Versioning and Testing Data Solutions: Applying CI and Unit Tests on Interview-style QueriesKDnuggets Learn how to apply unit testing, version control, and continuous integration to data analysis scripts using Python and GitHub Actions.
Learn how to apply unit testing, version control, and continuous integration to data analysis scripts using Python and GitHub Actions. Read More
Not All RecSys Problems Are Created EqualTowards Data Science How baseline strength, churn, and subjectivity determine complexity
The post Not All RecSys Problems Are Created Equal appeared first on Towards Data Science.
How baseline strength, churn, and subjectivity determine complexity
The post Not All RecSys Problems Are Created Equal appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
Building an AI Agent to Detect and Handle Anomalies in Time-Series DataTowards Data Science Combining statistical detection with agentic decision-making
The post Building an AI Agent to Detect and Handle Anomalies in Time-Series Data appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Combining statistical detection with agentic decision-making
The post Building an AI Agent to Detect and Handle Anomalies in Time-Series Data appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
How LinqAlpha assesses investment theses using Devil’s Advocate on Amazon BedrockArtificial Intelligence LinqAlpha is a Boston-based multi-agent AI system built specifically for institutional investors. The system supports and streamlines agentic workflows across company screening, primer generation, stock price catalyst mapping, and now, pressure-testing investment ideas through a new AI agent called Devil’s Advocate. In this post, we share how LinqAlpha uses Amazon Bedrock to build and scale Devil’s Advocate.
LinqAlpha is a Boston-based multi-agent AI system built specifically for institutional investors. The system supports and streamlines agentic workflows across company screening, primer generation, stock price catalyst mapping, and now, pressure-testing investment ideas through a new AI agent called Devil’s Advocate. In this post, we share how LinqAlpha uses Amazon Bedrock to build and scale Devil’s Advocate. Read More
Swann provides Generative AI to millions of IoT Devices using Amazon Bedrock Artificial Intelligence
Swann provides Generative AI to millions of IoT Devices using Amazon BedrockArtificial Intelligence This post shows you how to implement intelligent notification filtering using Amazon Bedrock and its gen-AI capabilities. You’ll learn model selection strategies, cost optimization techniques, and architectural patterns for deploying gen-AI at IoT scale, based on Swann Communications deployment across millions of devices.
This post shows you how to implement intelligent notification filtering using Amazon Bedrock and its gen-AI capabilities. You’ll learn model selection strategies, cost optimization techniques, and architectural patterns for deploying gen-AI at IoT scale, based on Swann Communications deployment across millions of devices. Read More
Mastering Amazon Bedrock throttling and service availability: A comprehensive guideArtificial Intelligence This post shows you how to implement robust error handling strategies that can help improve application reliability and user experience when using Amazon Bedrock. We’ll dive deep into strategies for optimizing performances for the application with these errors. Whether this is for a fairly new application or matured AI application, in this post you will be able to find the practical guidelines to operate with on these errors.
This post shows you how to implement robust error handling strategies that can help improve application reliability and user experience when using Amazon Bedrock. We’ll dive deep into strategies for optimizing performances for the application with these errors. Whether this is for a fairly new application or matured AI application, in this post you will be able to find the practical guidelines to operate with on these errors. Read More
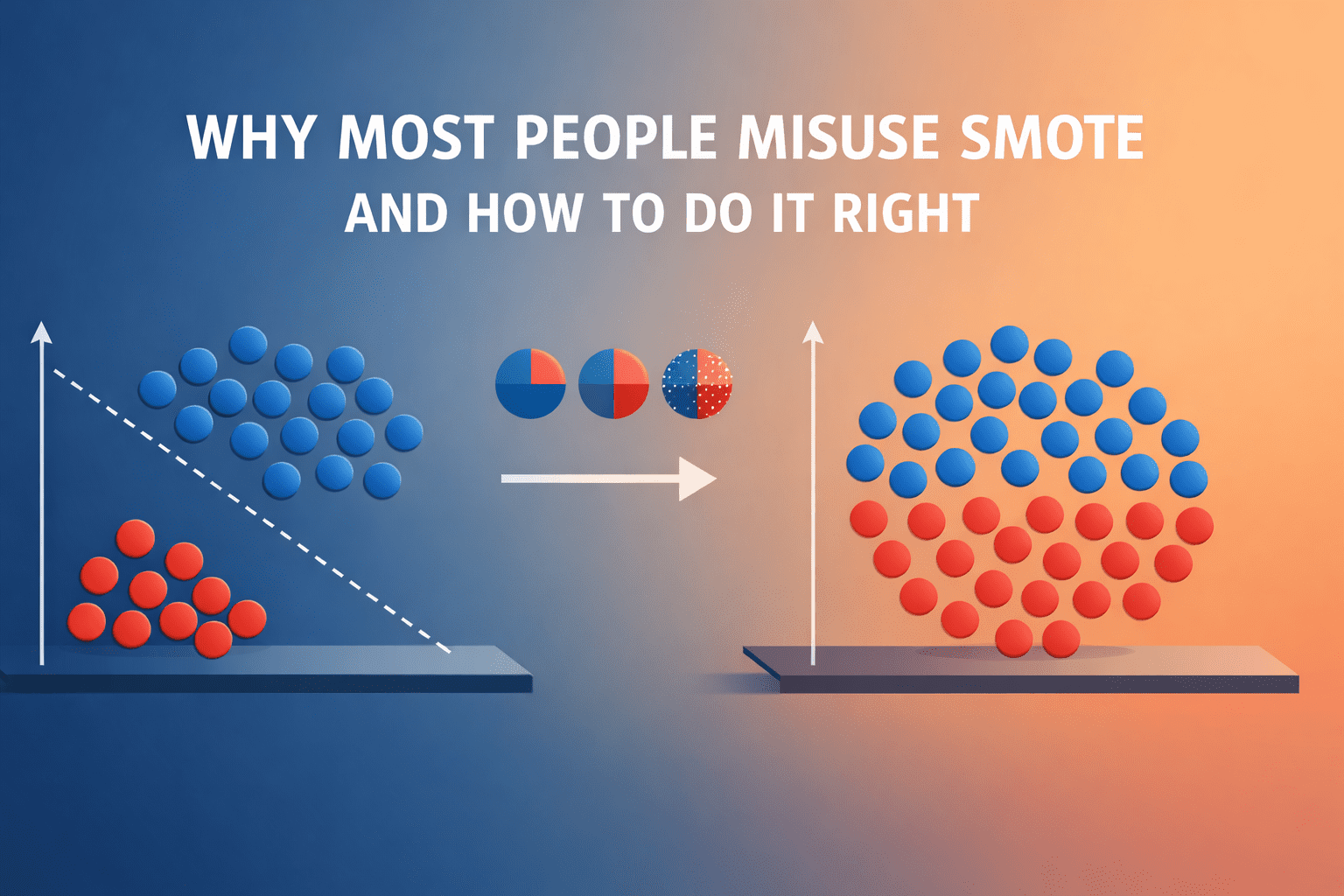
Why Most People Misuse SMOTE, And How to Do It RightKDnuggets Keys for oversampling your data for addressing class imbalance issues, the right way.
Keys for oversampling your data for addressing class imbalance issues, the right way. Read More
How to Build an Atomic-Agents RAG Pipeline with Typed Schemas, Dynamic Context Injection, and Agent ChainingMarkTechPost In this tutorial, we build an advanced, end-to-end learning pipeline around Atomic-Agents by wiring together typed agent interfaces, structured prompting, and a compact retrieval layer that grounds outputs in real project documentation. Also, we demonstrate how to plan retrieval, retrieve relevant context, inject it dynamically into an answering agent, and run an interactive loop that
The post How to Build an Atomic-Agents RAG Pipeline with Typed Schemas, Dynamic Context Injection, and Agent Chaining appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In this tutorial, we build an advanced, end-to-end learning pipeline around Atomic-Agents by wiring together typed agent interfaces, structured prompting, and a compact retrieval layer that grounds outputs in real project documentation. Also, we demonstrate how to plan retrieval, retrieve relevant context, inject it dynamically into an answering agent, and run an interactive loop that
The post How to Build an Atomic-Agents RAG Pipeline with Typed Schemas, Dynamic Context Injection, and Agent Chaining appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Debugging code world modelscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2602.07672v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Code World Models (CWMs) are language models trained to simulate program execution by predicting explicit runtime state after every executed command. This execution-based world modeling enables internal verification within the model, offering an alternative to natural language chain-of-thought reasoning. However, the sources of errors and the nature of CWMs’ limitations remain poorly understood. We study CWMs from two complementary perspectives: local semantic execution and long-horizon state tracking. On real-code benchmarks, we identify two dominant failure regimes. First, dense runtime state reveals produce token-intensive execution traces, leading to token-budget exhaustion on programs with long execution histories. Second, failures disproportionately concentrate in string-valued state, which we attribute to limitations of subword tokenization rather than program structure. To study long-horizon behavior, we use a controlled permutation-tracking benchmark that isolates state propagation under action execution. We show that long-horizon degradation is driven primarily by incorrect action generation: when actions are replaced with ground-truth commands, a Transformer-based CWM propagates state accurately over long horizons, despite known limitations of Transformers in long-horizon state tracking. These findings suggest directions for more efficient supervision and state representations in CWMs that are better aligned with program execution and data types.
arXiv:2602.07672v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Code World Models (CWMs) are language models trained to simulate program execution by predicting explicit runtime state after every executed command. This execution-based world modeling enables internal verification within the model, offering an alternative to natural language chain-of-thought reasoning. However, the sources of errors and the nature of CWMs’ limitations remain poorly understood. We study CWMs from two complementary perspectives: local semantic execution and long-horizon state tracking. On real-code benchmarks, we identify two dominant failure regimes. First, dense runtime state reveals produce token-intensive execution traces, leading to token-budget exhaustion on programs with long execution histories. Second, failures disproportionately concentrate in string-valued state, which we attribute to limitations of subword tokenization rather than program structure. To study long-horizon behavior, we use a controlled permutation-tracking benchmark that isolates state propagation under action execution. We show that long-horizon degradation is driven primarily by incorrect action generation: when actions are replaced with ground-truth commands, a Transformer-based CWM propagates state accurately over long horizons, despite known limitations of Transformers in long-horizon state tracking. These findings suggest directions for more efficient supervision and state representations in CWMs that are better aligned with program execution and data types. Read More
Intentionally vulnerable training applications are widely used for security education, internal testing, and product demonstrations. Tools such as OWASP Juice Shop, DVWA, Hackazon, and bWAPP are designed to be insecure by default, making them useful for learning how common attack techniques work in controlled environments. The issue is not the applications themselves, but how they […]