Live-SWE-agent: Can Software Engineering Agents Self-Evolve on the Fly?cs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.13646v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Large Language Models (LLMs) are reshaping almost all industries, including software engineering. In recent years, a number of LLM agents have been proposed to solve real-world software problems. Such software agents are typically equipped with a suite of coding tools and can autonomously decide the next actions to form complete trajectories to solve end-to-end software tasks. While promising, they typically require dedicated design and may still be suboptimal, since it can be extremely challenging and costly to exhaust the entire agent scaffold design space. Recognizing that software agents are inherently software themselves that can be further refined/modified, researchers have proposed a number of self-improving software agents recently, including the Darwin-G”odel Machine (DGM). Meanwhile, such self-improving agents require costly offline training on specific benchmarks and may not generalize well across different LLMs or benchmarks. In this paper, we propose Live-SWE-agent, the first live software agent that can autonomously and continuously evolve itself on-the-fly during runtime when solving real-world software problems. More specifically, Live-SWE-agent starts with the most basic agent scaffold with only access to bash tools (e.g., mini-SWE-agent), and autonomously evolves its own scaffold implementation while solving real-world software problems. Our evaluation on the widely studied SWE-bench Verified benchmark shows that LIVE-SWE-AGENT can achieve an impressive solve rate of 77.4% without test-time scaling, outperforming all existing software agents, including the best proprietary solution. Moreover, Live-SWE-agent outperforms state-of-the-art manually crafted software agents on the recent SWE-Bench Pro benchmark, achieving the best-known solve rate of 45.8%.
arXiv:2511.13646v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Large Language Models (LLMs) are reshaping almost all industries, including software engineering. In recent years, a number of LLM agents have been proposed to solve real-world software problems. Such software agents are typically equipped with a suite of coding tools and can autonomously decide the next actions to form complete trajectories to solve end-to-end software tasks. While promising, they typically require dedicated design and may still be suboptimal, since it can be extremely challenging and costly to exhaust the entire agent scaffold design space. Recognizing that software agents are inherently software themselves that can be further refined/modified, researchers have proposed a number of self-improving software agents recently, including the Darwin-G”odel Machine (DGM). Meanwhile, such self-improving agents require costly offline training on specific benchmarks and may not generalize well across different LLMs or benchmarks. In this paper, we propose Live-SWE-agent, the first live software agent that can autonomously and continuously evolve itself on-the-fly during runtime when solving real-world software problems. More specifically, Live-SWE-agent starts with the most basic agent scaffold with only access to bash tools (e.g., mini-SWE-agent), and autonomously evolves its own scaffold implementation while solving real-world software problems. Our evaluation on the widely studied SWE-bench Verified benchmark shows that LIVE-SWE-AGENT can achieve an impressive solve rate of 77.4% without test-time scaling, outperforming all existing software agents, including the best proprietary solution. Moreover, Live-SWE-agent outperforms state-of-the-art manually crafted software agents on the recent SWE-Bench Pro benchmark, achieving the best-known solve rate of 45.8%. Read More
Thousands of credentials, authentication keys, and configuration data impacting organizations in sensitive sectors have been sitting in publicly accessible JSON snippets submitted to the JSONFormatter and CodeBeautify online tools that format and structure code. […] Read More
(c) SANS Internet Storm Center. https://isc.sans.edu Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 United States License. Read More
2026 will mark a pivotal shift in cybersecurity. Threat actors are moving from experimenting with AI to making it their primary weapon, using it to scale attacks, automate reconnaissance, and craft hyper-realistic social engineering campaigns. The Storm on the Horizon Global world instability, coupled with rapid technological advancement, will force security teams to adapt not […]
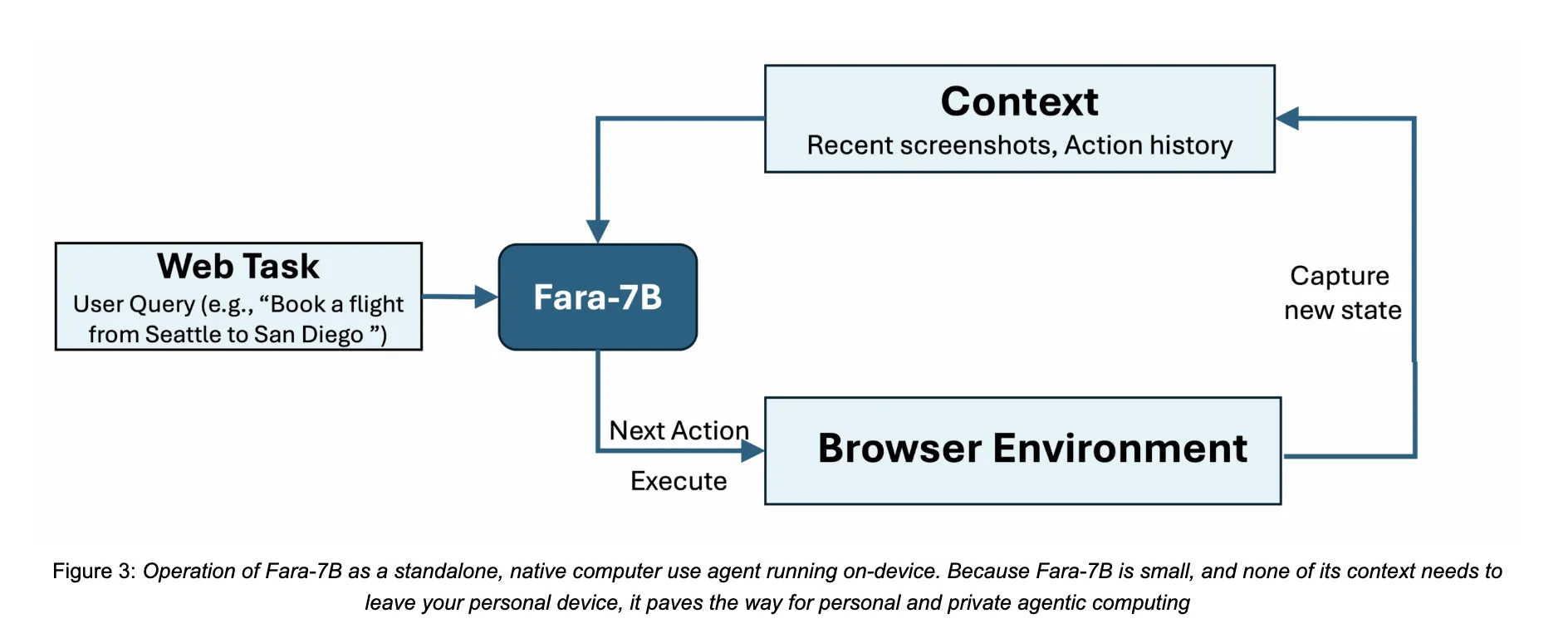
Microsoft AI Releases Fara-7B: An Efficient Agentic Model for Computer UseMarkTechPost How do we safely let an AI agent handle real web tasks like booking, searching, and form filling directly on our own devices without sending everything to the cloud? Microsoft Research has released Fara-7B, a 7 billion parameter agentic small language model designed specifically for computer use. It is an open weight Computer Use Agent
The post Microsoft AI Releases Fara-7B: An Efficient Agentic Model for Computer Use appeared first on MarkTechPost.
How do we safely let an AI agent handle real web tasks like booking, searching, and form filling directly on our own devices without sending everything to the cloud? Microsoft Research has released Fara-7B, a 7 billion parameter agentic small language model designed specifically for computer use. It is an open weight Computer Use Agent
The post Microsoft AI Releases Fara-7B: An Efficient Agentic Model for Computer Use appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Expanding data residency access to business customers worldwideOpenAI News OpenAI expands data residency for ChatGPT Enterprise, ChatGPT Edu, and the API Platform, enabling eligible customers to store data at rest in-region.
OpenAI expands data residency for ChatGPT Enterprise, ChatGPT Edu, and the API Platform, enabling eligible customers to store data at rest in-region. Read More
How to Create Professional Articles with LaTeX in CursorTowards Data Science Learn how to rapidly create professional articles and presentations with LaTeX in Cursor
The post How to Create Professional Articles with LaTeX in Cursor appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Learn how to rapidly create professional articles and presentations with LaTeX in Cursor
The post How to Create Professional Articles with LaTeX in Cursor appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
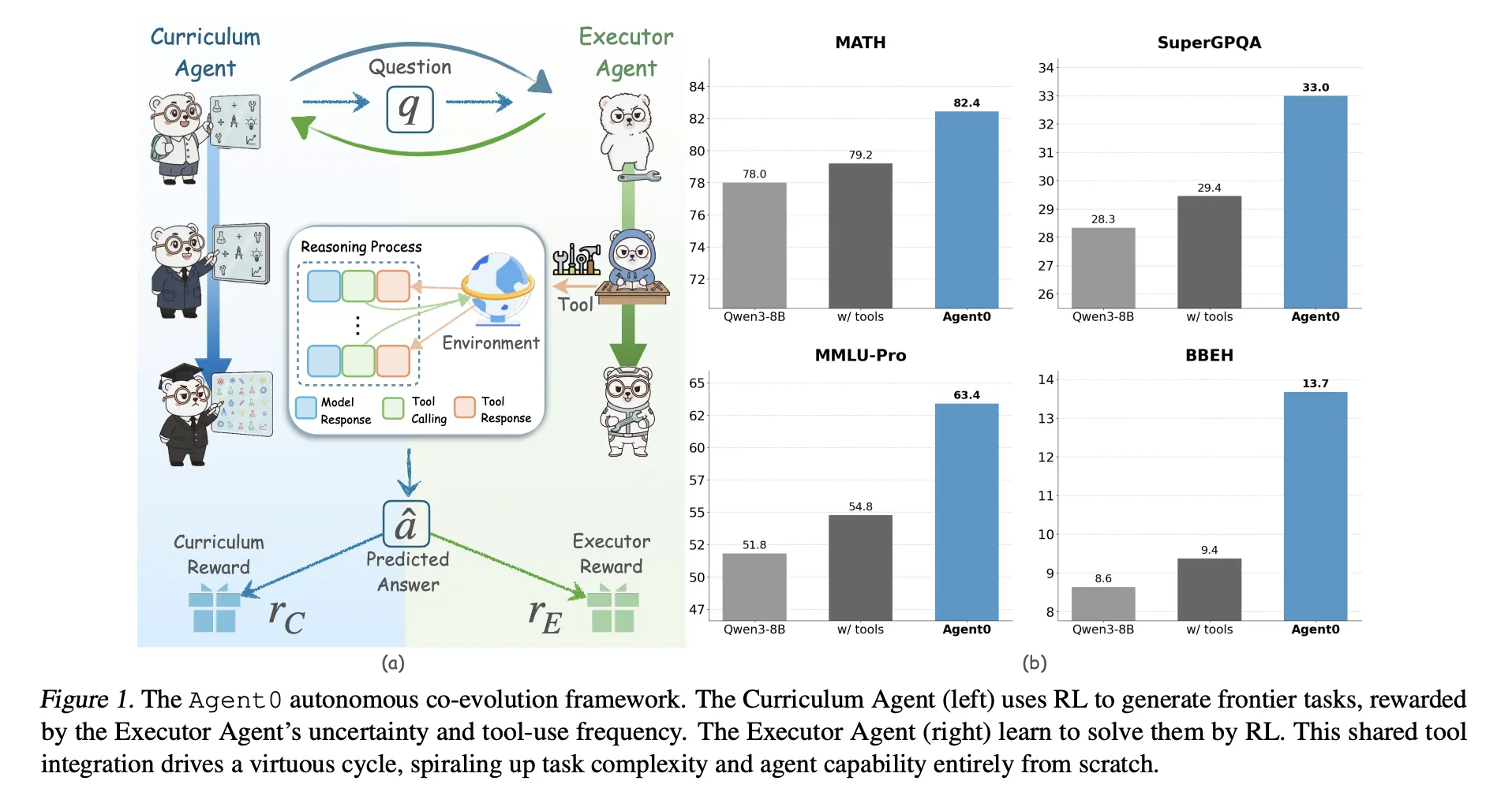
Agent0: A Fully Autonomous AI Framework that Evolves High-Performing Agents without External Data through Multi-Step Co-EvolutionMarkTechPost Large language models need huge human datasets, so what happens if the model must create all its own curriculum and teach itself to use tools? A team of researchers from UNC-Chapel Hill, Salesforce Research and Stanford University introduce ‘Agent0’, a fully autonomous framework that evolves high-performing agents without external data through multi-step co-evolution and seamless
The post Agent0: A Fully Autonomous AI Framework that Evolves High-Performing Agents without External Data through Multi-Step Co-Evolution appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Large language models need huge human datasets, so what happens if the model must create all its own curriculum and teach itself to use tools? A team of researchers from UNC-Chapel Hill, Salesforce Research and Stanford University introduce ‘Agent0’, a fully autonomous framework that evolves high-performing agents without external data through multi-step co-evolution and seamless
The post Agent0: A Fully Autonomous AI Framework that Evolves High-Performing Agents without External Data through Multi-Step Co-Evolution appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
How to Build a Neuro-Symbolic Hybrid Agent that Combines Logical Planning with Neural Perception for Robust Autonomous Decision-MakingMarkTechPost In this tutorial, we demonstrate how to combine the strengths of symbolic reasoning with neural learning to build a powerful hybrid agent. We focus on creating a neuro-symbolic architecture that uses classical planning for structure, rules, and goal-directed behavior, while neural networks handle perception and action refinement. As we walk through the code, we see
The post How to Build a Neuro-Symbolic Hybrid Agent that Combines Logical Planning with Neural Perception for Robust Autonomous Decision-Making appeared first on MarkTechPost.
In this tutorial, we demonstrate how to combine the strengths of symbolic reasoning with neural learning to build a powerful hybrid agent. We focus on creating a neuro-symbolic architecture that uses classical planning for structure, rules, and goal-directed behavior, while neural networks handle perception and action refinement. As we walk through the code, we see
The post How to Build a Neuro-Symbolic Hybrid Agent that Combines Logical Planning with Neural Perception for Robust Autonomous Decision-Making appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
AI Debaters are More Persuasive when Arguing in Alignment with Their Own Beliefscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2510.13912v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: The core premise of AI debate as a scalable oversight technique is that it is harder to lie convincingly than to refute a lie, enabling the judge to identify the correct position. Yet, existing debate experiments have relied on datasets with ground truth, where lying is reduced to defending an incorrect proposition. This overlooks a subjective dimension: lying also requires the belief that the claim defended is false. In this work, we apply debate to subjective questions and explicitly measure large language models’ prior beliefs before experiments. Debaters were asked to select their preferred position, then presented with a judge persona deliberately designed to conflict with their identified priors. This setup tested whether models would adopt sycophantic strategies, aligning with the judge’s presumed perspective to maximize persuasiveness, or remain faithful to their prior beliefs. We implemented and compared two debate protocols, sequential and simultaneous, to evaluate potential systematic biases. Finally, we assessed whether models were more persuasive and produced higher-quality arguments when defending positions consistent with their prior beliefs versus when arguing against them. Our main findings show that models tend to prefer defending stances aligned with the judge persona rather than their prior beliefs, sequential debate introduces significant bias favoring the second debater, models are more persuasive when defending positions aligned with their prior beliefs, and paradoxically, arguments misaligned with prior beliefs are rated as higher quality in pairwise comparison. These results can inform human judges to provide higher-quality training signals and contribute to more aligned AI systems, while revealing important aspects of human-AI interaction regarding persuasion dynamics in language models.
arXiv:2510.13912v3 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: The core premise of AI debate as a scalable oversight technique is that it is harder to lie convincingly than to refute a lie, enabling the judge to identify the correct position. Yet, existing debate experiments have relied on datasets with ground truth, where lying is reduced to defending an incorrect proposition. This overlooks a subjective dimension: lying also requires the belief that the claim defended is false. In this work, we apply debate to subjective questions and explicitly measure large language models’ prior beliefs before experiments. Debaters were asked to select their preferred position, then presented with a judge persona deliberately designed to conflict with their identified priors. This setup tested whether models would adopt sycophantic strategies, aligning with the judge’s presumed perspective to maximize persuasiveness, or remain faithful to their prior beliefs. We implemented and compared two debate protocols, sequential and simultaneous, to evaluate potential systematic biases. Finally, we assessed whether models were more persuasive and produced higher-quality arguments when defending positions consistent with their prior beliefs versus when arguing against them. Our main findings show that models tend to prefer defending stances aligned with the judge persona rather than their prior beliefs, sequential debate introduces significant bias favoring the second debater, models are more persuasive when defending positions aligned with their prior beliefs, and paradoxically, arguments misaligned with prior beliefs are rated as higher quality in pairwise comparison. These results can inform human judges to provide higher-quality training signals and contribute to more aligned AI systems, while revealing important aspects of human-AI interaction regarding persuasion dynamics in language models. Read More