Generating Data-Driven Reasoning Rubrics for Domain-Adaptive Reward Modeling AI updates on arXiv.org
Generating Data-Driven Reasoning Rubrics for Domain-Adaptive Reward Modelingcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2602.06795v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: An impediment to using Large Language Models (LLMs) for reasoning output verification is that LLMs struggle to reliably identify errors in thinking traces, particularly in long outputs, domains requiring expert knowledge, and problems without verifiable rewards. We propose a data-driven approach to automatically construct highly granular reasoning error taxonomies to enhance LLM-driven error detection on unseen reasoning traces. Our findings indicate that classification approaches that leverage these error taxonomies, or “rubrics”, demonstrate strong error identification compared to baseline methods in technical domains like coding, math, and chemical engineering. These rubrics can be used to build stronger LLM-as-judge reward functions for reasoning model training via reinforcement learning. Experimental results show that these rewards have the potential to improve models’ task accuracy on difficult domains over models trained by general LLMs-as-judges by +45%, and approach performance of models trained by verifiable rewards while using as little as 20% as many gold labels. Through our approach, we extend the usage of reward rubrics from assessing qualitative model behavior to assessing quantitative model correctness on tasks typically learned via RLVR rewards. This extension opens the door for teaching models to solve complex technical problems without a full dataset of gold labels, which are often highly costly to procure.
arXiv:2602.06795v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: An impediment to using Large Language Models (LLMs) for reasoning output verification is that LLMs struggle to reliably identify errors in thinking traces, particularly in long outputs, domains requiring expert knowledge, and problems without verifiable rewards. We propose a data-driven approach to automatically construct highly granular reasoning error taxonomies to enhance LLM-driven error detection on unseen reasoning traces. Our findings indicate that classification approaches that leverage these error taxonomies, or “rubrics”, demonstrate strong error identification compared to baseline methods in technical domains like coding, math, and chemical engineering. These rubrics can be used to build stronger LLM-as-judge reward functions for reasoning model training via reinforcement learning. Experimental results show that these rewards have the potential to improve models’ task accuracy on difficult domains over models trained by general LLMs-as-judges by +45%, and approach performance of models trained by verifiable rewards while using as little as 20% as many gold labels. Through our approach, we extend the usage of reward rubrics from assessing qualitative model behavior to assessing quantitative model correctness on tasks typically learned via RLVR rewards. This extension opens the door for teaching models to solve complex technical problems without a full dataset of gold labels, which are often highly costly to procure. Read More
A Coding Implementation to Establish Rigorous Prompt Versioning and Regression Testing Workflows for Large Language Models using MLflowMarkTechPost In this tutorial, we show how we treat prompts as first-class, versioned artifacts and apply rigorous regression testing to large language model behavior using MLflow. We design an evaluation pipeline that logs prompt versions, prompt diffs, model outputs, and multiple quality metrics in a fully reproducible manner. By combining classical text metrics with semantic similarity
The post A Coding Implementation to Establish Rigorous Prompt Versioning and Regression Testing Workflows for Large Language Models using MLflow appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In this tutorial, we show how we treat prompts as first-class, versioned artifacts and apply rigorous regression testing to large language model behavior using MLflow. We design an evaluation pipeline that logs prompt versions, prompt diffs, model outputs, and multiple quality metrics in a fully reproducible manner. By combining classical text metrics with semantic similarity
The post A Coding Implementation to Establish Rigorous Prompt Versioning and Regression Testing Workflows for Large Language Models using MLflow appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Men charged in FanDuel scheme fueled by thousands of stolen identities BleepingComputerSergiu Gatlan
Two Connecticut men face federal charges for allegedly defrauding FanDuel and other online gambling sites of $3 million over several years using the stolen identities of approximately 3,000 victims. […] Read More
Why do SOC teams keep burning out and missing SLAs even after spending big on security tools? Routine triage piles up, senior specialists get dragged into basic validation, and MTTR climbs, while stealthy threats still find room to slip through. Top CISOs have realized the solution isn’t hiring more people or stacking yet another tool […]
Cybersecurity researchers have called attention to a “massive campaign” that has systematically targeted cloud native environments to set up malicious infrastructure for follow-on exploitation. The activity, observed around December 25, 2025, and described as “worm-driven,” leveraged exposed Docker APIs, Kubernetes clusters, Ray dashboards, and Redis servers, along with the recently disclosed Read More
BeyondTrust has released updates to address a critical security flaw impacting Remote Support (RS) and Privileged Remote Access (PRA) products that, if successfully exploited, could result in remote code execution. “BeyondTrust Remote Support (RS) and certain older versions of Privileged Remote Access (PRA) contain a critical pre-authentication remote code execution vulnerability,” the company Read More
How to Design Production-Grade Mock Data Pipelines Using Polyfactory with Dataclasses, Pydantic, Attrs, and Nested ModelsMarkTechPost In this tutorial, we walk through an advanced, end-to-end exploration of Polyfactory, focusing on how we can generate rich, realistic mock data directly from Python type hints. We start by setting up the environment and progressively build factories for data classes, Pydantic models, and attrs-based classes, while demonstrating customization, overrides, calculated fields, and the generation
The post How to Design Production-Grade Mock Data Pipelines Using Polyfactory with Dataclasses, Pydantic, Attrs, and Nested Models appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In this tutorial, we walk through an advanced, end-to-end exploration of Polyfactory, focusing on how we can generate rich, realistic mock data directly from Python type hints. We start by setting up the environment and progressively build factories for data classes, Pydantic models, and attrs-based classes, while demonstrating customization, overrides, calculated fields, and the generation
The post How to Design Production-Grade Mock Data Pipelines Using Polyfactory with Dataclasses, Pydantic, Attrs, and Nested Models appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
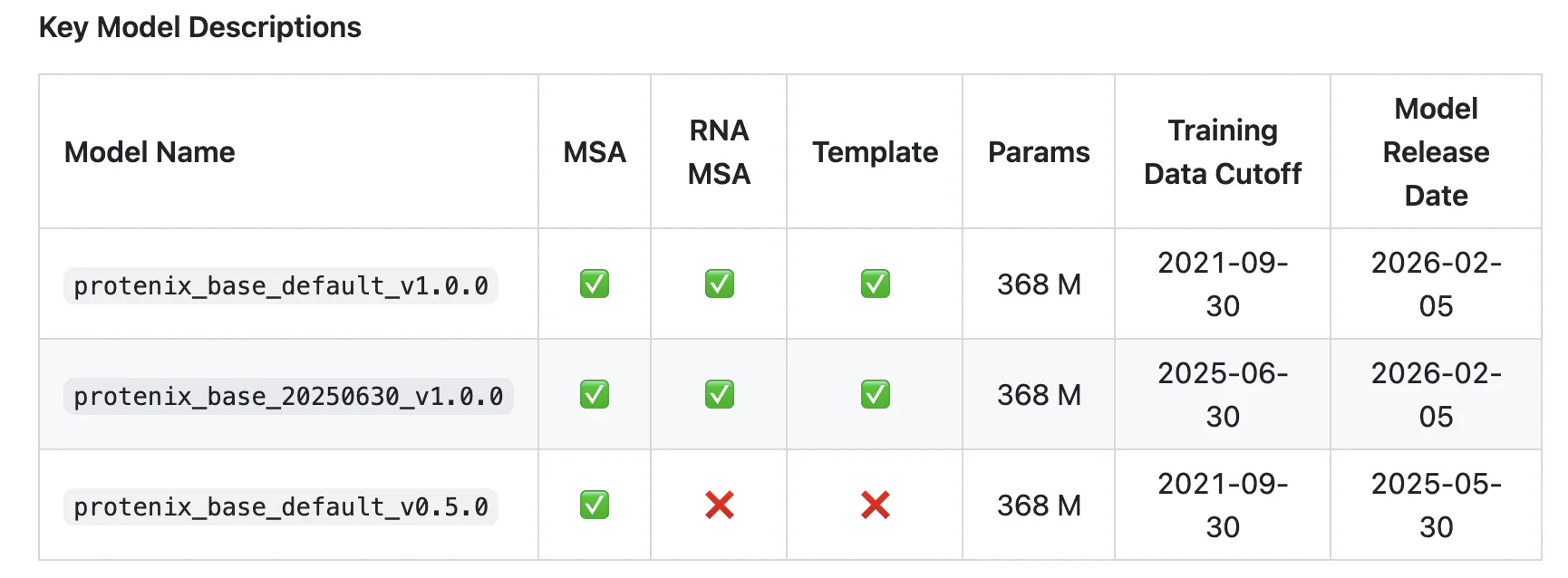
ByteDance Releases Protenix-v1: A New Open-Source Model Achieving AF3-Level Performance in Biomolecular Structure PredictionMarkTechPost How close can an open model get to AlphaFold3-level accuracy when it matches training data, model scale and inference budget? ByteDance has introduced Protenix-v1, a comprehensive AlphaFold3 (AF3) reproduction for biomolecular structure prediction, released with code and model parameters under Apache 2.0. The model targets AF3-level performance across protein, DNA, RNA and ligand structures while
The post ByteDance Releases Protenix-v1: A New Open-Source Model Achieving AF3-Level Performance in Biomolecular Structure Prediction appeared first on MarkTechPost.
How close can an open model get to AlphaFold3-level accuracy when it matches training data, model scale and inference budget? ByteDance has introduced Protenix-v1, a comprehensive AlphaFold3 (AF3) reproduction for biomolecular structure prediction, released with code and model parameters under Apache 2.0. The model targets AF3-level performance across protein, DNA, RNA and ligand structures while
The post ByteDance Releases Protenix-v1: A New Open-Source Model Achieving AF3-Level Performance in Biomolecular Structure Prediction appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
OpenClaw (formerly Moltbot and Clawdbot) has announced that it’s partnering with Google-owned VirusTotal to scan skills that are being uploaded to ClawHub, its skill marketplace, as part of broader efforts to bolster the security of the agentic ecosystem. “All skills published to ClawHub are now scanned using VirusTotal’s threat intelligence, including their new Code Insight […]
A new open-source and cross-platform tool called Tirith can detect homoglyph attacks over command-line environments by analyzing URLs in typed commands and stopping their execution. […] Read More