The Benefits of an “Everything” Notebook in NotebookLMKDnuggets The goal of an “everything” notebook in NotebookLM is having your entire professional memory instantly accessible and understandable.
The goal of an “everything” notebook in NotebookLM is having your entire professional memory instantly accessible and understandable. Read More
Building ReAct Agents with LangGraph: A Beginner’s GuideMachineLearningMastery.com
Neuro drives national retail wins with ChatGPT BusinessOpenAI News Neuro uses ChatGPT Business to scale nationwide with fewer than seventy employees. From drafting contracts to uncovering insights in customer data, the team saves time, cuts costs, and turns ideas into growth.
Neuro uses ChatGPT Business to scale nationwide with fewer than seventy employees. From drafting contracts to uncovering insights in customer data, the team saves time, cuts costs, and turns ideas into growth. Read More
Procedural Knowledge Improves Agentic LLM Workflowscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.07568v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) often struggle when performing agentic tasks without substantial tool support, prom-pt engineering, or fine tuning. Despite research showing that domain-dependent, procedural knowledge can dramatically increase planning efficiency, little work evaluates its potential for improving LLM performance on agentic tasks that may require implicit planning. We formalize, implement, and evaluate an agentic LLM workflow that leverages procedural knowledge in the form of a hierarchical task network (HTN). Empirical results of our implementation show that hand-coded HTNs can dramatically improve LLM performance on agentic tasks, and using HTNs can boost a 20b or 70b parameter LLM to outperform a much larger 120b parameter LLM baseline. Furthermore, LLM-created HTNs improve overall performance, though less so. The results suggest that leveraging expertise–from humans, documents, or LLMs–to curate procedural knowledge will become another important tool for improving LLM workflows.
arXiv:2511.07568v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) often struggle when performing agentic tasks without substantial tool support, prom-pt engineering, or fine tuning. Despite research showing that domain-dependent, procedural knowledge can dramatically increase planning efficiency, little work evaluates its potential for improving LLM performance on agentic tasks that may require implicit planning. We formalize, implement, and evaluate an agentic LLM workflow that leverages procedural knowledge in the form of a hierarchical task network (HTN). Empirical results of our implementation show that hand-coded HTNs can dramatically improve LLM performance on agentic tasks, and using HTNs can boost a 20b or 70b parameter LLM to outperform a much larger 120b parameter LLM baseline. Furthermore, LLM-created HTNs improve overall performance, though less so. The results suggest that leveraging expertise–from humans, documents, or LLMs–to curate procedural knowledge will become another important tool for improving LLM workflows. Read More
How to Build an End-to-End Interactive Analytics Dashboard Using PyGWalker Features for Insightful Data ExplorationMarkTechPost In this tutorial, we explore the advanced capabilities of PyGWalker, a powerful tool for visual data analysis that integrates seamlessly with pandas. We begin by generating a realistic e-commerce dataset enriched with time, demographic, and marketing features to mimic real-world business data. We then prepare multiple analytical views, including daily sales, category performance, and customer
The post How to Build an End-to-End Interactive Analytics Dashboard Using PyGWalker Features for Insightful Data Exploration appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In this tutorial, we explore the advanced capabilities of PyGWalker, a powerful tool for visual data analysis that integrates seamlessly with pandas. We begin by generating a realistic e-commerce dataset enriched with time, demographic, and marketing features to mimic real-world business data. We then prepare multiple analytical views, including daily sales, category performance, and customer
The post How to Build an End-to-End Interactive Analytics Dashboard Using PyGWalker Features for Insightful Data Exploration appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
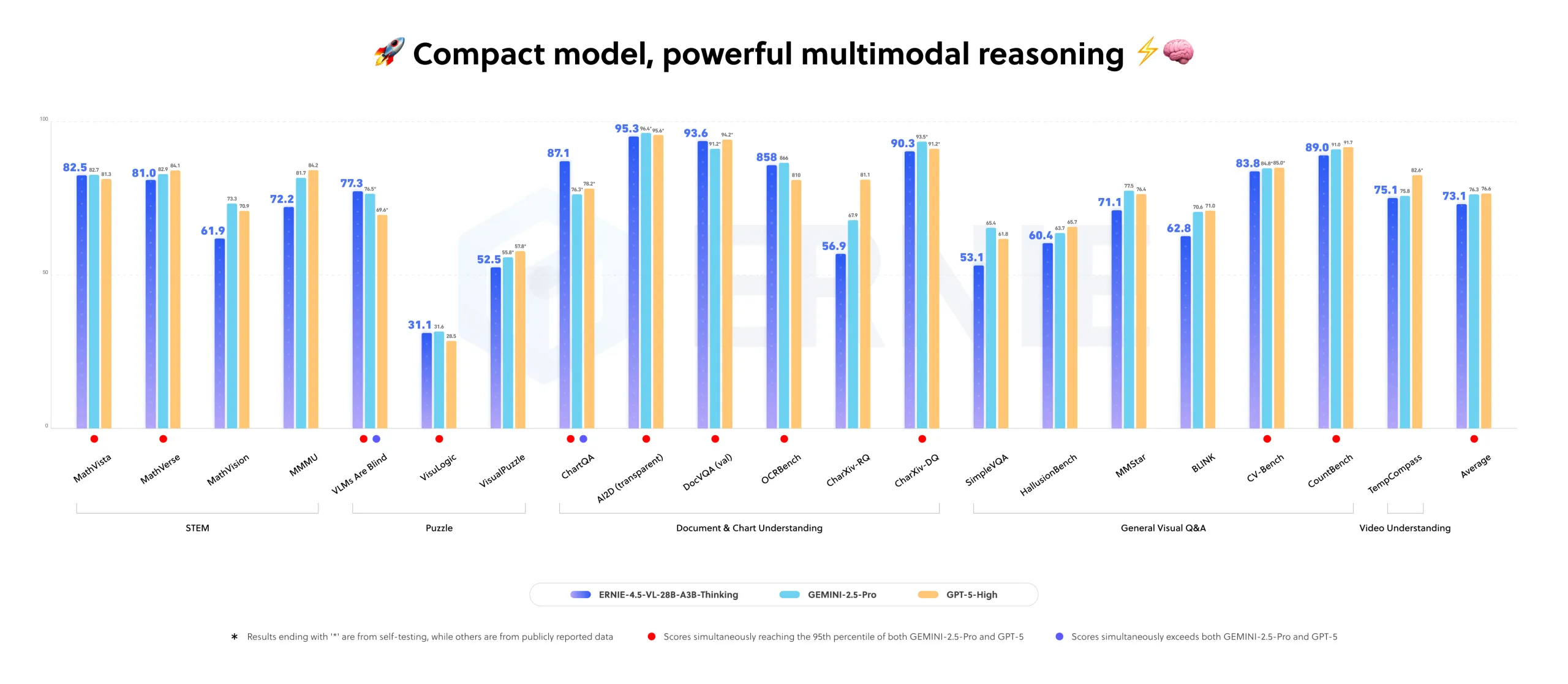
Baidu Releases ERNIE-4.5-VL-28B-A3B-Thinking: An Open-Source and Compact Multimodal Reasoning Model Under the ERNIE-4.5 FamilyMarkTechPost How can we get large model level multimodal reasoning for documents, charts and videos while running only a 3B class model in production? Baidu has added a new model to the ERNIE-4.5 open source family. ERNIE-4.5-VL-28B-A3B-Thinking is a vision language model that focuses on document, chart and video understanding with a small active parameter budget.
The post Baidu Releases ERNIE-4.5-VL-28B-A3B-Thinking: An Open-Source and Compact Multimodal Reasoning Model Under the ERNIE-4.5 Family appeared first on MarkTechPost.
How can we get large model level multimodal reasoning for documents, charts and videos while running only a 3B class model in production? Baidu has added a new model to the ERNIE-4.5 open source family. ERNIE-4.5-VL-28B-A3B-Thinking is a vision language model that focuses on document, chart and video understanding with a small active parameter budget.
The post Baidu Releases ERNIE-4.5-VL-28B-A3B-Thinking: An Open-Source and Compact Multimodal Reasoning Model Under the ERNIE-4.5 Family appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
AI-Driven Contribution Evaluation and Conflict Resolution: A Framework & Design for Group Workload Investigationcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.07667v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: The equitable assessment of individual contribution in teams remains a persistent challenge, where conflict and disparity in workload can result in unfair performance evaluation, often requiring manual intervention – a costly and challenging process. We survey existing tool features and identify a gap in conflict resolution methods and AI integration. To address this, we propose a framework and implementation design for a novel AI-enhanced tool that assists in dispute investigation. The framework organises heterogeneous artefacts – submissions (code, text, media), communications (chat, email), coordination records (meeting logs, tasks), peer assessments, and contextual information – into three dimensions with nine benchmarks: Contribution, Interaction, and Role. Objective measures are normalised, aggregated per dimension, and paired with inequality measures (Gini index) to surface conflict markers. A Large Language Model (LLM) architecture performs validated and contextual analysis over these measures to generate interpretable and transparent advisory judgments. We argue for feasibility under current statutory and institutional policy, and outline practical analytics (sentimental, task fidelity, word/line count, etc.), bias safeguards, limitations, and practical challenges.
arXiv:2511.07667v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: The equitable assessment of individual contribution in teams remains a persistent challenge, where conflict and disparity in workload can result in unfair performance evaluation, often requiring manual intervention – a costly and challenging process. We survey existing tool features and identify a gap in conflict resolution methods and AI integration. To address this, we propose a framework and implementation design for a novel AI-enhanced tool that assists in dispute investigation. The framework organises heterogeneous artefacts – submissions (code, text, media), communications (chat, email), coordination records (meeting logs, tasks), peer assessments, and contextual information – into three dimensions with nine benchmarks: Contribution, Interaction, and Role. Objective measures are normalised, aggregated per dimension, and paired with inequality measures (Gini index) to surface conflict markers. A Large Language Model (LLM) architecture performs validated and contextual analysis over these measures to generate interpretable and transparent advisory judgments. We argue for feasibility under current statutory and institutional policy, and outline practical analytics (sentimental, task fidelity, word/line count, etc.), bias safeguards, limitations, and practical challenges. Read More
Google reveals its own version of Apple’s AI cloudAI News Google has rolled out Private AI Compute, a new cloud-based processing system designed to bring the privacy of on-device AI to the cloud. The platform aims to give users faster, more capable AI experiences without compromising data security. It combines Google’s most advanced Gemini models with strict privacy safeguards, reflecting the company’s ongoing effort to
The post Google reveals its own version of Apple’s AI cloud appeared first on AI News.
Google has rolled out Private AI Compute, a new cloud-based processing system designed to bring the privacy of on-device AI to the cloud. The platform aims to give users faster, more capable AI experiences without compromising data security. It combines Google’s most advanced Gemini models with strict privacy safeguards, reflecting the company’s ongoing effort to
The post Google reveals its own version of Apple’s AI cloud appeared first on AI News. Read More
ResearchRubrics: A Benchmark of Prompts and Rubrics For Evaluating Deep Research Agentscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.07685v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Deep Research (DR) is an emerging agent application that leverages large language models (LLMs) to address open-ended queries. It requires the integration of several capabilities, including multi-step reasoning, cross-document synthesis, and the generation of evidence-backed, long-form answers. Evaluating DR remains challenging because responses are lengthy and diverse, admit many valid solutions, and often depend on dynamic information sources. We introduce ResearchRubrics, a standardized benchmark for DR built with over 2,800+ hours of human labor that pairs realistic, domain-diverse prompts with 2,500+ expert-written, fine-grained rubrics to assess factual grounding, reasoning soundness, and clarity. We also propose a new complexity framework for categorizing DR tasks along three axes: conceptual breadth, logical nesting, and exploration. In addition, we develop human and model-based evaluation protocols that measure rubric adherence for DR agents. We evaluate several state-of-the-art DR systems and find that even leading agents like Gemini’s DR and OpenAI’s DR achieve under 68% average compliance with our rubrics, primarily due to missed implicit context and inadequate reasoning about retrieved information. Our results highlight the need for robust, scalable assessment of deep research capabilities, to which end we release ResearchRubrics(including all prompts, rubrics, and evaluation code) to facilitate progress toward well-justified research assistants.
arXiv:2511.07685v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Deep Research (DR) is an emerging agent application that leverages large language models (LLMs) to address open-ended queries. It requires the integration of several capabilities, including multi-step reasoning, cross-document synthesis, and the generation of evidence-backed, long-form answers. Evaluating DR remains challenging because responses are lengthy and diverse, admit many valid solutions, and often depend on dynamic information sources. We introduce ResearchRubrics, a standardized benchmark for DR built with over 2,800+ hours of human labor that pairs realistic, domain-diverse prompts with 2,500+ expert-written, fine-grained rubrics to assess factual grounding, reasoning soundness, and clarity. We also propose a new complexity framework for categorizing DR tasks along three axes: conceptual breadth, logical nesting, and exploration. In addition, we develop human and model-based evaluation protocols that measure rubric adherence for DR agents. We evaluate several state-of-the-art DR systems and find that even leading agents like Gemini’s DR and OpenAI’s DR achieve under 68% average compliance with our rubrics, primarily due to missed implicit context and inadequate reasoning about retrieved information. Our results highlight the need for robust, scalable assessment of deep research capabilities, to which end we release ResearchRubrics(including all prompts, rubrics, and evaluation code) to facilitate progress toward well-justified research assistants. Read More
Text-based Aerial-Ground Person Retrievalcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.08369v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: This work introduces Text-based Aerial-Ground Person Retrieval (TAG-PR), which aims to retrieve person images from heterogeneous aerial and ground views with textual descriptions. Unlike traditional Text-based Person Retrieval (T-PR), which focuses solely on ground-view images, TAG-PR introduces greater practical significance and presents unique challenges due to the large viewpoint discrepancy across images. To support this task, we contribute: (1) TAG-PEDES dataset, constructed from public benchmarks with automatically generated textual descriptions, enhanced by a diversified text generation paradigm to ensure robustness under view heterogeneity; and (2) TAG-CLIP, a novel retrieval framework that addresses view heterogeneity through a hierarchically-routed mixture of experts module to learn view-specific and view-agnostic features and a viewpoint decoupling strategy to decouple view-specific features for better cross-modal alignment. We evaluate the effectiveness of TAG-CLIP on both the proposed TAG-PEDES dataset and existing T-PR benchmarks. The dataset and code are available at https://github.com/Flame-Chasers/TAG-PR.
arXiv:2511.08369v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: This work introduces Text-based Aerial-Ground Person Retrieval (TAG-PR), which aims to retrieve person images from heterogeneous aerial and ground views with textual descriptions. Unlike traditional Text-based Person Retrieval (T-PR), which focuses solely on ground-view images, TAG-PR introduces greater practical significance and presents unique challenges due to the large viewpoint discrepancy across images. To support this task, we contribute: (1) TAG-PEDES dataset, constructed from public benchmarks with automatically generated textual descriptions, enhanced by a diversified text generation paradigm to ensure robustness under view heterogeneity; and (2) TAG-CLIP, a novel retrieval framework that addresses view heterogeneity through a hierarchically-routed mixture of experts module to learn view-specific and view-agnostic features and a viewpoint decoupling strategy to decouple view-specific features for better cross-modal alignment. We evaluate the effectiveness of TAG-CLIP on both the proposed TAG-PEDES dataset and existing T-PR benchmarks. The dataset and code are available at https://github.com/Flame-Chasers/TAG-PR. Read More