Introducing structured output for Custom Model Import in Amazon BedrockArtificial Intelligence Today, we are excited to announce the addition of structured output to Custom Model Import. Structured output constrains a model’s generation process in real time so that every token it produces conforms to a schema you define. Rather than relying on prompt-engineering tricks or brittle post-processing scripts, you can now generate structured outputs directly at inference time.
Today, we are excited to announce the addition of structured output to Custom Model Import. Structured output constrains a model’s generation process in real time so that every token it produces conforms to a schema you define. Rather than relying on prompt-engineering tricks or brittle post-processing scripts, you can now generate structured outputs directly at inference time. Read More
ChatLLM. An Honest Review of Our All-in-One AI PlatformKDnuggets ChatLLM brings together every major AI model—GPT-5, Claude, Gemini, Grok, and more—into one affordable platform. For just $10 a month, you get a Swiss Army knife of AI tools for writing, coding, analysis, and automation.
ChatLLM brings together every major AI model—GPT-5, Claude, Gemini, Grok, and more—into one affordable platform. For just $10 a month, you get a Swiss Army knife of AI tools for writing, coding, analysis, and automation. Read More
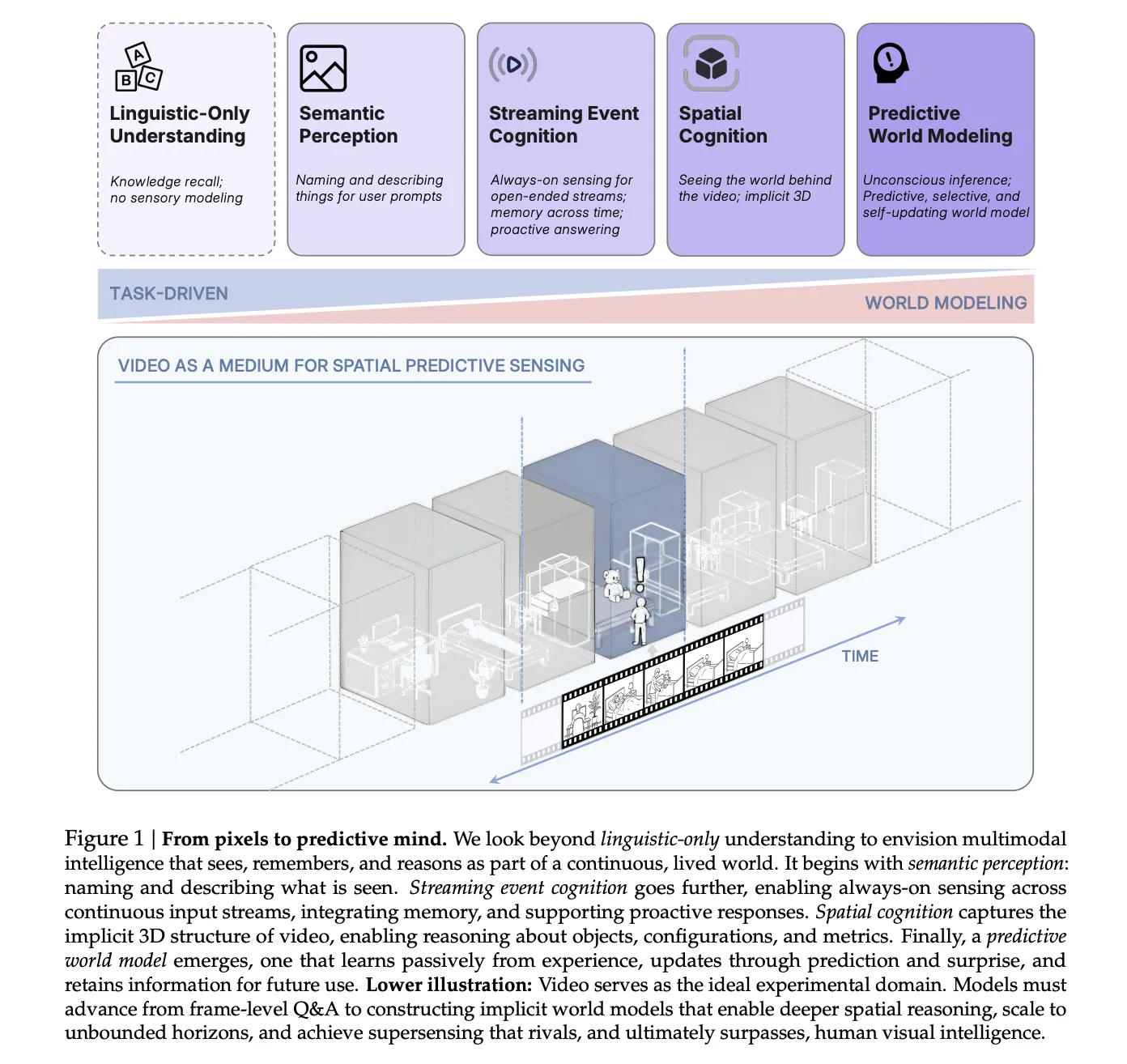
Why Spatial Supersensing is Emerging as the Core Capability for Multimodal AI Systems?MarkTechPost Even strong ‘long-context’ AI models fail badly when they must track objects and counts over long, messy video streams, so the next competitive edge will come from models that predict what comes next and selectively remember only surprising, important events, not from just buying more compute and bigger context windows. A team of researchers from
The post Why Spatial Supersensing is Emerging as the Core Capability for Multimodal AI Systems? appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Even strong ‘long-context’ AI models fail badly when they must track objects and counts over long, messy video streams, so the next competitive edge will come from models that predict what comes next and selectively remember only surprising, important events, not from just buying more compute and bigger context windows. A team of researchers from
The post Why Spatial Supersensing is Emerging as the Core Capability for Multimodal AI Systems? appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Building Full Stack Apps with Firebase StudioKDnuggets Firebase Studio revolutionizes full-stack app development by unifying a cloud-based IDE, the robust Firebase platform, and the power of Gemini’s AI agents.
Firebase Studio revolutionizes full-stack app development by unifying a cloud-based IDE, the robust Firebase platform, and the power of Gemini’s AI agents. Read More
From Dataset to DataFrame to Deployed: Your First Project with Pandas & Scikit-learnKDnuggets In this article, I will take you through a gentle, beginner-friendly machine learning project in which we will build together a regression model that predicts employee income based on socio-economic attributes.
In this article, I will take you through a gentle, beginner-friendly machine learning project in which we will build together a regression model that predicts employee income based on socio-economic attributes. Read More
Understanding prompt injections: a frontier security challengeOpenAI News Prompt injections are a frontier security challenge for AI systems. Learn how these attacks work and how OpenAI is advancing research, training models, and building safeguards for users.
Prompt injections are a frontier security challenge for AI systems. Learn how these attacks work and how OpenAI is advancing research, training models, and building safeguards for users. Read More
Efficient Neural Networks with Discrete Cosine Transform Activationscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.03531v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: In this paper, we extend our previous work on the Expressive Neural Network (ENN), a multilayer perceptron with adaptive activation functions parametrized using the Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT). Building upon previous work that demonstrated the strong expressiveness of ENNs with compact architectures, we now emphasize their efficiency, interpretability and pruning capabilities. The DCT-based parameterization provides a structured and decorrelated representation that reveals the functional role of each neuron and allows direct identification of redundant components. Leveraging this property, we propose an efficient pruning strategy that removes unnecessary DCT coefficients with negligible or no loss in performance. Experimental results across classification and implicit neural representation tasks confirm that ENNs achieve state-of-the-art accuracy while maintaining a low number of parameters. Furthermore, up to 40% of the activation coefficients can be safely pruned, thanks to the orthogonality and bounded nature of the DCT basis. Overall, these findings demonstrate that the ENN framework offers a principled integration of signal processing concepts into neural network design, achieving a balanced trade-off between expressiveness, compactness, and interpretability.
arXiv:2511.03531v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: In this paper, we extend our previous work on the Expressive Neural Network (ENN), a multilayer perceptron with adaptive activation functions parametrized using the Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT). Building upon previous work that demonstrated the strong expressiveness of ENNs with compact architectures, we now emphasize their efficiency, interpretability and pruning capabilities. The DCT-based parameterization provides a structured and decorrelated representation that reveals the functional role of each neuron and allows direct identification of redundant components. Leveraging this property, we propose an efficient pruning strategy that removes unnecessary DCT coefficients with negligible or no loss in performance. Experimental results across classification and implicit neural representation tasks confirm that ENNs achieve state-of-the-art accuracy while maintaining a low number of parameters. Furthermore, up to 40% of the activation coefficients can be safely pruned, thanks to the orthogonality and bounded nature of the DCT basis. Overall, these findings demonstrate that the ENN framework offers a principled integration of signal processing concepts into neural network design, achieving a balanced trade-off between expressiveness, compactness, and interpretability. Read More
PerfDojo: Automated ML Library Generation for Heterogeneous Architecturescs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.03586v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: The increasing complexity of machine learning models and the proliferation of diverse hardware architectures (CPUs, GPUs, accelerators) make achieving optimal performance a significant challenge. Heterogeneity in instruction sets, specialized kernel requirements for different data types and model features (e.g., sparsity, quantization), and architecture-specific optimizations complicate performance tuning. Manual optimization is resource-intensive, while existing automatic approaches often rely on complex hardware-specific heuristics and uninterpretable intermediate representations, hindering performance portability. We introduce PerfLLM, a novel automatic optimization methodology leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) and Reinforcement Learning (RL). Central to this is PerfDojo, an environment framing optimization as an RL game using a human-readable, mathematically-inspired code representation that guarantees semantic validity through transformations. This allows effective optimization without prior hardware knowledge, facilitating both human analysis and RL agent training. We demonstrate PerfLLM’s ability to achieve significant performance gains across diverse CPU (x86, Arm, RISC-V) and GPU architectures.
arXiv:2511.03586v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: The increasing complexity of machine learning models and the proliferation of diverse hardware architectures (CPUs, GPUs, accelerators) make achieving optimal performance a significant challenge. Heterogeneity in instruction sets, specialized kernel requirements for different data types and model features (e.g., sparsity, quantization), and architecture-specific optimizations complicate performance tuning. Manual optimization is resource-intensive, while existing automatic approaches often rely on complex hardware-specific heuristics and uninterpretable intermediate representations, hindering performance portability. We introduce PerfLLM, a novel automatic optimization methodology leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) and Reinforcement Learning (RL). Central to this is PerfDojo, an environment framing optimization as an RL game using a human-readable, mathematically-inspired code representation that guarantees semantic validity through transformations. This allows effective optimization without prior hardware knowledge, facilitating both human analysis and RL agent training. We demonstrate PerfLLM’s ability to achieve significant performance gains across diverse CPU (x86, Arm, RISC-V) and GPU architectures. Read More
When Generative Artificial Intelligence meets Extended Reality: A Systematic Reviewcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.03282v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: With the continuous advancement of technology, the application of generative artificial intelligence (AI) in various fields is gradually demonstrating great potential, particularly when combined with Extended Reality (XR), creating unprecedented possibilities. This survey article systematically reviews the applications of generative AI in XR, covering as much relevant literature as possible from 2023 to 2025. The application areas of generative AI in XR and its key technology implementations are summarised through PRISMA screening and analysis of the final 26 articles. The survey highlights existing articles from the last three years related to how XR utilises generative AI, providing insights into current trends and research gaps. We also explore potential opportunities for future research to further empower XR through generative AI, providing guidance and information for future generative XR research.
arXiv:2511.03282v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: With the continuous advancement of technology, the application of generative artificial intelligence (AI) in various fields is gradually demonstrating great potential, particularly when combined with Extended Reality (XR), creating unprecedented possibilities. This survey article systematically reviews the applications of generative AI in XR, covering as much relevant literature as possible from 2023 to 2025. The application areas of generative AI in XR and its key technology implementations are summarised through PRISMA screening and analysis of the final 26 articles. The survey highlights existing articles from the last three years related to how XR utilises generative AI, providing insights into current trends and research gaps. We also explore potential opportunities for future research to further empower XR through generative AI, providing guidance and information for future generative XR research. Read More
Whisper Leak: a side-channel attack on Large Language Modelscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.03675v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in sensitive domains including healthcare, legal services, and confidential communications, where privacy is paramount. This paper introduces Whisper Leak, a side-channel attack that infers user prompt topics from encrypted LLM traffic by analyzing packet size and timing patterns in streaming responses. Despite TLS encryption protecting content, these metadata patterns leak sufficient information to enable topic classification. We demonstrate the attack across 28 popular LLMs from major providers, achieving near-perfect classification (often >98% AUPRC) and high precision even at extreme class imbalance (10,000:1 noise-to-target ratio). For many models, we achieve 100% precision in identifying sensitive topics like “money laundering” while recovering 5-20% of target conversations. This industry-wide vulnerability poses significant risks for users under network surveillance by ISPs, governments, or local adversaries. We evaluate three mitigation strategies – random padding, token batching, and packet injection – finding that while each reduces attack effectiveness, none provides complete protection. Through responsible disclosure, we have collaborated with providers to implement initial countermeasures. Our findings underscore the need for LLM providers to address metadata leakage as AI systems handle increasingly sensitive information.
arXiv:2511.03675v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in sensitive domains including healthcare, legal services, and confidential communications, where privacy is paramount. This paper introduces Whisper Leak, a side-channel attack that infers user prompt topics from encrypted LLM traffic by analyzing packet size and timing patterns in streaming responses. Despite TLS encryption protecting content, these metadata patterns leak sufficient information to enable topic classification. We demonstrate the attack across 28 popular LLMs from major providers, achieving near-perfect classification (often >98% AUPRC) and high precision even at extreme class imbalance (10,000:1 noise-to-target ratio). For many models, we achieve 100% precision in identifying sensitive topics like “money laundering” while recovering 5-20% of target conversations. This industry-wide vulnerability poses significant risks for users under network surveillance by ISPs, governments, or local adversaries. We evaluate three mitigation strategies – random padding, token batching, and packet injection – finding that while each reduces attack effectiveness, none provides complete protection. Through responsible disclosure, we have collaborated with providers to implement initial countermeasures. Our findings underscore the need for LLM providers to address metadata leakage as AI systems handle increasingly sensitive information. Read More