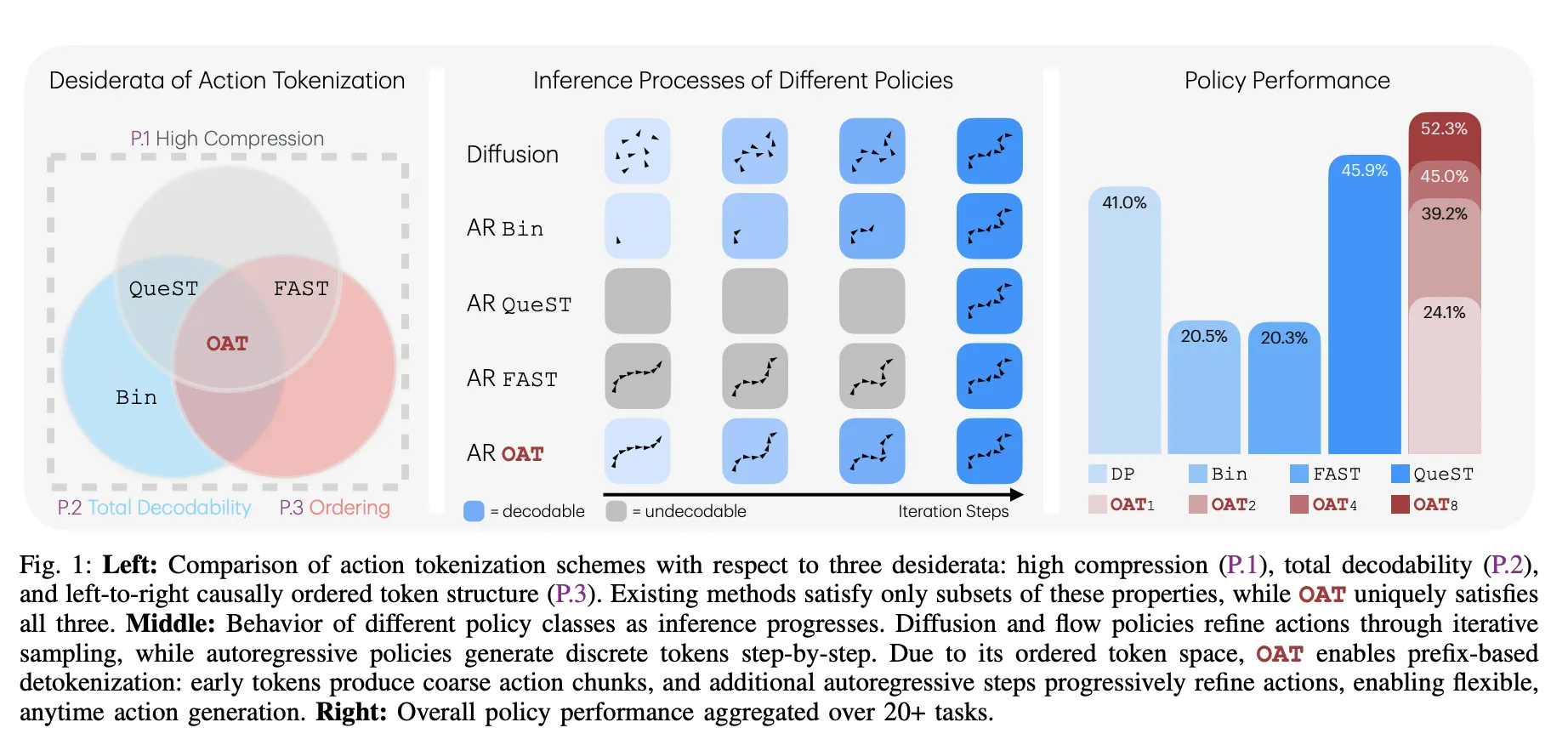
Meet OAT: The New Action Tokenizer Bringing LLM-Style Scaling and Flexible, Anytime Inference to the Robotics WorldMarkTechPost Robots are entering their GPT-3 era. For years, researchers have tried to train robots using the same autoregressive (AR) models that power large language models (LLMs). If a model can predict the next word in a sentence, it should be able to predict the next move for a robotic arm. However, a technical wall has
The post Meet OAT: The New Action Tokenizer Bringing LLM-Style Scaling and Flexible, Anytime Inference to the Robotics World appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Robots are entering their GPT-3 era. For years, researchers have tried to train robots using the same autoregressive (AR) models that power large language models (LLMs). If a model can predict the next word in a sentence, it should be able to predict the next move for a robotic arm. However, a technical wall has
The post Meet OAT: The New Action Tokenizer Bringing LLM-Style Scaling and Flexible, Anytime Inference to the Robotics World appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Cryptocurrency markets a testbed for AI forecasting modelsAI News Cryptocurrency markets have become a high-speed playground where developers optimise the next generation of predictive software. Using real-time data flows and decentralised platforms, scientists develop prediction models that can extend the scope of traditional finance. The digital asset landscape offers an unparalleled environment for machine learning. When you track cryptocurrency prices today, you are observing
The post Cryptocurrency markets a testbed for AI forecasting models appeared first on AI News.
Cryptocurrency markets have become a high-speed playground where developers optimise the next generation of predictive software. Using real-time data flows and decentralised platforms, scientists develop prediction models that can extend the scope of traditional finance. The digital asset landscape offers an unparalleled environment for machine learning. When you track cryptocurrency prices today, you are observing
The post Cryptocurrency markets a testbed for AI forecasting models appeared first on AI News. Read More
Exclusive: Why are Chinese AI models dominating open-source as Western labs step back?AI News Because Western AI labs won’t—or can’t—anymore. As OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google face mounting pressure to restrict their most powerful models, Chinese developers have filled the open-source void with AI explicitly built for what operators need: powerful models that run on commodity hardware. A new security study reveals just how thoroughly Chinese AI has captured this space. Research published by SentinelOne
The post Exclusive: Why are Chinese AI models dominating open-source as Western labs step back? appeared first on AI News.
Because Western AI labs won’t—or can’t—anymore. As OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google face mounting pressure to restrict their most powerful models, Chinese developers have filled the open-source void with AI explicitly built for what operators need: powerful models that run on commodity hardware. A new security study reveals just how thoroughly Chinese AI has captured this space. Research published by SentinelOne
The post Exclusive: Why are Chinese AI models dominating open-source as Western labs step back? appeared first on AI News. Read More
What AI can (and can’t) tell us about XRP in ETF-driven marketsAI News For a long time, cryptocurrency prices moved quickly. A headline would hit, sentiment would spike, and charts would react almost immediately. That pattern no longer holds. Today’s market is slow, heavier than before, and shaped by forces that do not always announce themselves clearly. Capital allocation, ETF mechanics, and macro positioning now influence price behaviour
The post What AI can (and can’t) tell us about XRP in ETF-driven markets appeared first on AI News.
For a long time, cryptocurrency prices moved quickly. A headline would hit, sentiment would spike, and charts would react almost immediately. That pattern no longer holds. Today’s market is slow, heavier than before, and shaped by forces that do not always announce themselves clearly. Capital allocation, ETF mechanics, and macro positioning now influence price behaviour
The post What AI can (and can’t) tell us about XRP in ETF-driven markets appeared first on AI News. Read More
The threat actor known as Bloody Wolf has been linked to a campaign targeting Uzbekistan and Russia to infect systems with a remote access trojan known as NetSupport RAT. Cybersecurity vendor Kaspersky is tracking the activity under the moniker Stan Ghouls. The threat actor is known to be active since at least 2023, orchestrating spear-phishing […]
The European Commission is investigating a breach after finding evidence that its mobile device management platform was hacked. […] Read More
Microsoft is investigating an ongoing Exchange Online issue that mistakenly flags legitimate emails as phishing and quarantines them. […] Read More
Efficient Perplexity Bound and Ratio Matching in Discrete Diffusion Language Modelscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2507.04341v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: While continuous diffusion models excel in modeling continuous distributions, their application to categorical data has been less effective. Recent work has shown that ratio-matching through score-entropy within a continuous-time discrete Markov chain (CTMC) framework serves as a competitive alternative to autoregressive models in language modeling. To enhance this framework, we first introduce three new theorems concerning the KL divergence between the data and learned distribution. Our results serve as the discrete counterpart to those established for continuous diffusion models and allow us to derive an improved upper bound of the perplexity. Second, we empirically show that ratio-matching performed by minimizing the denoising cross-entropy between the clean and corrupted data enables models to outperform those utilizing score-entropy with up to 10% lower perplexity/generative-perplexity, and 15% faster training steps. To further support our findings, we introduce and evaluate a novel CTMC transition-rate matrix that allows prediction refinement, and derive the analytic expression for its matrix exponential which facilitates the computation of conditional ratios thus enabling efficient training and generation.
arXiv:2507.04341v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: While continuous diffusion models excel in modeling continuous distributions, their application to categorical data has been less effective. Recent work has shown that ratio-matching through score-entropy within a continuous-time discrete Markov chain (CTMC) framework serves as a competitive alternative to autoregressive models in language modeling. To enhance this framework, we first introduce three new theorems concerning the KL divergence between the data and learned distribution. Our results serve as the discrete counterpart to those established for continuous diffusion models and allow us to derive an improved upper bound of the perplexity. Second, we empirically show that ratio-matching performed by minimizing the denoising cross-entropy between the clean and corrupted data enables models to outperform those utilizing score-entropy with up to 10% lower perplexity/generative-perplexity, and 15% faster training steps. To further support our findings, we introduce and evaluate a novel CTMC transition-rate matrix that allows prediction refinement, and derive the analytic expression for its matrix exponential which facilitates the computation of conditional ratios thus enabling efficient training and generation. Read More
Unlocking Noisy Real-World Corpora for Foundation Model Pre-Training via Quality-Aware Tokenizationcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2602.06394v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Current tokenization methods process sequential data without accounting for signal quality, limiting their effectiveness on noisy real-world corpora. We present QA-Token (Quality-Aware Tokenization), which incorporates data reliability directly into vocabulary construction. We make three key contributions: (i) a bilevel optimization formulation that jointly optimizes vocabulary construction and downstream performance, (ii) a reinforcement learning approach that learns merge policies through quality-aware rewards with convergence guarantees, and (iii) an adaptive parameter learning mechanism via Gumbel-Softmax relaxation for end-to-end optimization. Our experimental evaluation demonstrates consistent improvements: genomics (6.7 percentage point F1 gain in variant calling over BPE), finance (30% Sharpe ratio improvement). At foundation scale, we tokenize a pretraining corpus comprising 1.7 trillion base-pairs and achieve state-of-the-art pathogen detection (94.53 MCC) while reducing token count by 15%. We unlock noisy real-world corpora, spanning petabases of genomic sequences and terabytes of financial time series, for foundation model training with zero inference overhead.
arXiv:2602.06394v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Current tokenization methods process sequential data without accounting for signal quality, limiting their effectiveness on noisy real-world corpora. We present QA-Token (Quality-Aware Tokenization), which incorporates data reliability directly into vocabulary construction. We make three key contributions: (i) a bilevel optimization formulation that jointly optimizes vocabulary construction and downstream performance, (ii) a reinforcement learning approach that learns merge policies through quality-aware rewards with convergence guarantees, and (iii) an adaptive parameter learning mechanism via Gumbel-Softmax relaxation for end-to-end optimization. Our experimental evaluation demonstrates consistent improvements: genomics (6.7 percentage point F1 gain in variant calling over BPE), finance (30% Sharpe ratio improvement). At foundation scale, we tokenize a pretraining corpus comprising 1.7 trillion base-pairs and achieve state-of-the-art pathogen detection (94.53 MCC) while reducing token count by 15%. We unlock noisy real-world corpora, spanning petabases of genomic sequences and terabytes of financial time series, for foundation model training with zero inference overhead. Read More
Malicious Agent Skills in the Wild: A Large-Scale Security Empirical Studycs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2602.06547v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Third-party agent skills extend LLM-based agents with instruction files and executable code that run on users’ machines. Skills execute with user privileges and are distributed through community registries with minimal vetting, but no ground-truth dataset exists to characterize the resulting threats. We construct the first labeled dataset of malicious agent skills by behaviorally verifying 98,380 skills from two community registries, confirming 157 malicious skills with 632 vulnerabilities. These attacks are not incidental. Malicious skills average 4.03 vulnerabilities across a median of three kill chain phases, and the ecosystem has split into two archetypes: Data Thieves that exfiltrate credentials through supply chain techniques, and Agent Hijackers that subvert agent decision-making through instruction manipulation. A single actor accounts for 54.1% of confirmed cases through templated brand impersonation. Shadow features, capabilities absent from public documentation, appear in 0% of basic attacks but 100% of advanced ones; several skills go further by exploiting the AI platform’s own hook system and permission flags. Responsible disclosure led to 93.6% removal within 30 days. We release the dataset and analysis pipeline to support future work on agent skill security.
arXiv:2602.06547v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Third-party agent skills extend LLM-based agents with instruction files and executable code that run on users’ machines. Skills execute with user privileges and are distributed through community registries with minimal vetting, but no ground-truth dataset exists to characterize the resulting threats. We construct the first labeled dataset of malicious agent skills by behaviorally verifying 98,380 skills from two community registries, confirming 157 malicious skills with 632 vulnerabilities. These attacks are not incidental. Malicious skills average 4.03 vulnerabilities across a median of three kill chain phases, and the ecosystem has split into two archetypes: Data Thieves that exfiltrate credentials through supply chain techniques, and Agent Hijackers that subvert agent decision-making through instruction manipulation. A single actor accounts for 54.1% of confirmed cases through templated brand impersonation. Shadow features, capabilities absent from public documentation, appear in 0% of basic attacks but 100% of advanced ones; several skills go further by exploiting the AI platform’s own hook system and permission flags. Responsible disclosure led to 93.6% removal within 30 days. We release the dataset and analysis pipeline to support future work on agent skill security. Read More