaved Thinking for Agentic Coding Workflows appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Building a Simple Data Quality DSL in PythonKDnuggets Build a lightweight Python DSL to define and check data quality rules in a clear, expressive way. Turn complex validation logic into simple, reusable configurations that anyone on your data team can understand.
Build a lightweight Python DSL to define and check data quality rules in a clear, expressive way. Turn complex validation logic into simple, reusable configurations that anyone on your data team can understand. Read More
Agentic AI autonomy grows in North American enterprisesAI News North American enterprises are now actively deploying agentic AI systems intended to reason, adapt, and act with complete autonomy. Data from Digitate’s three-year global programme indicates that, while adoption is universal across the board, regional maturity paths are diverging. North American firms are scaling toward full autonomy, whereas their European counterparts are prioritising governance frameworks
The post Agentic AI autonomy grows in North American enterprises appeared first on AI News.
North American enterprises are now actively deploying agentic AI systems intended to reason, adapt, and act with complete autonomy. Data from Digitate’s three-year global programme indicates that, while adoption is universal across the board, regional maturity paths are diverging. North American firms are scaling toward full autonomy, whereas their European counterparts are prioritising governance frameworks
The post Agentic AI autonomy grows in North American enterprises appeared first on AI News. Read More
Learning, Hacking, and Shipping MLTowards Data Science Vyacheslav Efimov on AI hackathons, data science roadmaps, and how AI meaningfully changed day-to-day ML Engineer work
The post Learning, Hacking, and Shipping ML appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Vyacheslav Efimov on AI hackathons, data science roadmaps, and how AI meaningfully changed day-to-day ML Engineer work
The post Learning, Hacking, and Shipping ML appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
Context Engineering is the New Prompt EngineeringKDnuggets It’s not about clever wording anymore. It’s about designing environments where AI can think with depth, consistency, and purpose.
It’s not about clever wording anymore. It’s about designing environments where AI can think with depth, consistency, and purpose. Read More
Funding grants for new research into AI and mental healthOpenAI News OpenAI is awarding up to $2 million in grants for research at the intersection of AI and mental health. The program supports projects that study real-world risks, benefits, and applications to improve safety and well-being.
OpenAI is awarding up to $2 million in grants for research at the intersection of AI and mental health. The program supports projects that study real-world risks, benefits, and applications to improve safety and well-being. Read More