Oligo Security has warned of ongoing attacks exploiting a two-year-old security flaw in the Ray open-source artificial intelligence (AI) framework to turn infected clusters with NVIDIA GPUs into a self-replicating cryptocurrency mining botnet. The activity, codenamed ShadowRay 2.0, is an evolution of a prior wave that was observed between September 2023 and March 2024. The […]
A unique take on the software update gambit has allowed “PlushDaemon” to evade attention as it mostly targets Chinese organizations. Read More
Editors from Dark Reading, Cybersecurity Dive, and TechTarget Search Security break down the depressing state of cybersecurity awareness campaigns and how organizations can overcome basic struggles with password hygiene and phishing attacks. Read More
A major spike in malicious scanning against Palo Alto Networks GlobalProtect portals has been detected, starting on November 14, 2025. […] Read More
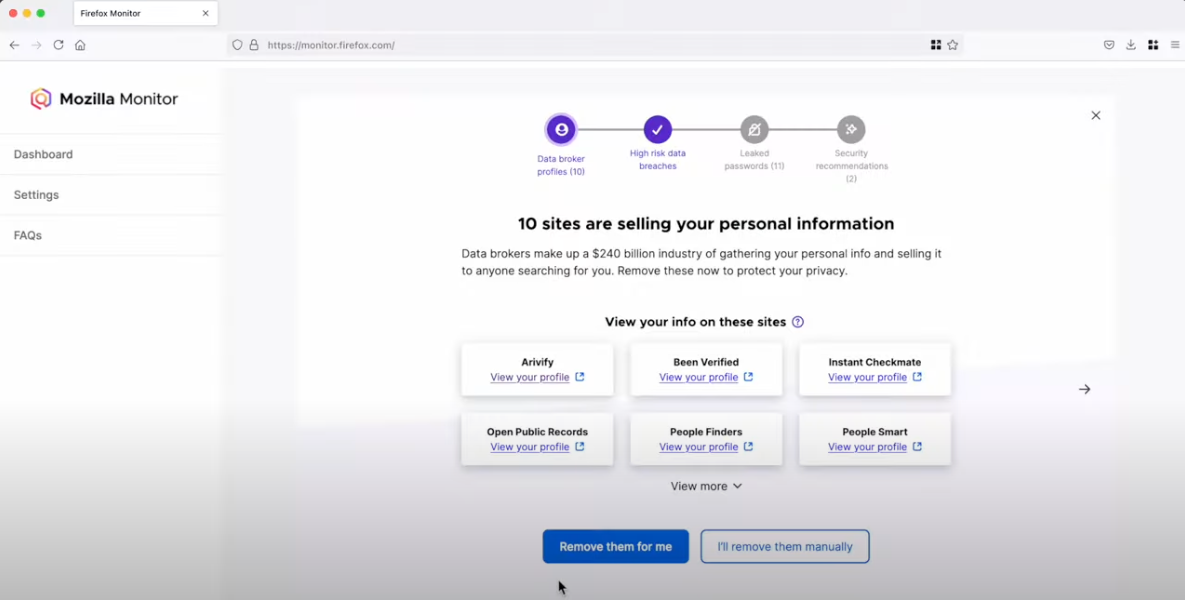
In March 2024, Mozilla said it was winding down its collaboration with Onerep — an identity protection service offered with the Firefox web browser that promises to remove users from hundreds of people-search sites — after KrebsOnSecurity revealed Onerep’s founder had created dozens of people-search services and was continuing to operate at least one of […]
Near-Lossless Model Compression Enables Longer Context Inference in DNA Large Language Modelscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.14694v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Trained on massive cross-species DNA corpora, DNA large language models (LLMs) learn the fundamental “grammar” and evolutionary patterns of genomic sequences. This makes them powerful priors for DNA sequence modeling, particularly over long ranges. However, two major constraints hinder their use in practice: the quadratic computational cost of self-attention and the growing memory required for key-value (KV) caches during autoregressive decoding. These constraints force the use of heuristics such as fixed-window truncation or sliding windows, which compromise fidelity on ultra-long sequences by discarding distant information. We introduce FOCUS (Feature-Oriented Compression for Ultra-long Self-attention), a progressive context-compression module that can be plugged into pretrained DNA LLMs. FOCUS combines the established k-mer representation in genomics with learnable hierarchical compression: it inserts summary tokens at k-mer granularity and progressively compresses attention key and value activations across multiple Transformer layers, retaining only the summary KV states across windows while discarding ordinary-token KV. A shared-boundary windowing scheme yields a stationary cross-window interface that propagates long-range information with minimal loss. We validate FOCUS on an Evo-2-based DNA LLM fine-tuned on GRCh38 chromosome 1 with self-supervised training and randomized compression schedules to promote robustness across compression ratios. On held-out human chromosomes, FOCUS achieves near-lossless fidelity: compressing a 1 kb context into only 10 summary tokens (about 100x) shifts the average per-nucleotide probability by only about 0.0004. Compared to a baseline without compression, FOCUS reduces KV-cache memory and converts effective inference scaling from O(N^2) to near-linear O(N), enabling about 100x longer inference windows on commodity GPUs with near-lossless fidelity.
arXiv:2511.14694v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Trained on massive cross-species DNA corpora, DNA large language models (LLMs) learn the fundamental “grammar” and evolutionary patterns of genomic sequences. This makes them powerful priors for DNA sequence modeling, particularly over long ranges. However, two major constraints hinder their use in practice: the quadratic computational cost of self-attention and the growing memory required for key-value (KV) caches during autoregressive decoding. These constraints force the use of heuristics such as fixed-window truncation or sliding windows, which compromise fidelity on ultra-long sequences by discarding distant information. We introduce FOCUS (Feature-Oriented Compression for Ultra-long Self-attention), a progressive context-compression module that can be plugged into pretrained DNA LLMs. FOCUS combines the established k-mer representation in genomics with learnable hierarchical compression: it inserts summary tokens at k-mer granularity and progressively compresses attention key and value activations across multiple Transformer layers, retaining only the summary KV states across windows while discarding ordinary-token KV. A shared-boundary windowing scheme yields a stationary cross-window interface that propagates long-range information with minimal loss. We validate FOCUS on an Evo-2-based DNA LLM fine-tuned on GRCh38 chromosome 1 with self-supervised training and randomized compression schedules to promote robustness across compression ratios. On held-out human chromosomes, FOCUS achieves near-lossless fidelity: compressing a 1 kb context into only 10 summary tokens (about 100x) shifts the average per-nucleotide probability by only about 0.0004. Compared to a baseline without compression, FOCUS reduces KV-cache memory and converts effective inference scaling from O(N^2) to near-linear O(N), enabling about 100x longer inference windows on commodity GPUs with near-lossless fidelity. Read More
Deep Learning-Based Regional White Matter Hyperintensity Mapping as a Robust Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Diseasecs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.14588v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: White matter hyperintensities (WMH) are key imaging markers in cognitive aging, Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and related dementias. Although automated methods for WMH segmentation have advanced, most provide only global lesion load and overlook their spatial distribution across distinct white matter regions. We propose a deep learning framework for robust WMH segmentation and localization, evaluated across public datasets and an independent Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) cohort. Our results show that the predicted lesion loads are in line with the reference WMH estimates, confirming the robustness to variations in lesion load, acquisition, and demographics. Beyond accurate segmentation, we quantify WMH load within anatomically defined regions and combine these measures with brain structure volumes to assess diagnostic value. Regional WMH volumes consistently outperform global lesion burden for disease classification, and integration with brain atrophy metrics further improves performance, reaching area under the curve (AUC) values up to 0.97. Several spatially distinct regions, particularly within anterior white matter tracts, are reproducibly associated with diagnostic status, indicating localized vulnerability in AD. These results highlight the added value of regional WMH quantification. Incorporating localized lesion metrics alongside atrophy markers may enhance early diagnosis and stratification in neurodegenerative disorders.
arXiv:2511.14588v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: White matter hyperintensities (WMH) are key imaging markers in cognitive aging, Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and related dementias. Although automated methods for WMH segmentation have advanced, most provide only global lesion load and overlook their spatial distribution across distinct white matter regions. We propose a deep learning framework for robust WMH segmentation and localization, evaluated across public datasets and an independent Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) cohort. Our results show that the predicted lesion loads are in line with the reference WMH estimates, confirming the robustness to variations in lesion load, acquisition, and demographics. Beyond accurate segmentation, we quantify WMH load within anatomically defined regions and combine these measures with brain structure volumes to assess diagnostic value. Regional WMH volumes consistently outperform global lesion burden for disease classification, and integration with brain atrophy metrics further improves performance, reaching area under the curve (AUC) values up to 0.97. Several spatially distinct regions, particularly within anterior white matter tracts, are reproducibly associated with diagnostic status, indicating localized vulnerability in AD. These results highlight the added value of regional WMH quantification. Incorporating localized lesion metrics alongside atrophy markers may enhance early diagnosis and stratification in neurodegenerative disorders. Read More
VisAidMath: Benchmarking Visual-Aided Mathematical Reasoningcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2410.22995v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: A hallmark of advanced artificial intelligence is the capacity to progress from passive visual perception to the strategic modification of visual information to facilitate complex reasoning. This advanced capability, however, remains critically underdeveloped in current Large Multi-modal Models (LMMs). The deficiency is often masked by evaluation metrics that prioritize final-answer accuracy, creating an illusion of competence where genuine reasoning is absent. Using the domain of geometric problem-solving as a precise instrument, we probe this issue through tasks that require constructing visual aids. To this end, we introduce textbf{VisAidMath}, a challenging benchmark, and our novel Three-Layered Funnel Evaluation Framework. This framework moves beyond simple accuracy (ACCU) to scrutinize the generation of valid visual aids (PVA) and the soundness of subsequent reasoning steps (SPRS). Our extensive experiments on state-of-the-art models, including Doubao-Seed-1.6 and o4, reveal a profound “Reasoning Illusion”. We observe that high surface-level accuracy conceals a catastrophic failure in the models’ ability to produce valid visual aids or to reason from them. Our findings expose a fundamental schism between visual perception and logical deduction in modern LMMs. We host an evaluation platform at CodaBench for testing publicly. Homepage: https://nlp2ct.github.io/VisAidMathHomepage/ Evaluation: https://www.codabench.org/competitions/7634/
arXiv:2410.22995v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: A hallmark of advanced artificial intelligence is the capacity to progress from passive visual perception to the strategic modification of visual information to facilitate complex reasoning. This advanced capability, however, remains critically underdeveloped in current Large Multi-modal Models (LMMs). The deficiency is often masked by evaluation metrics that prioritize final-answer accuracy, creating an illusion of competence where genuine reasoning is absent. Using the domain of geometric problem-solving as a precise instrument, we probe this issue through tasks that require constructing visual aids. To this end, we introduce textbf{VisAidMath}, a challenging benchmark, and our novel Three-Layered Funnel Evaluation Framework. This framework moves beyond simple accuracy (ACCU) to scrutinize the generation of valid visual aids (PVA) and the soundness of subsequent reasoning steps (SPRS). Our extensive experiments on state-of-the-art models, including Doubao-Seed-1.6 and o4, reveal a profound “Reasoning Illusion”. We observe that high surface-level accuracy conceals a catastrophic failure in the models’ ability to produce valid visual aids or to reason from them. Our findings expose a fundamental schism between visual perception and logical deduction in modern LMMs. We host an evaluation platform at CodaBench for testing publicly. Homepage: https://nlp2ct.github.io/VisAidMathHomepage/ Evaluation: https://www.codabench.org/competitions/7634/ Read More
Biased Minds Meet Biased AI: How Class Imbalance Shapes Appropriate Reliance and Interacts with Human Base Rate Neglectcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.14591v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Humans increasingly interact with artificial intelligence (AI) in decision-making. However, both AI and humans are prone to biases. While AI and human biases have been studied extensively in isolation, this paper examines their complex interaction. Specifically, we examined how class imbalance as an AI bias affects people’s ability to appropriately rely on an AI-based decision-support system, and how it interacts with base rate neglect as a human bias. In a within-subject online study (N= 46), participants classified three diseases using an AI-based decision-support system trained on either a balanced or unbalanced dataset. We found that class imbalance disrupted participants’ calibration of AI reliance. Moreover, we observed mutually reinforcing effects between class imbalance and base rate neglect, offering evidence of a compound human-AI bias. Based on these findings, we advocate for an interactionist perspective and further research into the mutually reinforcing effects of biases in human-AI interaction.
arXiv:2511.14591v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Humans increasingly interact with artificial intelligence (AI) in decision-making. However, both AI and humans are prone to biases. While AI and human biases have been studied extensively in isolation, this paper examines their complex interaction. Specifically, we examined how class imbalance as an AI bias affects people’s ability to appropriately rely on an AI-based decision-support system, and how it interacts with base rate neglect as a human bias. In a within-subject online study (N= 46), participants classified three diseases using an AI-based decision-support system trained on either a balanced or unbalanced dataset. We found that class imbalance disrupted participants’ calibration of AI reliance. Moreover, we observed mutually reinforcing effects between class imbalance and base rate neglect, offering evidence of a compound human-AI bias. Based on these findings, we advocate for an interactionist perspective and further research into the mutually reinforcing effects of biases in human-AI interaction. Read More
Can Machines Think Like Humans? A Behavioral Evaluation of LLM Agents in Dictator Gamescs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2410.21359v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: As Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents increasingly engage with human society, how well do we understand their prosocial behaviors? We (1) investigate how LLM agents’ prosocial behaviors can be induced by different personas and benchmarked against human behaviors; and (2) introduce a social science approach to evaluate LLM agents’ decision-making. We explored how different personas and experimental framings affect these AI agents’ altruistic behavior in dictator games and compared their behaviors within the same LLM family, across various families, and with human behaviors. The findings reveal that merely assigning a human-like identity to LLMs does not produce human-like behaviors. These findings suggest that LLM agents’ reasoning does not consistently exhibit textual markers of human decision-making in dictator games and that their alignment with human behavior varies substantially across model architectures and prompt formulations; even worse, such dependence does not follow a clear pattern. As society increasingly integrates machine intelligence, “Prosocial AI” emerges as a promising and urgent research direction in philanthropic studies.
arXiv:2410.21359v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: As Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents increasingly engage with human society, how well do we understand their prosocial behaviors? We (1) investigate how LLM agents’ prosocial behaviors can be induced by different personas and benchmarked against human behaviors; and (2) introduce a social science approach to evaluate LLM agents’ decision-making. We explored how different personas and experimental framings affect these AI agents’ altruistic behavior in dictator games and compared their behaviors within the same LLM family, across various families, and with human behaviors. The findings reveal that merely assigning a human-like identity to LLMs does not produce human-like behaviors. These findings suggest that LLM agents’ reasoning does not consistently exhibit textual markers of human decision-making in dictator games and that their alignment with human behavior varies substantially across model architectures and prompt formulations; even worse, such dependence does not follow a clear pattern. As society increasingly integrates machine intelligence, “Prosocial AI” emerges as a promising and urgent research direction in philanthropic studies. Read More