Implementing the Rock Paper Scissors Game in PythonTowards Data Science A beginner-friendly Python tutorial using conditionals and the random module
The post Implementing the Rock Paper Scissors Game in Python appeared first on Towards Data Science.
A beginner-friendly Python tutorial using conditionals and the random module
The post Implementing the Rock Paper Scissors Game in Python appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
Edge AI inside the human body: Cochlear’s machine learning implant breakthroughAI News The next frontier for edge AI medical devices isn’t wearables or bedside monitors—it’s inside the human body itself. Cochlear’s newly launched Nucleus Nexa System represents the first cochlear implant capable of running machine learning algorithms while managing extreme power constraints, storing personalised data on-device, and receiving over-the-air firmware updates to improve its AI models over time. For AI
The post Edge AI inside the human body: Cochlear’s machine learning implant breakthrough appeared first on AI News.
The next frontier for edge AI medical devices isn’t wearables or bedside monitors—it’s inside the human body itself. Cochlear’s newly launched Nucleus Nexa System represents the first cochlear implant capable of running machine learning algorithms while managing extreme power constraints, storing personalised data on-device, and receiving over-the-air firmware updates to improve its AI models over time. For AI
The post Edge AI inside the human body: Cochlear’s machine learning implant breakthrough appeared first on AI News. Read More
BotaCLIP: Contrastive Learning for Botany-Aware Representation of Earth Observation Datacs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.21194v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Foundation models have demonstrated a remarkable ability to learn rich, transferable representations across diverse modalities such as images, text, and audio. In modern machine learning pipelines, these representations often replace raw data as the primary input for downstream tasks. In this paper, we address the challenge of adapting a pre-trained foundation model to inject domain-specific knowledge, without retraining from scratch or incurring significant computational costs. To this end, we introduce BotaCLIP, a lightweight multimodal contrastive framework that adapts a pre-trained Earth Observation foundation model (DOFA) by aligning high-resolution aerial imagery with botanical relev’es. Unlike generic embeddings, BotaCLIP internalizes ecological structure through contrastive learning with a regularization strategy that mitigates catastrophic forgetting. Once trained, the resulting embeddings serve as transferable representations for downstream predictors. Motivated by real-world applications in biodiversity modeling, we evaluated BotaCLIP representations in three ecological tasks: plant presence prediction, butterfly occurrence modeling, and soil trophic group abundance estimation. The results showed consistent improvements over those derived from DOFA and supervised baselines. More broadly, this work illustrates how domain-aware adaptation of foundation models can inject expert knowledge into data-scarce settings, enabling frugal representation learning.
arXiv:2511.21194v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Foundation models have demonstrated a remarkable ability to learn rich, transferable representations across diverse modalities such as images, text, and audio. In modern machine learning pipelines, these representations often replace raw data as the primary input for downstream tasks. In this paper, we address the challenge of adapting a pre-trained foundation model to inject domain-specific knowledge, without retraining from scratch or incurring significant computational costs. To this end, we introduce BotaCLIP, a lightweight multimodal contrastive framework that adapts a pre-trained Earth Observation foundation model (DOFA) by aligning high-resolution aerial imagery with botanical relev’es. Unlike generic embeddings, BotaCLIP internalizes ecological structure through contrastive learning with a regularization strategy that mitigates catastrophic forgetting. Once trained, the resulting embeddings serve as transferable representations for downstream predictors. Motivated by real-world applications in biodiversity modeling, we evaluated BotaCLIP representations in three ecological tasks: plant presence prediction, butterfly occurrence modeling, and soil trophic group abundance estimation. The results showed consistent improvements over those derived from DOFA and supervised baselines. More broadly, this work illustrates how domain-aware adaptation of foundation models can inject expert knowledge into data-scarce settings, enabling frugal representation learning. Read More
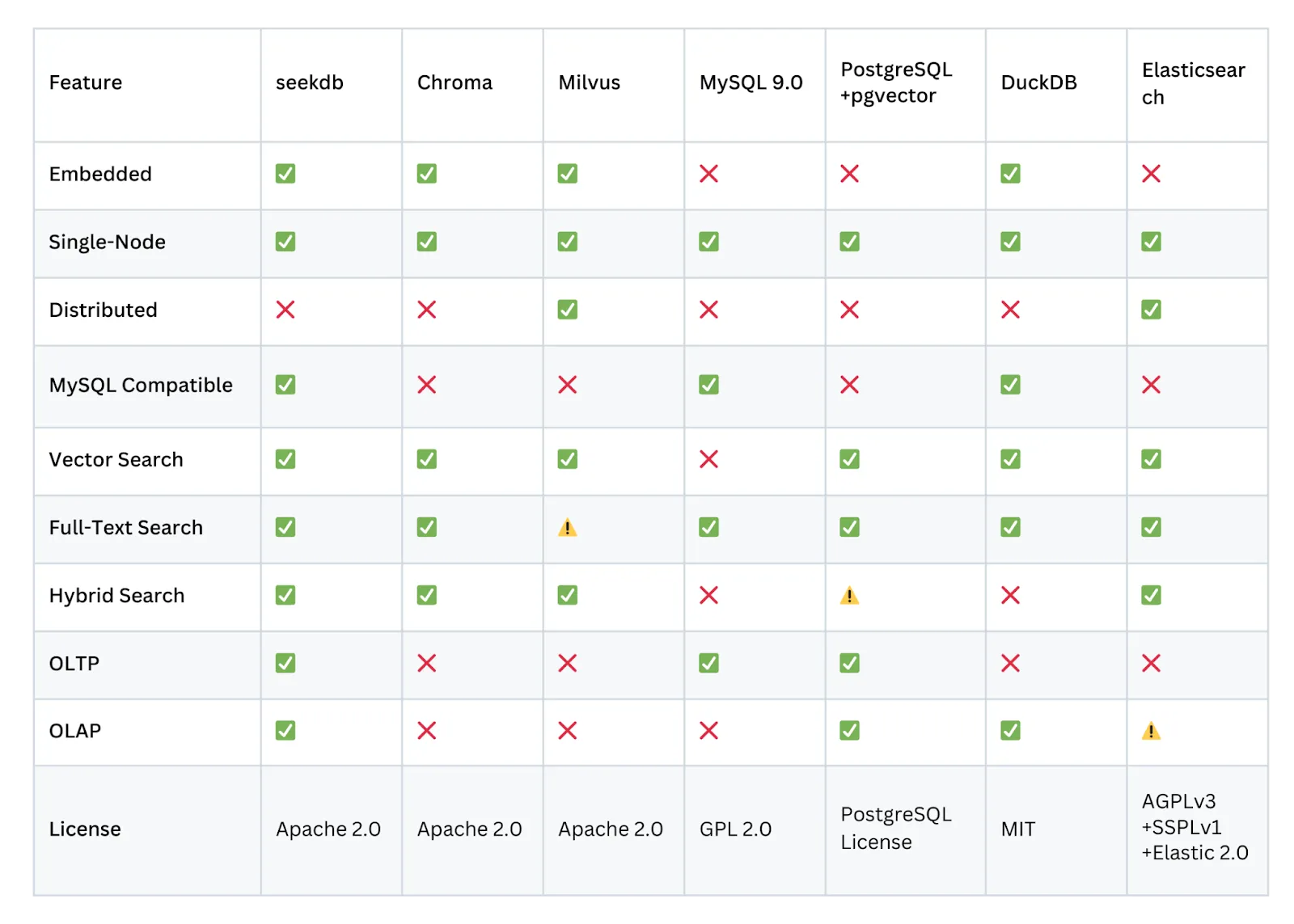
OceanBase Releases seekdb: An Open Source AI Native Hybrid Search Database for Multi-model RAG and AI AgentsMarkTechPost AI applications rarely deal with one clean table. They mix user profiles, chat logs, JSON metadata, embeddings, and sometimes spatial data. Most teams answer this with a patchwork of an OLTP database, a vector store, and a search engine. OceanBase released seekdb, an open source AI focused database (under the Apache 2.0 license). seekdb is
The post OceanBase Releases seekdb: An Open Source AI Native Hybrid Search Database for Multi-model RAG and AI Agents appeared first on MarkTechPost.
AI applications rarely deal with one clean table. They mix user profiles, chat logs, JSON metadata, embeddings, and sometimes spatial data. Most teams answer this with a patchwork of an OLTP database, a vector store, and a search engine. OceanBase released seekdb, an open source AI focused database (under the Apache 2.0 license). seekdb is
The post OceanBase Releases seekdb: An Open Source AI Native Hybrid Search Database for Multi-model RAG and AI Agents appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
SocialNav: Training Human-Inspired Foundation Model for Socially-Aware Embodied Navigationcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.21135v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Embodied navigation that adheres to social norms remains an open research challenge. Our textbf{SocialNav} is a foundational model for socially-aware navigation with a hierarchical “brain-action” architecture, capable of understanding high-level social norms and generating low-level, socially compliant trajectories. To enable such dual capabilities, we construct the SocNav Dataset, a large-scale collection of 7 million samples, comprising (1) a Cognitive Activation Dataset providing social reasoning signals such as chain-of-thought explanations and social traversability prediction, and (2) an Expert Trajectories Pyramid aggregating diverse navigation demonstrations from internet videos, simulated environments, and real-world robots. A multi-stage training pipeline is proposed to gradually inject and refine navigation intelligence: we first inject general navigation skills and social norms understanding into the model via imitation learning, and then refine such skills through a deliberately designed Socially-Aware Flow Exploration GRPO (SAFE-GRPO), the first flow-based reinforcement learning framework for embodied navigation that explicitly rewards socially compliant behaviors. SocialNav achieves +38% success rate and +46% social compliance rate compared to the state-of-the-art method, demonstrating strong gains in both navigation performance and social compliance. Our project page: https://amap-eai.github.io/SocialNav/
arXiv:2511.21135v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Embodied navigation that adheres to social norms remains an open research challenge. Our textbf{SocialNav} is a foundational model for socially-aware navigation with a hierarchical “brain-action” architecture, capable of understanding high-level social norms and generating low-level, socially compliant trajectories. To enable such dual capabilities, we construct the SocNav Dataset, a large-scale collection of 7 million samples, comprising (1) a Cognitive Activation Dataset providing social reasoning signals such as chain-of-thought explanations and social traversability prediction, and (2) an Expert Trajectories Pyramid aggregating diverse navigation demonstrations from internet videos, simulated environments, and real-world robots. A multi-stage training pipeline is proposed to gradually inject and refine navigation intelligence: we first inject general navigation skills and social norms understanding into the model via imitation learning, and then refine such skills through a deliberately designed Socially-Aware Flow Exploration GRPO (SAFE-GRPO), the first flow-based reinforcement learning framework for embodied navigation that explicitly rewards socially compliant behaviors. SocialNav achieves +38% success rate and +46% social compliance rate compared to the state-of-the-art method, demonstrating strong gains in both navigation performance and social compliance. Our project page: https://amap-eai.github.io/SocialNav/ Read More
Dynamic Test-Time Compute Scaling in Control Policy: Difficulty-Aware Stochastic Interpolant Policycs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.20906v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Diffusion- and flow-based policies deliver state-of-the-art performance on long-horizon robotic manipulation and imitation learning tasks. However, these controllers employ a fixed inference budget at every control step, regardless of task complexity, leading to computational inefficiency for simple subtasks while potentially underperforming on challenging ones. To address these issues, we introduce Difficulty-Aware Stochastic Interpolant Policy (DA-SIP), a framework that enables robotic controllers to adaptively adjust their integration horizon in real time based on task difficulty. Our approach employs a difficulty classifier that analyzes observations to dynamically select the step budget, the optimal solver variant, and ODE/SDE integration at each control cycle. DA-SIP builds upon the stochastic interpolant formulation to provide a unified framework that unlocks diverse training and inference configurations for diffusion- and flow-based policies. Through comprehensive benchmarks across diverse manipulation tasks, DA-SIP achieves 2.6-4.4x reduction in total computation time while maintaining task success rates comparable to fixed maximum-computation baselines. By implementing adaptive computation within this framework, DA-SIP transforms generative robot controllers into efficient, task-aware systems that intelligently allocate inference resources where they provide the greatest benefit.
arXiv:2511.20906v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Diffusion- and flow-based policies deliver state-of-the-art performance on long-horizon robotic manipulation and imitation learning tasks. However, these controllers employ a fixed inference budget at every control step, regardless of task complexity, leading to computational inefficiency for simple subtasks while potentially underperforming on challenging ones. To address these issues, we introduce Difficulty-Aware Stochastic Interpolant Policy (DA-SIP), a framework that enables robotic controllers to adaptively adjust their integration horizon in real time based on task difficulty. Our approach employs a difficulty classifier that analyzes observations to dynamically select the step budget, the optimal solver variant, and ODE/SDE integration at each control cycle. DA-SIP builds upon the stochastic interpolant formulation to provide a unified framework that unlocks diverse training and inference configurations for diffusion- and flow-based policies. Through comprehensive benchmarks across diverse manipulation tasks, DA-SIP achieves 2.6-4.4x reduction in total computation time while maintaining task success rates comparable to fixed maximum-computation baselines. By implementing adaptive computation within this framework, DA-SIP transforms generative robot controllers into efficient, task-aware systems that intelligently allocate inference resources where they provide the greatest benefit. Read More
Microsoft has announced plans to improve the security of Entra ID authentication by blocking unauthorized script injection attacks starting a year from now. The update to its Content Security Policy (CSP) aims to enhance the Entra ID sign-in experience at “login.microsoftonline[.]com” by only letting scripts from trusted Microsoft domains run. “This update strengthens security and […]
MNM : Multi-level Neuroimaging Meta-analysis with Hyperbolic Brain-Text Representationscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.21092v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Various neuroimaging studies suffer from small sample size problem which often limit their reliability. Meta-analysis addresses this challenge by aggregating findings from different studies to identify consistent patterns of brain activity. However, traditional approaches based on keyword retrieval or linear mappings often overlook the rich hierarchical structure in the brain. In this work, we propose a novel framework that leverages hyperbolic geometry to bridge the gap between neuroscience literature and brain activation maps. By embedding text from research articles and corresponding brain images into a shared hyperbolic space via the Lorentz model, our method captures both semantic similarity and hierarchical organization inherent in neuroimaging data. In the hyperbolic space, our method performs multi-level neuroimaging meta-analysis (MNM) by 1) aligning brain and text embeddings for semantic correspondence, 2) guiding hierarchy between text and brain activations, and 3) preserving the hierarchical relationships within brain activation patterns. Experimental results demonstrate that our model outperforms baselines, offering a robust and interpretable paradigm of multi-level neuroimaging meta-analysis via hyperbolic brain-text representation.
arXiv:2511.21092v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Various neuroimaging studies suffer from small sample size problem which often limit their reliability. Meta-analysis addresses this challenge by aggregating findings from different studies to identify consistent patterns of brain activity. However, traditional approaches based on keyword retrieval or linear mappings often overlook the rich hierarchical structure in the brain. In this work, we propose a novel framework that leverages hyperbolic geometry to bridge the gap between neuroscience literature and brain activation maps. By embedding text from research articles and corresponding brain images into a shared hyperbolic space via the Lorentz model, our method captures both semantic similarity and hierarchical organization inherent in neuroimaging data. In the hyperbolic space, our method performs multi-level neuroimaging meta-analysis (MNM) by 1) aligning brain and text embeddings for semantic correspondence, 2) guiding hierarchy between text and brain activations, and 3) preserving the hierarchical relationships within brain activation patterns. Experimental results demonstrate that our model outperforms baselines, offering a robust and interpretable paradigm of multi-level neuroimaging meta-analysis via hyperbolic brain-text representation. Read More
OpenApps: Simulating Environment Variations to Measure UI-Agent Reliabilitycs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.20766v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Reliability is key to realizing the promise of autonomous UI-Agents, multimodal agents that directly interact with apps in the same manner as humans, as users must be able to trust an agent to complete a given task. Current evaluations rely on fixed environments, often clones of existing apps, which are limited in that they can only shed light on whether or how often an agent can complete a task within a specific environment. When deployed however, agents are likely to encounter variations in app design and content that can affect an agent’s ability to complete a task. To address this blind spot of measuring agent reliability across app variations, we develop OpenApps, a light-weight open-source ecosystem with six apps (messenger, calendar, maps, etc.) that are configurable in appearance and content. OpenApps requires just a single CPU to run, enabling easy generation and deployment of thousands of versions of each app. Specifically, we run more than 10,000 independent evaluations to study reliability across seven leading multimodal agents. We find that while standard reliability within a fixed app is relatively stable, reliability can vary drastically when measured across app variations. Task success rates for many agents can fluctuate by more than $50%$ across app variations. For example, Kimi-VL-3B’s average success across all tasks fluctuates from $63%$ to just $4%$ across app versions. We also find agent behaviors such as looping or hallucinating actions can differ drastically depending on the environment configuration. These initial findings highlight the importance of measuring reliability along this new dimension of app variations. OpenApps is available at https://facebookresearch.github.io/OpenApps/
arXiv:2511.20766v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Reliability is key to realizing the promise of autonomous UI-Agents, multimodal agents that directly interact with apps in the same manner as humans, as users must be able to trust an agent to complete a given task. Current evaluations rely on fixed environments, often clones of existing apps, which are limited in that they can only shed light on whether or how often an agent can complete a task within a specific environment. When deployed however, agents are likely to encounter variations in app design and content that can affect an agent’s ability to complete a task. To address this blind spot of measuring agent reliability across app variations, we develop OpenApps, a light-weight open-source ecosystem with six apps (messenger, calendar, maps, etc.) that are configurable in appearance and content. OpenApps requires just a single CPU to run, enabling easy generation and deployment of thousands of versions of each app. Specifically, we run more than 10,000 independent evaluations to study reliability across seven leading multimodal agents. We find that while standard reliability within a fixed app is relatively stable, reliability can vary drastically when measured across app variations. Task success rates for many agents can fluctuate by more than $50%$ across app variations. For example, Kimi-VL-3B’s average success across all tasks fluctuates from $63%$ to just $4%$ across app versions. We also find agent behaviors such as looping or hallucinating actions can differ drastically depending on the environment configuration. These initial findings highlight the importance of measuring reliability along this new dimension of app variations. OpenApps is available at https://facebookresearch.github.io/OpenApps/ Read More
Length-MAX Tokenizer for Language Modelscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2511.20849v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: We introduce a new tokenizer for language models that minimizes the average tokens per character, thereby reducing the number of tokens needed to represent text during training and to generate text during inference. Our method, which we refer to as the Length-MAX tokenizer, obtains its vocabulary by casting a length-weighted objective maximization as a graph partitioning problem and developing a greedy approximation algorithm. On FineWeb and diverse domains, it yields 14–18% fewer tokens than Byte Pair Encoding (BPE) across vocabulary sizes from 10K to 50K, and the reduction is 13.0% when the size is 64K. Training GPT-2 models at 124M, 355M, and 1.3B parameters from scratch with five runs each shows 18.5%, 17.2%, and 18.5% fewer steps, respectively, to reach a fixed validation loss, and 13.7%, 12.7%, and 13.7% lower inference latency, together with a 16% throughput gain at 124M, while consistently improving on downstream tasks including reducing LAMBADA perplexity by 11.7% and enhancing HellaSwag accuracy by 4.3%. Moreover, the Length-MAX tokenizer achieves 99.62% vocabulary coverage and the out-of-vocabulary rate remains low at 0.12% on test sets. These results demonstrate that optimizing for average token length, rather than frequency alone, offers an effective approach to more efficient language modeling without sacrificing — and often improving — downstream performance. The tokenizer is compatible with production systems and reduces embedding and KV-cache memory by 18% at inference.
arXiv:2511.20849v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: We introduce a new tokenizer for language models that minimizes the average tokens per character, thereby reducing the number of tokens needed to represent text during training and to generate text during inference. Our method, which we refer to as the Length-MAX tokenizer, obtains its vocabulary by casting a length-weighted objective maximization as a graph partitioning problem and developing a greedy approximation algorithm. On FineWeb and diverse domains, it yields 14–18% fewer tokens than Byte Pair Encoding (BPE) across vocabulary sizes from 10K to 50K, and the reduction is 13.0% when the size is 64K. Training GPT-2 models at 124M, 355M, and 1.3B parameters from scratch with five runs each shows 18.5%, 17.2%, and 18.5% fewer steps, respectively, to reach a fixed validation loss, and 13.7%, 12.7%, and 13.7% lower inference latency, together with a 16% throughput gain at 124M, while consistently improving on downstream tasks including reducing LAMBADA perplexity by 11.7% and enhancing HellaSwag accuracy by 4.3%. Moreover, the Length-MAX tokenizer achieves 99.62% vocabulary coverage and the out-of-vocabulary rate remains low at 0.12% on test sets. These results demonstrate that optimizing for average token length, rather than frequency alone, offers an effective approach to more efficient language modeling without sacrificing — and often improving — downstream performance. The tokenizer is compatible with production systems and reduces embedding and KV-cache memory by 18% at inference. Read More