Beyond Fact Retrieval: Episodic Memory for RAG with Generative Semantic Workspacescs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.07587v2 Announce Type: replace
Abstract: Large Language Models (LLMs) face fundamental challenges in long-context reasoning: many documents exceed their finite context windows, while performance on texts that do fit degrades with sequence length, necessitating their augmentation with external memory frameworks. Current solutions, which have evolved from retrieval using semantic embeddings to more sophisticated structured knowledge graphs representations for improved sense-making and associativity, are tailored for fact-based retrieval and fail to build the space-time-anchored narrative representations required for tracking entities through episodic events. To bridge this gap, we propose the textbf{Generative Semantic Workspace} (GSW), a neuro-inspired generative memory framework that builds structured, interpretable representations of evolving situations, enabling LLMs to reason over evolving roles, actions, and spatiotemporal contexts. Our framework comprises an textit{Operator}, which maps incoming observations to intermediate semantic structures, and a textit{Reconciler}, which integrates these into a persistent workspace that enforces temporal, spatial, and logical coherence. On the Episodic Memory Benchmark (EpBench) cite{huet_episodic_2025} comprising corpora ranging from 100k to 1M tokens in length, GSW outperforms existing RAG based baselines by up to textbf{20%}. Furthermore, GSW is highly efficient, reducing query-time context tokens by textbf{51%} compared to the next most token-efficient baseline, reducing inference time costs considerably. More broadly, GSW offers a concrete blueprint for endowing LLMs with human-like episodic memory, paving the way for more capable agents that can reason over long horizons. Code is available at https://github.com/roychowdhuryresearch/gsw-memory.
arXiv:2511.07587v2 Announce Type: replace
Abstract: Large Language Models (LLMs) face fundamental challenges in long-context reasoning: many documents exceed their finite context windows, while performance on texts that do fit degrades with sequence length, necessitating their augmentation with external memory frameworks. Current solutions, which have evolved from retrieval using semantic embeddings to more sophisticated structured knowledge graphs representations for improved sense-making and associativity, are tailored for fact-based retrieval and fail to build the space-time-anchored narrative representations required for tracking entities through episodic events. To bridge this gap, we propose the textbf{Generative Semantic Workspace} (GSW), a neuro-inspired generative memory framework that builds structured, interpretable representations of evolving situations, enabling LLMs to reason over evolving roles, actions, and spatiotemporal contexts. Our framework comprises an textit{Operator}, which maps incoming observations to intermediate semantic structures, and a textit{Reconciler}, which integrates these into a persistent workspace that enforces temporal, spatial, and logical coherence. On the Episodic Memory Benchmark (EpBench) cite{huet_episodic_2025} comprising corpora ranging from 100k to 1M tokens in length, GSW outperforms existing RAG based baselines by up to textbf{20%}. Furthermore, GSW is highly efficient, reducing query-time context tokens by textbf{51%} compared to the next most token-efficient baseline, reducing inference time costs considerably. More broadly, GSW offers a concrete blueprint for endowing LLMs with human-like episodic memory, paving the way for more capable agents that can reason over long horizons. Code is available at https://github.com/roychowdhuryresearch/gsw-memory. Read More
LogiPart: Local Large Language Models for Data Exploration at Scale with Logical Partitioningcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2509.22211v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: The discovery of deep, steerable taxonomies in large text corpora is currently restricted by a trade-off between the surface-level efficiency of topic models and the prohibitive, non-scalable assignment costs of LLM-integrated frameworks. We introduce textbf{LogiPart}, a scalable, hypothesis-first framework for building interpretable hierarchical partitions that decouples hierarchy growth from expensive full-corpus LLM conditioning. LogiPart utilizes locally hosted LLMs on compact, embedding-aware samples to generate concise natural-language taxonomic predicates. These predicates are then evaluated efficiently across the entire corpus using zero-shot Natural Language Inference (NLI) combined with fast graph-based label propagation, achieving constant $O(1)$ generative token complexity per node relative to corpus size. We evaluate LogiPart across four diverse text corpora (totaling $approx$140,000 documents). Using structured manifolds for textbf{calibration}, we identify an empirical reasoning threshold at the 14B-parameter scale required for stable semantic grounding. On complex, high-entropy corpora (Wikipedia, US Bills), where traditional thematic metrics reveal an “alignment gap,” inverse logic validation confirms the stability of the induced logic, with individual taxonomic bisections maintaining an average per-node routing accuracy of up to 96%. A qualitative audit by an independent LLM-as-a-judge confirms the discovery of meaningful functional axes, such as policy intent, that thematic ground-truth labels fail to capture. LogiPart enables frontier-level exploratory analysis on consumer-grade hardware, making hypothesis-driven taxonomic discovery feasible under realistic computational and governance constraints.
arXiv:2509.22211v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: The discovery of deep, steerable taxonomies in large text corpora is currently restricted by a trade-off between the surface-level efficiency of topic models and the prohibitive, non-scalable assignment costs of LLM-integrated frameworks. We introduce textbf{LogiPart}, a scalable, hypothesis-first framework for building interpretable hierarchical partitions that decouples hierarchy growth from expensive full-corpus LLM conditioning. LogiPart utilizes locally hosted LLMs on compact, embedding-aware samples to generate concise natural-language taxonomic predicates. These predicates are then evaluated efficiently across the entire corpus using zero-shot Natural Language Inference (NLI) combined with fast graph-based label propagation, achieving constant $O(1)$ generative token complexity per node relative to corpus size. We evaluate LogiPart across four diverse text corpora (totaling $approx$140,000 documents). Using structured manifolds for textbf{calibration}, we identify an empirical reasoning threshold at the 14B-parameter scale required for stable semantic grounding. On complex, high-entropy corpora (Wikipedia, US Bills), where traditional thematic metrics reveal an “alignment gap,” inverse logic validation confirms the stability of the induced logic, with individual taxonomic bisections maintaining an average per-node routing accuracy of up to 96%. A qualitative audit by an independent LLM-as-a-judge confirms the discovery of meaningful functional axes, such as policy intent, that thematic ground-truth labels fail to capture. LogiPart enables frontier-level exploratory analysis on consumer-grade hardware, making hypothesis-driven taxonomic discovery feasible under realistic computational and governance constraints. Read More
Robust Deep Reinforcement Learning against Adversarial Behavior Manipulation AI updates on arXiv.org
Robust Deep Reinforcement Learning against Adversarial Behavior Manipulationcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2406.03862v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: This study investigates behavior-targeted attacks on reinforcement learning and their countermeasures. Behavior-targeted attacks aim to manipulate the victim’s behavior as desired by the adversary through adversarial interventions in state observations. Existing behavior-targeted attacks have some limitations, such as requiring white-box access to the victim’s policy. To address this, we propose a novel attack method using imitation learning from adversarial demonstrations, which works under limited access to the victim’s policy and is environment-agnostic. In addition, our theoretical analysis proves that the policy’s sensitivity to state changes impacts defense performance, particularly in the early stages of the trajectory. Based on this insight, we propose time-discounted regularization, which enhances robustness against attacks while maintaining task performance. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first defense strategy specifically designed for behavior-targeted attacks.
arXiv:2406.03862v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: This study investigates behavior-targeted attacks on reinforcement learning and their countermeasures. Behavior-targeted attacks aim to manipulate the victim’s behavior as desired by the adversary through adversarial interventions in state observations. Existing behavior-targeted attacks have some limitations, such as requiring white-box access to the victim’s policy. To address this, we propose a novel attack method using imitation learning from adversarial demonstrations, which works under limited access to the victim’s policy and is environment-agnostic. In addition, our theoretical analysis proves that the policy’s sensitivity to state changes impacts defense performance, particularly in the early stages of the trajectory. Based on this insight, we propose time-discounted regularization, which enhances robustness against attacks while maintaining task performance. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first defense strategy specifically designed for behavior-targeted attacks. Read More
Multi-Agent Comedy Club: Investigating Community Discussion Effects on LLM Humor Generationcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2602.14770v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Prior work has explored multi-turn interaction and feedback for LLM writing, but evaluations still largely center on prompts and localized feedback, leaving persistent public reception in online communities underexamined. We test whether broadcast community discussion improves stand-up comedy writing in a controlled multi-agent sandbox: in the discussion condition, critic and audience threads are recorded, filtered, stored as social memory, and later retrieved to condition subsequent generations, whereas the baseline omits discussion. Across 50 rounds (250 paired monologues) judged by five expert annotators using A/B preference and a 15-item rubric, discussion wins 75.6% of instances and improves Craft/Clarity ({Delta} = 0.440) and Social Response ({Delta} = 0.422), with occasional increases in aggressive humor.
arXiv:2602.14770v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Prior work has explored multi-turn interaction and feedback for LLM writing, but evaluations still largely center on prompts and localized feedback, leaving persistent public reception in online communities underexamined. We test whether broadcast community discussion improves stand-up comedy writing in a controlled multi-agent sandbox: in the discussion condition, critic and audience threads are recorded, filtered, stored as social memory, and later retrieved to condition subsequent generations, whereas the baseline omits discussion. Across 50 rounds (250 paired monologues) judged by five expert annotators using A/B preference and a 15-item rubric, discussion wins 75.6% of instances and improves Craft/Clarity ({Delta} = 0.440) and Social Response ({Delta} = 0.422), with occasional increases in aggressive humor. Read More
Text-Guided Layer Fusion Mitigates Hallucination in Multimodal LLMscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2601.03100v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) typically rely on a single late-layer feature from a frozen vision encoder, leaving the encoder’s rich hierarchy of visual cues under-utilized. MLLMs still suffer from visually ungrounded hallucinations, often relying on language priors rather than image evidence. While many prior mitigation strategies operate on the text side, they leave the visual representation unchanged and do not exploit the rich hierarchy of features encoded across vision layers. Existing multi-layer fusion methods partially address this limitation but remain static, applying the same layer mixture regardless of the query. In this work, we introduce TGIF (Text-Guided Inter-layer Fusion), a lightweight module that treats encoder layers as depth-wise “experts” and predicts a prompt-dependent fusion of visual features. TGIF follows the principle of direct external fusion, requires no vision-encoder updates, and adds minimal overhead. Integrated into LLaVA-1.5-7B, TGIF provides consistent improvements across hallucination, OCR, and VQA benchmarks, while preserving or improving performance on ScienceQA, GQA, and MMBench. These results suggest that query-conditioned, hierarchy-aware fusion is an effective way to strengthen visual grounding and reduce hallucination in modern MLLMs.
arXiv:2601.03100v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) typically rely on a single late-layer feature from a frozen vision encoder, leaving the encoder’s rich hierarchy of visual cues under-utilized. MLLMs still suffer from visually ungrounded hallucinations, often relying on language priors rather than image evidence. While many prior mitigation strategies operate on the text side, they leave the visual representation unchanged and do not exploit the rich hierarchy of features encoded across vision layers. Existing multi-layer fusion methods partially address this limitation but remain static, applying the same layer mixture regardless of the query. In this work, we introduce TGIF (Text-Guided Inter-layer Fusion), a lightweight module that treats encoder layers as depth-wise “experts” and predicts a prompt-dependent fusion of visual features. TGIF follows the principle of direct external fusion, requires no vision-encoder updates, and adds minimal overhead. Integrated into LLaVA-1.5-7B, TGIF provides consistent improvements across hallucination, OCR, and VQA benchmarks, while preserving or improving performance on ScienceQA, GQA, and MMBench. These results suggest that query-conditioned, hierarchy-aware fusion is an effective way to strengthen visual grounding and reduce hallucination in modern MLLMs. Read More
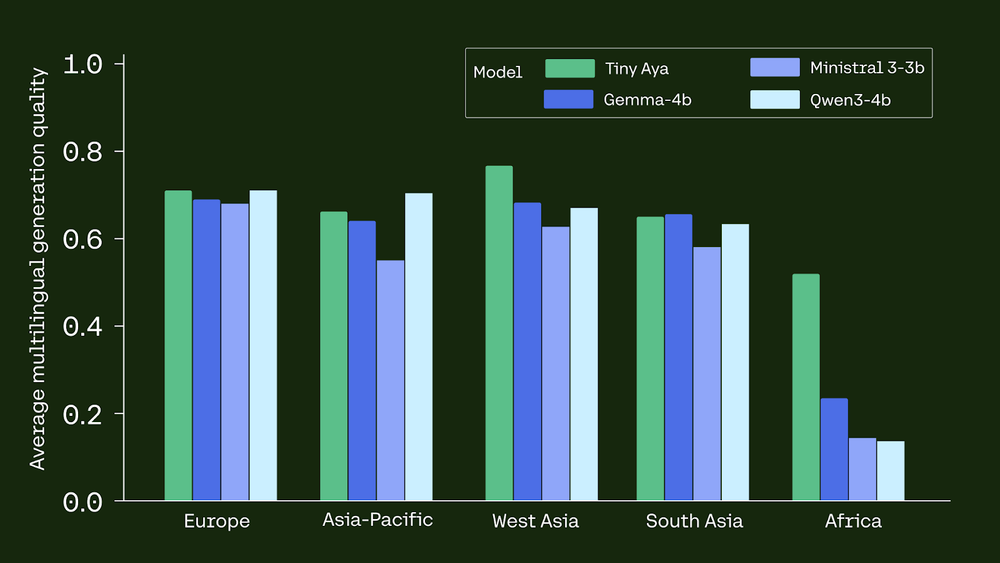
Cohere Releases Tiny Aya: A 3B-Parameter Small Language Model that Supports 70 Languages and Runs Locally Even on a PhoneMarkTechPost Cohere AI Labs has released Tiny Aya, a family of small language models (SLMs) that redefines multilingual performance. While many models scale by increasing parameters, Tiny Aya uses a 3.35B-parameter architecture to deliver state-of-the-art translation and generation across 70 languages. The release includes 5 models: Tiny Aya Base (pretrained), Tiny Aya Global (balanced instruction-tuned), and
The post Cohere Releases Tiny Aya: A 3B-Parameter Small Language Model that Supports 70 Languages and Runs Locally Even on a Phone appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Cohere AI Labs has released Tiny Aya, a family of small language models (SLMs) that redefines multilingual performance. While many models scale by increasing parameters, Tiny Aya uses a 3.35B-parameter architecture to deliver state-of-the-art translation and generation across 70 languages. The release includes 5 models: Tiny Aya Base (pretrained), Tiny Aya Global (balanced instruction-tuned), and
The post Cohere Releases Tiny Aya: A 3B-Parameter Small Language Model that Supports 70 Languages and Runs Locally Even on a Phone appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
A maximum severity security vulnerability in Dell RecoverPoint for Virtual Machines has been exploited as a zero-day by a suspected China-nexus threat cluster dubbed UNC6201 since mid-2024, according to a new report from Google Mandiant and Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG). The activity involves the exploitation of CVE-2026-22769 (CVSS score: 10.0), a case of hard-coded […]
Security, IT, and engineering teams today are under relentless pressure to accelerate outcomes, cut operational drag, and unlock the full potential of AI and automation. But simply investing in tools isn’t enough. 88% of AI proofs-of-concept never make it to production, even though 70% of workers cite freeing time for high-value work as the primary […]
SS&C Blue Prism: On the journey from RPA to agentic automationAI News For organizations who are still wedded to the rules and structures of robotic process automation (RPA), then considering agentic AI as the next step for automation may be faintly terrifying. SS&C Blue Prism, however, is here to help, taking customers on the journey from RPA to agentic automation at a pace with which they’re comfortable.
The post SS&C Blue Prism: On the journey from RPA to agentic automation appeared first on AI News.
For organizations who are still wedded to the rules and structures of robotic process automation (RPA), then considering agentic AI as the next step for automation may be faintly terrifying. SS&C Blue Prism, however, is here to help, taking customers on the journey from RPA to agentic automation at a pace with which they’re comfortable.
The post SS&C Blue Prism: On the journey from RPA to agentic automation appeared first on AI News. Read More
Goldman Sachs deploys Anthropic systems with successAI News Goldman Sachs plans to deploy Anthropic’s Claude model in trade accounting and client onboarding, and, according to an article in American Banker, presents this as part of a broader push among large banks to use generative artificial intelligence to improve efficiency. The focus is on operational processes that sit in the back office and have
The post Goldman Sachs deploys Anthropic systems with success appeared first on AI News.
Goldman Sachs plans to deploy Anthropic’s Claude model in trade accounting and client onboarding, and, according to an article in American Banker, presents this as part of a broader push among large banks to use generative artificial intelligence to improve efficiency. The focus is on operational processes that sit in the back office and have
The post Goldman Sachs deploys Anthropic systems with success appeared first on AI News. Read More