Cloud attacks move fast — faster than most incident response teams. In data centers, investigations had time. Teams could collect disk images, review logs, and build timelines over days. In the cloud, infrastructure is short-lived. A compromised instance can disappear in minutes. Identities rotate. Logs expire. Evidence can vanish before analysis even begins. Cloud forensics […]
End-to-End NOMA with Perfect and Quantized CSI Over Rayleigh Fading Channels AI updates on arXiv.org
End-to-End NOMA with Perfect and Quantized CSI Over Rayleigh Fading Channelscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2602.13446v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: An end-to-end autoencoder (AE) framework is developed for downlink non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) over Rayleigh fading channels, which learns interference-aware and channel-adaptive super-constellations. While existing works either assume additive white Gaussian noise channels or treat fading channels without a fully end-to-end learning approach, our framework directly embeds the wireless channel into both training and inference. To account for practical channel state information (CSI), we further incorporate limited feedback via both uniform and Lloyd-Max quantization of channel gains and analyze their impact on AE training and bit error rate (BER) performance. Simulation results show that, with perfect CSI, the proposed AE outperforms the existing analytical NOMA schemes. In addition, Lloyd-Max quantization achieves superior BER performance compared to uniform quantization. These results demonstrate that end-to-end AEs trained directly over Rayleigh fading can effectively learn robust, interference-aware signaling strategies, paving the way for NOMA deployment in fading environments with realistic CSI constraints.
arXiv:2602.13446v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: An end-to-end autoencoder (AE) framework is developed for downlink non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) over Rayleigh fading channels, which learns interference-aware and channel-adaptive super-constellations. While existing works either assume additive white Gaussian noise channels or treat fading channels without a fully end-to-end learning approach, our framework directly embeds the wireless channel into both training and inference. To account for practical channel state information (CSI), we further incorporate limited feedback via both uniform and Lloyd-Max quantization of channel gains and analyze their impact on AE training and bit error rate (BER) performance. Simulation results show that, with perfect CSI, the proposed AE outperforms the existing analytical NOMA schemes. In addition, Lloyd-Max quantization achieves superior BER performance compared to uniform quantization. These results demonstrate that end-to-end AEs trained directly over Rayleigh fading can effectively learn robust, interference-aware signaling strategies, paving the way for NOMA deployment in fading environments with realistic CSI constraints. Read More
The Sufficiency-Conciseness Trade-off in LLM Self-Explanation from an Information Bottleneck Perspectivecs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2602.14002v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Large Language Models increasingly rely on self-explanations, such as chain of thought reasoning, to improve performance on multi step question answering. While these explanations enhance accuracy, they are often verbose and costly to generate, raising the question of how much explanation is truly necessary. In this paper, we examine the trade-off between sufficiency, defined as the ability of an explanation to justify the correct answer, and conciseness, defined as the reduction in explanation length. Building on the information bottleneck principle, we conceptualize explanations as compressed representations that retain only the information essential for producing correct answers.To operationalize this view, we introduce an evaluation pipeline that constrains explanation length and assesses sufficiency using multiple language models on the ARC Challenge dataset. To broaden the scope, we conduct experiments in both English, using the original dataset, and Persian, as a resource-limited language through translation. Our experiments show that more concise explanations often remain sufficient, preserving accuracy while substantially reducing explanation length, whereas excessive compression leads to performance degradation.
arXiv:2602.14002v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Large Language Models increasingly rely on self-explanations, such as chain of thought reasoning, to improve performance on multi step question answering. While these explanations enhance accuracy, they are often verbose and costly to generate, raising the question of how much explanation is truly necessary. In this paper, we examine the trade-off between sufficiency, defined as the ability of an explanation to justify the correct answer, and conciseness, defined as the reduction in explanation length. Building on the information bottleneck principle, we conceptualize explanations as compressed representations that retain only the information essential for producing correct answers.To operationalize this view, we introduce an evaluation pipeline that constrains explanation length and assesses sufficiency using multiple language models on the ARC Challenge dataset. To broaden the scope, we conduct experiments in both English, using the original dataset, and Persian, as a resource-limited language through translation. Our experiments show that more concise explanations often remain sufficient, preserving accuracy while substantially reducing explanation length, whereas excessive compression leads to performance degradation. Read More
What happens when reviewers receive AI feedback in their reviews?cs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2602.13817v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: AI is reshaping academic research, yet its role in peer review remains polarising and contentious. Advocates see its potential to reduce reviewer burden and improve quality, while critics warn of risks to fairness, accountability, and trust. At ICLR 2025, an official AI feedback tool was deployed to provide reviewers with post-review suggestions. We studied this deployment through surveys and interviews, investigating how reviewers engaged with the tool and perceived its usability and impact. Our findings surface both opportunities and tensions when AI augments in peer review. This work contributes the first empirical evidence of such an AI tool in a live review process, documenting how reviewers respond to AI-generated feedback in a high-stakes review context. We further offer design implications for AI-assisted reviewing that aim to enhance quality while safeguarding human expertise, agency, and responsibility.
arXiv:2602.13817v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: AI is reshaping academic research, yet its role in peer review remains polarising and contentious. Advocates see its potential to reduce reviewer burden and improve quality, while critics warn of risks to fairness, accountability, and trust. At ICLR 2025, an official AI feedback tool was deployed to provide reviewers with post-review suggestions. We studied this deployment through surveys and interviews, investigating how reviewers engaged with the tool and perceived its usability and impact. Our findings surface both opportunities and tensions when AI augments in peer review. This work contributes the first empirical evidence of such an AI tool in a live review process, documenting how reviewers respond to AI-generated feedback in a high-stakes review context. We further offer design implications for AI-assisted reviewing that aim to enhance quality while safeguarding human expertise, agency, and responsibility. Read More
Agoda Open Sources APIAgent to Convert Any REST pr GraphQL API into an MCP Server with Zero CodeMarkTechPost Building AI agents is the new gold rush. But every developer knows the biggest bottleneck: getting the AI to actually communicate to your data. Today, travel giant Agoda is tackling this problem head-on. They have officially launched APIAgent, an open-source tool designed to turn any REST or GraphQL API into a Model Context Protocol (MCP)
The post Agoda Open Sources APIAgent to Convert Any REST pr GraphQL API into an MCP Server with Zero Code appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Building AI agents is the new gold rush. But every developer knows the biggest bottleneck: getting the AI to actually communicate to your data. Today, travel giant Agoda is tackling this problem head-on. They have officially launched APIAgent, an open-source tool designed to turn any REST or GraphQL API into a Model Context Protocol (MCP)
The post Agoda Open Sources APIAgent to Convert Any REST pr GraphQL API into an MCP Server with Zero Code appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
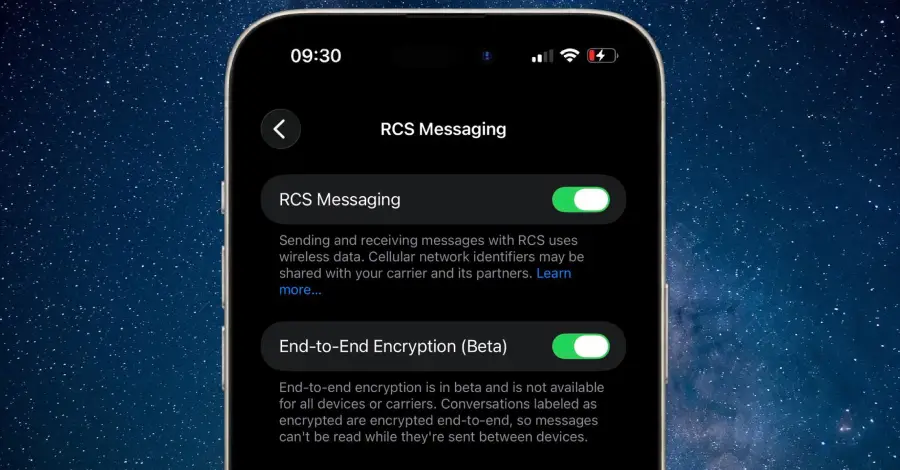
Apple on Monday released a new developer beta of iOS and iPadOS with support for end-to-end encryption (E2EE) in Rich Communications Services (RCS) messages. The feature is currently available for testing in iOS and iPadOS 26.4 Beta, and is expected to be shipped to customers in a future update for iOS, iPadOS, macOS, and watchOS. […]
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed details of a new SmartLoader campaign that involves distributing a trojanized version of a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server associated with Oura Health to deliver an information stealer known as StealC. “The threat actors cloned a legitimate Oura MCP Server – a tool that connects AI assistants to Oura Ring health […]
Polish police have detained a 47-year-old man suspected of ties to the Phobos ransomware group and seized computers and mobile phones containing stolen credentials, credit card numbers, and server access data. […] Read More
New research from Microsoft has revealed that legitimate businesses are gaming artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots via the “Summarize with AI” button that’s being increasingly placed on websites in ways that mirror classic search engine poisoning (AI). The new AI hijacking technique has been codenamed AI Recommendation Poisoning by the Microsoft Defender Security Research Team. The […]
A Pragmatist Robot: Learning to Plan Tasks by Experiencing the Real Worldcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2507.16713v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) have emerged as the dominant paradigm for robotic task planning using natural language instructions. However, trained on general internet data, LLMs are not inherently aligned with the embodiment, skill sets, and limitations of real-world robotic systems. Inspired by the emerging paradigm of verbal reinforcement learning-where LLM agents improve through self-reflection and few-shot learning without parameter updates-we introduce PragmaBot, a framework that enables robots to learn task planning through real-world experience. PragmaBot employs a vision-language model (VLM) as the robot’s “brain” and “eye”, allowing it to visually evaluate action outcomes and self-reflect on failures. These reflections are stored in a short-term memory (STM), enabling the robot to quickly adapt its behavior during ongoing tasks. Upon task completion, the robot summarizes the lessons learned into its long-term memory (LTM). When facing new tasks, it can leverage retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to plan more grounded action sequences by drawing on relevant past experiences and knowledge. Experiments on four challenging robotic tasks show that STM-based self-reflection increases task success rates from 35% to 84%, with emergent intelligent object interactions. In 12 real-world scenarios (including eight previously unseen tasks), the robot effectively learns from the LTM and improves single-trial success rates from 22% to 80%, with RAG outperforming naive prompting. These results highlight the effectiveness and generalizability of PragmaBot. Project webpage: https://pragmabot.github.io/
arXiv:2507.16713v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) have emerged as the dominant paradigm for robotic task planning using natural language instructions. However, trained on general internet data, LLMs are not inherently aligned with the embodiment, skill sets, and limitations of real-world robotic systems. Inspired by the emerging paradigm of verbal reinforcement learning-where LLM agents improve through self-reflection and few-shot learning without parameter updates-we introduce PragmaBot, a framework that enables robots to learn task planning through real-world experience. PragmaBot employs a vision-language model (VLM) as the robot’s “brain” and “eye”, allowing it to visually evaluate action outcomes and self-reflect on failures. These reflections are stored in a short-term memory (STM), enabling the robot to quickly adapt its behavior during ongoing tasks. Upon task completion, the robot summarizes the lessons learned into its long-term memory (LTM). When facing new tasks, it can leverage retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to plan more grounded action sequences by drawing on relevant past experiences and knowledge. Experiments on four challenging robotic tasks show that STM-based self-reflection increases task success rates from 35% to 84%, with emergent intelligent object interactions. In 12 real-world scenarios (including eight previously unseen tasks), the robot effectively learns from the LTM and improves single-trial success rates from 22% to 80%, with RAG outperforming naive prompting. These results highlight the effectiveness and generalizability of PragmaBot. Project webpage: https://pragmabot.github.io/ Read More