Is AI in a bubble? Succeed despite a market correctionAI News Amid pressure to deploy generative and agentic solutions, a familiar question is surfacing: “Is there an AI bubble, and is it about to burst?” For many organisations, this new wave of generative and agentic AI is still very much in experimental stages. The primary focus, and the low-hanging fruit, has been internal. Most businesses are
The post Is AI in a bubble? Succeed despite a market correction appeared first on AI News.
Amid pressure to deploy generative and agentic solutions, a familiar question is surfacing: “Is there an AI bubble, and is it about to burst?” For many organisations, this new wave of generative and agentic AI is still very much in experimental stages. The primary focus, and the low-hanging fruit, has been internal. Most businesses are
The post Is AI in a bubble? Succeed despite a market correction appeared first on AI News. Read More
The Reinforcement Learning Handbook: A Guide to Foundational QuestionsTowards Data Science Simplifying all the concepts required to master reinforcement learning
The post The Reinforcement Learning Handbook: A Guide to Foundational Questions appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Simplifying all the concepts required to master reinforcement learning
The post The Reinforcement Learning Handbook: A Guide to Foundational Questions appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
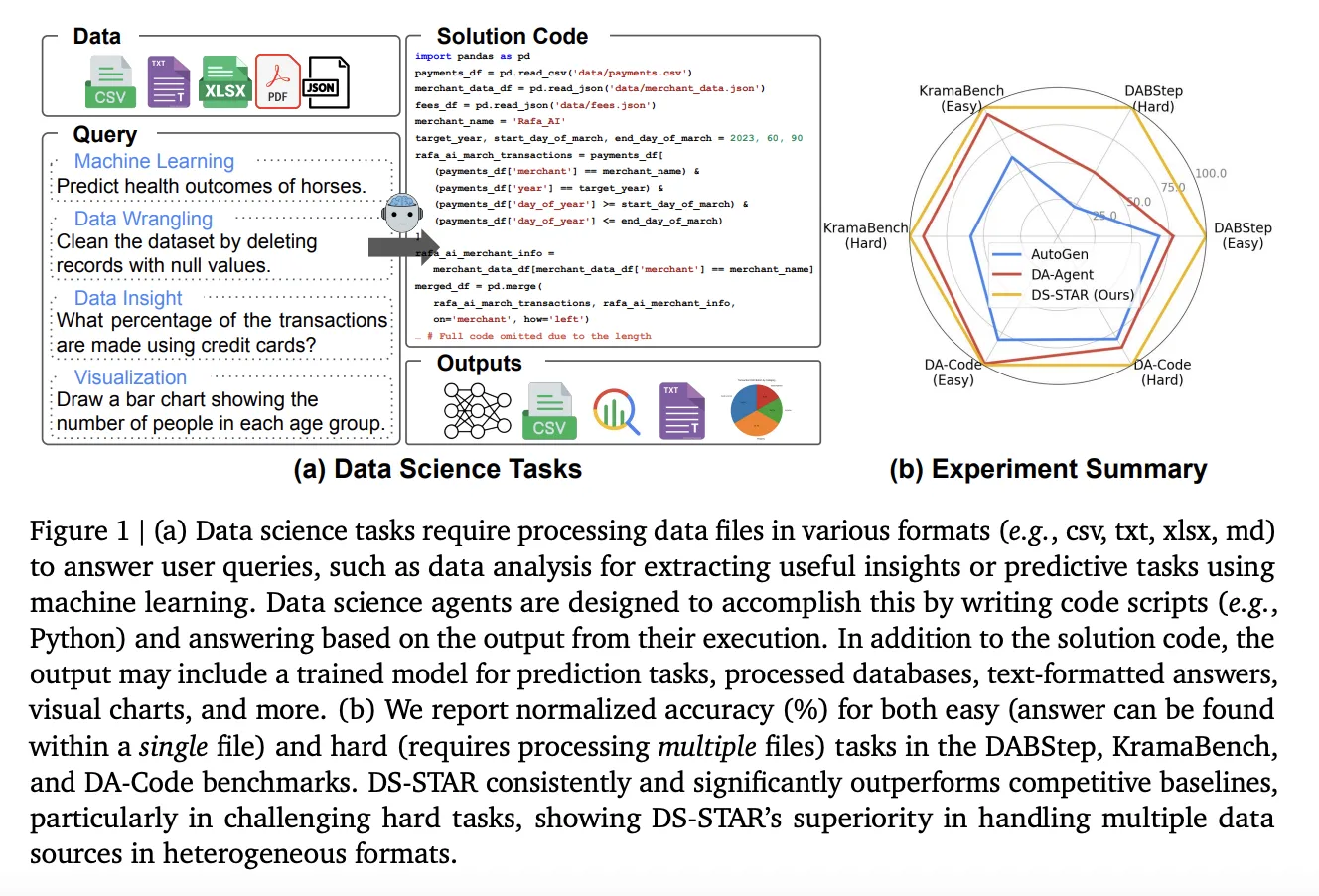
Google AI Introduces DS STAR: A Multi Agent Data Science System That Plans, Codes And Verifies End To End AnalyticsMarkTechPost How do you turn a vague business style question over messy folders of CSV, JSON and text into reliable Python code without a human analyst in the loop? Google researchers introduce DS STAR (Data Science Agent via Iterative Planning and Verification), a multi agent framework that turns open ended data science questions into executable Python
The post Google AI Introduces DS STAR: A Multi Agent Data Science System That Plans, Codes And Verifies End To End Analytics appeared first on MarkTechPost.
How do you turn a vague business style question over messy folders of CSV, JSON and text into reliable Python code without a human analyst in the loop? Google researchers introduce DS STAR (Data Science Agent via Iterative Planning and Verification), a multi agent framework that turns open ended data science questions into executable Python
The post Google AI Introduces DS STAR: A Multi Agent Data Science System That Plans, Codes And Verifies End To End Analytics appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
How to Use GPT-5 EffectivelyTowards Data Science Learn about GPT-5’s features and settings, and how to optimally apply them to your use case
The post How to Use GPT-5 Effectively appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Learn about GPT-5’s features and settings, and how to optimally apply them to your use case
The post How to Use GPT-5 Effectively appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
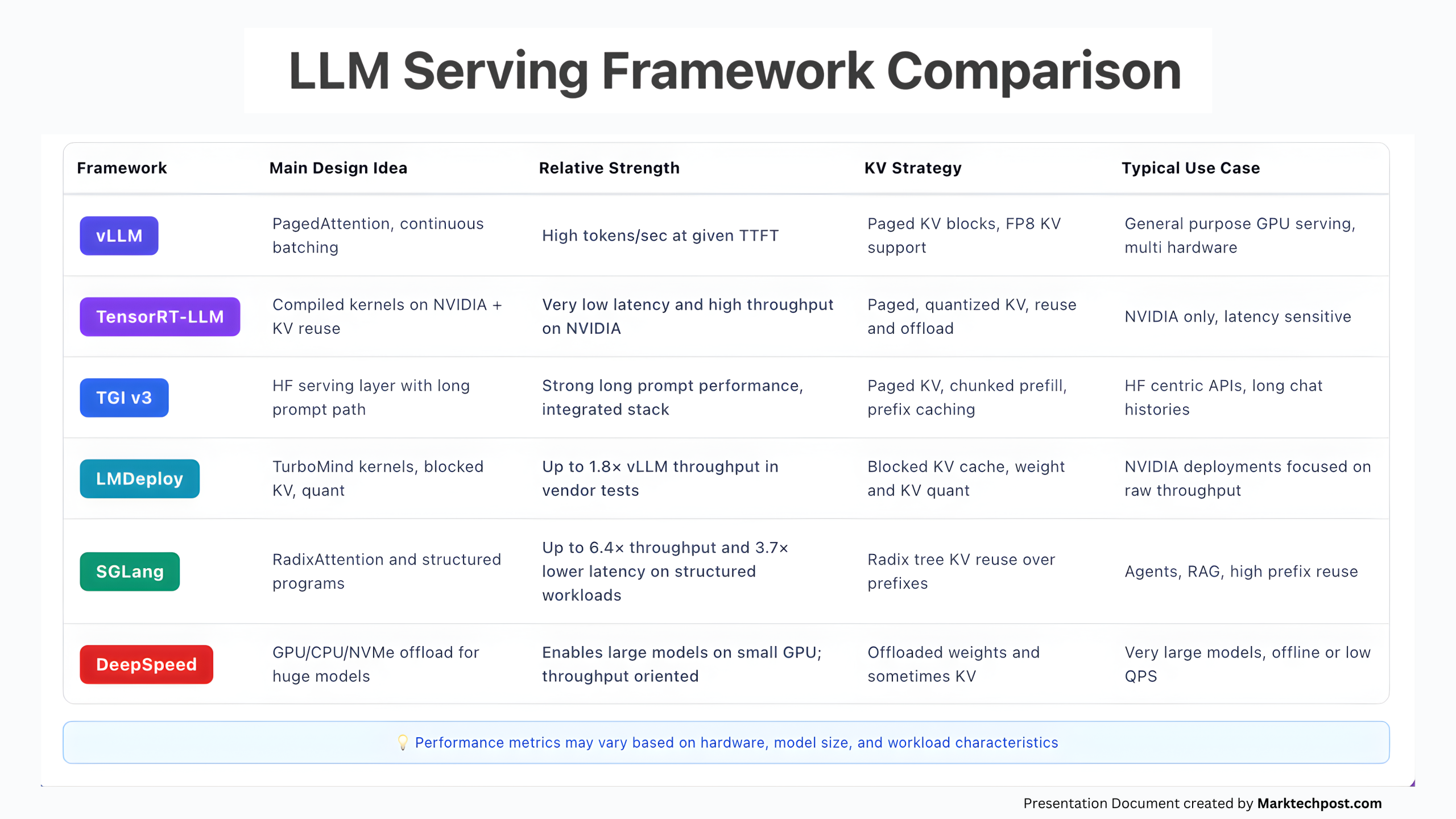
Comparing the Top 6 Inference Runtimes for LLM Serving in 2025MarkTechPost Large language models are now limited less by training and more by how fast and cheaply we can serve tokens under real traffic. That comes down to three implementation details: how the runtime batches requests, how it overlaps prefill and decode, and how it stores and reuses the KV cache. Different engines make different tradeoffs
The post Comparing the Top 6 Inference Runtimes for LLM Serving in 2025 appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Large language models are now limited less by training and more by how fast and cheaply we can serve tokens under real traffic. That comes down to three implementation details: how the runtime batches requests, how it overlaps prefill and decode, and how it stores and reuses the KV cache. Different engines make different tradeoffs
The post Comparing the Top 6 Inference Runtimes for LLM Serving in 2025 appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Nvidia AI chip ban: Can tech giants navigate a geopolitical zero-sum game?AI News When Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang initially told the Financial Times that China would “win the AI race” before softening his stance, it crystallised a predicament that’s been years in the making. The world’s most valuable chipmaker now finds itself caught between two superpowers, each wielding the Nvidia AI chip ban as a weapon in a broader technological
The post Nvidia AI chip ban: Can tech giants navigate a geopolitical zero-sum game? appeared first on AI News.
When Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang initially told the Financial Times that China would “win the AI race” before softening his stance, it crystallised a predicament that’s been years in the making. The world’s most valuable chipmaker now finds itself caught between two superpowers, each wielding the Nvidia AI chip ban as a weapon in a broader technological
The post Nvidia AI chip ban: Can tech giants navigate a geopolitical zero-sum game? appeared first on AI News. Read More
Microsoft’s next big AI bet: building a ‘humanist superintelligence’AI News Microsoft is forming a new team to research superintelligence and other advanced forms of artificial intelligence. Mustafa Suleyman, who leads Microsoft’s AI division overseeing Bing and Copilot, announced the creation of the MAI Superintelligence Team in a blog post. He said he will head the group and that Microsoft plans to put “a lot of
The post Microsoft’s next big AI bet: building a ‘humanist superintelligence’ appeared first on AI News.
Microsoft is forming a new team to research superintelligence and other advanced forms of artificial intelligence. Mustafa Suleyman, who leads Microsoft’s AI division overseeing Bing and Copilot, announced the creation of the MAI Superintelligence Team in a blog post. He said he will head the group and that Microsoft plans to put “a lot of
The post Microsoft’s next big AI bet: building a ‘humanist superintelligence’ appeared first on AI News. Read More
Build a Multi-Agent System for Integrated Transcriptomic, Proteomic, and Metabolomic Data Interpretation with Pathway ReasoningMarkTechPost In this tutorial, we build an advanced multi-agent pipeline that interprets integrated omics data, including transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, to uncover key biological insights. We begin by generating coherent synthetic datasets that mimic realistic biological trends and then move step by step through agents designed for statistical analysis, network inference, pathway enrichment, and drug repurposing.
The post Build a Multi-Agent System for Integrated Transcriptomic, Proteomic, and Metabolomic Data Interpretation with Pathway Reasoning appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In this tutorial, we build an advanced multi-agent pipeline that interprets integrated omics data, including transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, to uncover key biological insights. We begin by generating coherent synthetic datasets that mimic realistic biological trends and then move step by step through agents designed for statistical analysis, network inference, pathway enrichment, and drug repurposing.
The post Build a Multi-Agent System for Integrated Transcriptomic, Proteomic, and Metabolomic Data Interpretation with Pathway Reasoning appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Divide by Question, Conquer by Agent: SPLIT-RAG with Question-Driven Graph Partitioningcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2505.13994v2 Announce Type: replace
Abstract: Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems empower large language models (LLMs) with external knowledge, yet struggle with efficiency-accuracy trade-offs when scaling to large knowledge graphs. Existing approaches often rely on monolithic graph retrieval, incurring unnecessary latency for simple queries and fragmented reasoning for complex multi-hop questions. To address these challenges, this paper propose SPLIT-RAG, a multi-agent RAG framework that addresses these limitations with question-driven semantic graph partitioning and collaborative subgraph retrieval. The innovative framework first create Semantic Partitioning of Linked Information, then use the Type-Specialized knowledge base to achieve Multi-Agent RAG. The attribute-aware graph segmentation manages to divide knowledge graphs into semantically coherent subgraphs, ensuring subgraphs align with different query types, while lightweight LLM agents are assigned to partitioned subgraphs, and only relevant partitions are activated during retrieval, thus reduce search space while enhancing efficiency. Finally, a hierarchical merging module resolves inconsistencies across subgraph-derived answers through logical verifications. Extensive experimental validation demonstrates considerable improvements compared to existing approaches.
arXiv:2505.13994v2 Announce Type: replace
Abstract: Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems empower large language models (LLMs) with external knowledge, yet struggle with efficiency-accuracy trade-offs when scaling to large knowledge graphs. Existing approaches often rely on monolithic graph retrieval, incurring unnecessary latency for simple queries and fragmented reasoning for complex multi-hop questions. To address these challenges, this paper propose SPLIT-RAG, a multi-agent RAG framework that addresses these limitations with question-driven semantic graph partitioning and collaborative subgraph retrieval. The innovative framework first create Semantic Partitioning of Linked Information, then use the Type-Specialized knowledge base to achieve Multi-Agent RAG. The attribute-aware graph segmentation manages to divide knowledge graphs into semantically coherent subgraphs, ensuring subgraphs align with different query types, while lightweight LLM agents are assigned to partitioned subgraphs, and only relevant partitions are activated during retrieval, thus reduce search space while enhancing efficiency. Finally, a hierarchical merging module resolves inconsistencies across subgraph-derived answers through logical verifications. Extensive experimental validation demonstrates considerable improvements compared to existing approaches. Read More
Voost: A Unified and Scalable Diffusion Transformer for Bidirectional Virtual Try-On and Try-Offcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2508.04825v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Virtual try-on aims to synthesize a realistic image of a person wearing a target garment, but accurately modeling garment-body correspondence remains a persistent challenge, especially under pose and appearance variation. In this paper, we propose Voost – a unified and scalable framework that jointly learns virtual try-on and try-off with a single diffusion transformer. By modeling both tasks jointly, Voost enables each garment-person pair to supervise both directions and supports flexible conditioning over generation direction and garment category, enhancing garment-body relational reasoning without task-specific networks, auxiliary losses, or additional labels. In addition, we introduce two inference-time techniques: attention temperature scaling for robustness to resolution or mask variation, and self-corrective sampling that leverages bidirectional consistency between tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Voost achieves state-of-the-art results on both try-on and try-off benchmarks, consistently outperforming strong baselines in alignment accuracy, visual fidelity, and generalization.
arXiv:2508.04825v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Virtual try-on aims to synthesize a realistic image of a person wearing a target garment, but accurately modeling garment-body correspondence remains a persistent challenge, especially under pose and appearance variation. In this paper, we propose Voost – a unified and scalable framework that jointly learns virtual try-on and try-off with a single diffusion transformer. By modeling both tasks jointly, Voost enables each garment-person pair to supervise both directions and supports flexible conditioning over generation direction and garment category, enhancing garment-body relational reasoning without task-specific networks, auxiliary losses, or additional labels. In addition, we introduce two inference-time techniques: attention temperature scaling for robustness to resolution or mask variation, and self-corrective sampling that leverages bidirectional consistency between tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Voost achieves state-of-the-art results on both try-on and try-off benchmarks, consistently outperforming strong baselines in alignment accuracy, visual fidelity, and generalization. Read More