GRAFT: GRaPH and Table Reasoning for Textual Alignment — A Benchmark for Structured Instruction Following and Visual Reasoningcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2508.15690v4 Announce Type: replace
Abstract: GRAFT is a structured multimodal benchmark designed to probe how well LLMs handle instruction following, visual reasoning, and tasks requiring tight visual textual alignment. The dataset is built around programmatically generated charts and synthetically rendered tables, each paired with a carefully constructed, multi step analytical question that depends solely on what can be inferred from the image itself. Responses are formatted in structured outputs such as JSON or YAML, enabling consistent and fine grained evaluation of both reasoning processes and adherence to output specifications. The benchmark further introduces a taxonomy of reasoning operations ranging from comparison and trend identification to ranking, aggregation, proportional estimation, and anomaly detection to support a comprehensive assessment of model capabilities. Taken together, GRAFT provides a unified and scalable framework for evaluating multimodal LLMs on visually grounded, structured reasoning tasks, offering a more rigorous standard for future benchmarking efforts.
arXiv:2508.15690v4 Announce Type: replace
Abstract: GRAFT is a structured multimodal benchmark designed to probe how well LLMs handle instruction following, visual reasoning, and tasks requiring tight visual textual alignment. The dataset is built around programmatically generated charts and synthetically rendered tables, each paired with a carefully constructed, multi step analytical question that depends solely on what can be inferred from the image itself. Responses are formatted in structured outputs such as JSON or YAML, enabling consistent and fine grained evaluation of both reasoning processes and adherence to output specifications. The benchmark further introduces a taxonomy of reasoning operations ranging from comparison and trend identification to ranking, aggregation, proportional estimation, and anomaly detection to support a comprehensive assessment of model capabilities. Taken together, GRAFT provides a unified and scalable framework for evaluating multimodal LLMs on visually grounded, structured reasoning tasks, offering a more rigorous standard for future benchmarking efforts. Read More
LORE: A Large Generative Model for Search Relevancecs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.03025v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Achievement. We introduce LORE, a systematic framework for Large Generative Model-based relevance in e-commerce search. Deployed and iterated over three years, LORE achieves a cumulative +27% improvement in online GoodRate metrics. This report shares the valuable experience gained throughout its development lifecycle, spanning data, features, training, evaluation, and deployment. Insight. While existing works apply Chain-of-Thought (CoT) to enhance relevance, they often hit a performance ceiling. We argue this stems from treating relevance as a monolithic task, lacking principled deconstruction. Our key insight is that relevance comprises distinct capabilities: knowledge and reasoning, multi-modal matching, and rule adherence. We contend that a qualitative-driven decomposition is essential for breaking through current performance bottlenecks. Contributions. LORE provides a complete blueprint for the LLM relevance lifecycle. Key contributions include: (1) A two-stage training paradigm combining progressive CoT synthesis via SFT with human preference alignment via RL. (2) A comprehensive benchmark, RAIR, designed to evaluate these core capabilities. (3) A query frequency-stratified deployment strategy that efficiently transfers offline LLM capabilities to the online system. LORE serves as both a practical solution and a methodological reference for other vertical domains.
arXiv:2512.03025v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Achievement. We introduce LORE, a systematic framework for Large Generative Model-based relevance in e-commerce search. Deployed and iterated over three years, LORE achieves a cumulative +27% improvement in online GoodRate metrics. This report shares the valuable experience gained throughout its development lifecycle, spanning data, features, training, evaluation, and deployment. Insight. While existing works apply Chain-of-Thought (CoT) to enhance relevance, they often hit a performance ceiling. We argue this stems from treating relevance as a monolithic task, lacking principled deconstruction. Our key insight is that relevance comprises distinct capabilities: knowledge and reasoning, multi-modal matching, and rule adherence. We contend that a qualitative-driven decomposition is essential for breaking through current performance bottlenecks. Contributions. LORE provides a complete blueprint for the LLM relevance lifecycle. Key contributions include: (1) A two-stage training paradigm combining progressive CoT synthesis via SFT with human preference alignment via RL. (2) A comprehensive benchmark, RAIR, designed to evaluate these core capabilities. (3) A query frequency-stratified deployment strategy that efficiently transfers offline LLM capabilities to the online system. LORE serves as both a practical solution and a methodological reference for other vertical domains. Read More
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a malicious Rust package that’s capable of targeting Windows, macOS, and Linux systems, and features malicious functionality to stealthily execute on developer machines by masquerading as an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) unit helper tool. The Rust crate, named “evm-units,” was uploaded to crates.io in mid-April 2025 by a user named “ablerust,” Read […]
Fine-tuning of lightweight large language models for sentiment classification on heterogeneous financial textual datacs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.00946v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) play an increasingly important role in finan- cial markets analysis by capturing signals from complex and heterogeneous textual data sources, such as tweets, news articles, reports, and microblogs. However, their performance is dependent on large computational resources and proprietary datasets, which are costly, restricted, and therefore inacces- sible to many researchers and practitioners. To reflect realistic situations we investigate the ability of lightweight open-source LLMs – smaller and publicly available models designed to operate with limited computational resources – to generalize sentiment understanding from financial datasets of varying sizes, sources, formats, and languages. We compare the benchmark finance natural language processing (NLP) model, FinBERT, and three open-source lightweight LLMs, DeepSeek-LLM 7B, Llama3 8B Instruct, and Qwen3 8B on five publicly available datasets: FinancialPhraseBank, Financial Question Answering, Gold News Sentiment, Twitter Sentiment and Chinese Finance Sentiment. We find that LLMs, specially Qwen3 8B and Llama3 8B, perform best in most scenarios, even from using only 5% of the available training data. These results hold in zero-shot and few-shot learning scenarios. Our findings indicate that lightweight, open-source large language models (LLMs) consti- tute a cost-effective option, as they can achieve competitive performance on heterogeneous textual data even when trained on only a limited subset of the extensive annotated corpora that are typically deemed necessary.
arXiv:2512.00946v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) play an increasingly important role in finan- cial markets analysis by capturing signals from complex and heterogeneous textual data sources, such as tweets, news articles, reports, and microblogs. However, their performance is dependent on large computational resources and proprietary datasets, which are costly, restricted, and therefore inacces- sible to many researchers and practitioners. To reflect realistic situations we investigate the ability of lightweight open-source LLMs – smaller and publicly available models designed to operate with limited computational resources – to generalize sentiment understanding from financial datasets of varying sizes, sources, formats, and languages. We compare the benchmark finance natural language processing (NLP) model, FinBERT, and three open-source lightweight LLMs, DeepSeek-LLM 7B, Llama3 8B Instruct, and Qwen3 8B on five publicly available datasets: FinancialPhraseBank, Financial Question Answering, Gold News Sentiment, Twitter Sentiment and Chinese Finance Sentiment. We find that LLMs, specially Qwen3 8B and Llama3 8B, perform best in most scenarios, even from using only 5% of the available training data. These results hold in zero-shot and few-shot learning scenarios. Our findings indicate that lightweight, open-source large language models (LLMs) consti- tute a cost-effective option, as they can achieve competitive performance on heterogeneous textual data even when trained on only a limited subset of the extensive annotated corpora that are typically deemed necessary. Read More
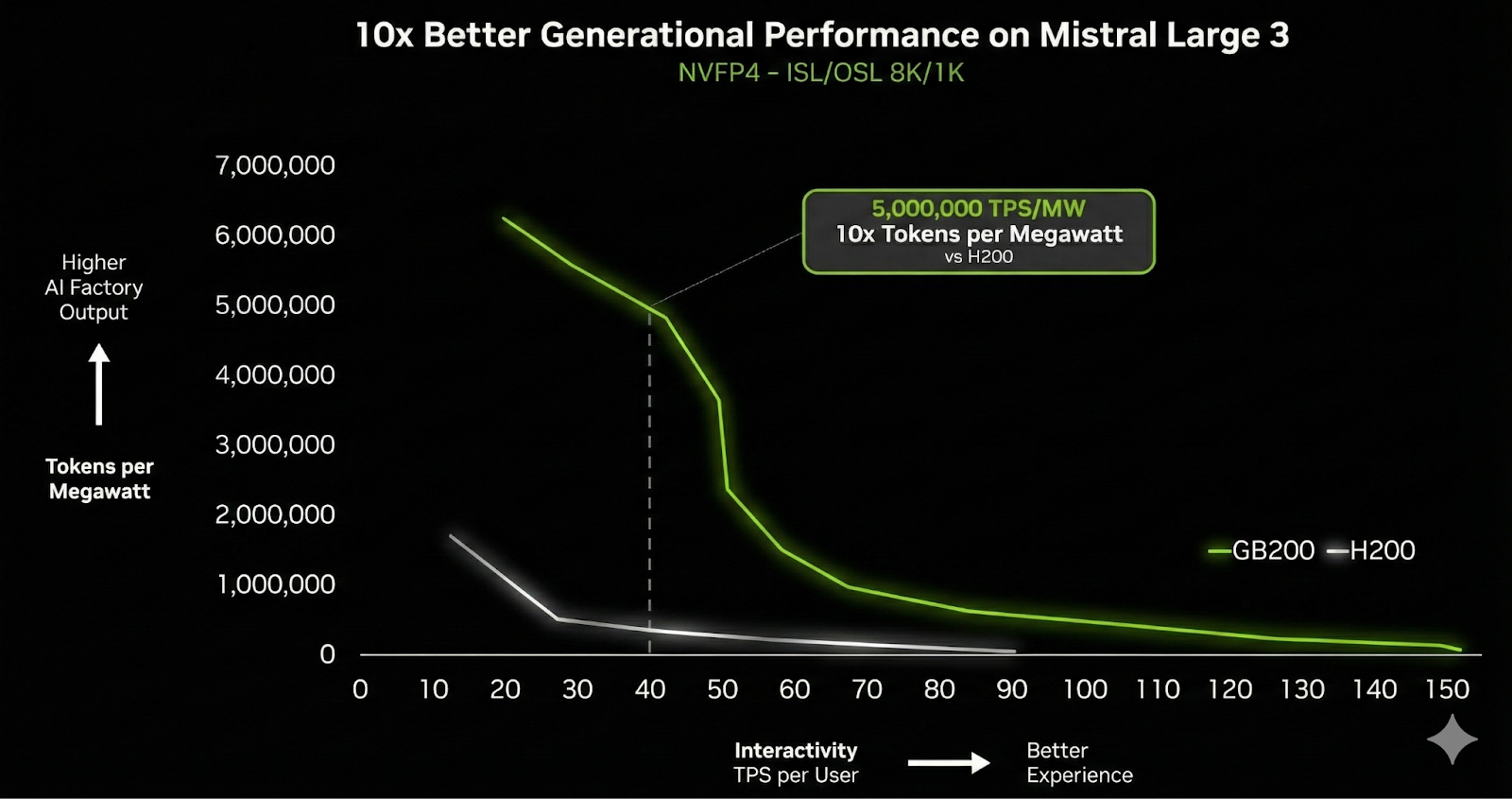
NVIDIA and Mistral AI Bring 10x Faster Inference for the Mistral 3 Family on GB200 NVL72 GPU SystemsMarkTechPost NVIDIA announced today a significant expansion of its strategic collaboration with Mistral AI. This partnership coincides with the release of the new Mistral 3 frontier open model family, marking a pivotal moment where hardware acceleration and open-source model architecture have converged to redefine performance benchmarks. This collaboration is a massive leap in inference speed: the
The post NVIDIA and Mistral AI Bring 10x Faster Inference for the Mistral 3 Family on GB200 NVL72 GPU Systems appeared first on MarkTechPost.
NVIDIA announced today a significant expansion of its strategic collaboration with Mistral AI. This partnership coincides with the release of the new Mistral 3 frontier open model family, marking a pivotal moment where hardware acceleration and open-source model architecture have converged to redefine performance benchmarks. This collaboration is a massive leap in inference speed: the
The post NVIDIA and Mistral AI Bring 10x Faster Inference for the Mistral 3 Family on GB200 NVL72 GPU Systems appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Frontier AI research lab tackles enterprise deployment challengesAI News Thomson Reuters and Imperial College London have established a frontier AI research lab to overcome historic deployment challenges. Speed and scale have defined the current AI boom. But for enterprises, the primary obstacles to deployment are different: trust, accuracy, and lineage. Addressing these barriers, Thomson Reuters and Imperial College London have announced a five-year partnership
The post Frontier AI research lab tackles enterprise deployment challenges appeared first on AI News.
Thomson Reuters and Imperial College London have established a frontier AI research lab to overcome historic deployment challenges. Speed and scale have defined the current AI boom. But for enterprises, the primary obstacles to deployment are different: trust, accuracy, and lineage. Addressing these barriers, Thomson Reuters and Imperial College London have announced a five-year partnership
The post Frontier AI research lab tackles enterprise deployment challenges appeared first on AI News. Read More
Toward a benchmark for CTR prediction in online advertising: datasets, evaluation protocols and perspectivescs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.01179v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: This research designs a unified architecture of CTR prediction benchmark (Bench-CTR) platform that offers flexible interfaces with datasets and components of a wide range of CTR prediction models. Moreover, we construct a comprehensive system of evaluation protocols encompassing real-world and synthetic datasets, a taxonomy of metrics, standardized procedures and experimental guidelines for calibrating the performance of CTR prediction models. Furthermore, we implement the proposed benchmark platform and conduct a comparative study to evaluate a wide range of state-of-the-art models from traditional multivariate statistical to modern large language model (LLM)-based approaches on three public datasets and two synthetic datasets. Experimental results reveal that, (1) high-order models largely outperform low-order models, though such advantage varies in terms of metrics and on different datasets; (2) LLM-based models demonstrate a remarkable data efficiency, i.e., achieving the comparable performance to other models while using only 2% of the training data; (3) the performance of CTR prediction models has achieved significant improvements from 2015 to 2016, then reached a stage with slow progress, which is consistent across various datasets. This benchmark is expected to facilitate model development and evaluation and enhance practitioners’ understanding of the underlying mechanisms of models in the area of CTR prediction. Code is available at https://github.com/NuriaNinja/Bench-CTR.
arXiv:2512.01179v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: This research designs a unified architecture of CTR prediction benchmark (Bench-CTR) platform that offers flexible interfaces with datasets and components of a wide range of CTR prediction models. Moreover, we construct a comprehensive system of evaluation protocols encompassing real-world and synthetic datasets, a taxonomy of metrics, standardized procedures and experimental guidelines for calibrating the performance of CTR prediction models. Furthermore, we implement the proposed benchmark platform and conduct a comparative study to evaluate a wide range of state-of-the-art models from traditional multivariate statistical to modern large language model (LLM)-based approaches on three public datasets and two synthetic datasets. Experimental results reveal that, (1) high-order models largely outperform low-order models, though such advantage varies in terms of metrics and on different datasets; (2) LLM-based models demonstrate a remarkable data efficiency, i.e., achieving the comparable performance to other models while using only 2% of the training data; (3) the performance of CTR prediction models has achieved significant improvements from 2015 to 2016, then reached a stage with slow progress, which is consistent across various datasets. This benchmark is expected to facilitate model development and evaluation and enhance practitioners’ understanding of the underlying mechanisms of models in the area of CTR prediction. Code is available at https://github.com/NuriaNinja/Bench-CTR. Read More
Anthropic just revealed how AI-orchestrated cyberattacks actually work—Here’s what enterprises need to knowAI News For years, cybersecurity experts debated when – not if – artificial intelligence would cross the threshold from advisor to autonomous attacker. That theoretical milestone has arrived. Anthropic’s recent investigation into a Chinese state-sponsored operation has documented [PDF] the first case of AI-orchestrated cyber attacks executing at scale with minimal human oversight, altering what enterprises must
The post Anthropic just revealed how AI-orchestrated cyberattacks actually work—Here’s what enterprises need to know appeared first on AI News.
For years, cybersecurity experts debated when – not if – artificial intelligence would cross the threshold from advisor to autonomous attacker. That theoretical milestone has arrived. Anthropic’s recent investigation into a Chinese state-sponsored operation has documented [PDF] the first case of AI-orchestrated cyber attacks executing at scale with minimal human oversight, altering what enterprises must
The post Anthropic just revealed how AI-orchestrated cyberattacks actually work—Here’s what enterprises need to know appeared first on AI News. Read More
DF-Mamba: Deformable State Space Modeling for 3D Hand Pose Estimation in Interactionscs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.02727v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Modeling daily hand interactions often struggles with severe occlusions, such as when two hands overlap, which highlights the need for robust feature learning in 3D hand pose estimation (HPE). To handle such occluded hand images, it is vital to effectively learn the relationship between local image features (e.g., for occluded joints) and global context (e.g., cues from inter-joints, inter-hands, or the scene). However, most current 3D HPE methods still rely on ResNet for feature extraction, and such CNN’s inductive bias may not be optimal for 3D HPE due to its limited capability to model the global context. To address this limitation, we propose an effective and efficient framework for visual feature extraction in 3D HPE using recent state space modeling (i.e., Mamba), dubbed Deformable Mamba (DF-Mamba). DF-Mamba is designed to capture global context cues beyond standard convolution through Mamba’s selective state modeling and the proposed deformable state scanning. Specifically, for local features after convolution, our deformable scanning aggregates these features within an image while selectively preserving useful cues that represent the global context. This approach significantly improves the accuracy of structured 3D HPE, with comparable inference speed to ResNet-50. Our experiments involve extensive evaluations on five divergent datasets including single-hand and two-hand scenarios, hand-only and hand-object interactions, as well as RGB and depth-based estimation. DF-Mamba outperforms the latest image backbones, including VMamba and Spatial-Mamba, on all datasets and achieves state-of-the-art performance.
arXiv:2512.02727v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Modeling daily hand interactions often struggles with severe occlusions, such as when two hands overlap, which highlights the need for robust feature learning in 3D hand pose estimation (HPE). To handle such occluded hand images, it is vital to effectively learn the relationship between local image features (e.g., for occluded joints) and global context (e.g., cues from inter-joints, inter-hands, or the scene). However, most current 3D HPE methods still rely on ResNet for feature extraction, and such CNN’s inductive bias may not be optimal for 3D HPE due to its limited capability to model the global context. To address this limitation, we propose an effective and efficient framework for visual feature extraction in 3D HPE using recent state space modeling (i.e., Mamba), dubbed Deformable Mamba (DF-Mamba). DF-Mamba is designed to capture global context cues beyond standard convolution through Mamba’s selective state modeling and the proposed deformable state scanning. Specifically, for local features after convolution, our deformable scanning aggregates these features within an image while selectively preserving useful cues that represent the global context. This approach significantly improves the accuracy of structured 3D HPE, with comparable inference speed to ResNet-50. Our experiments involve extensive evaluations on five divergent datasets including single-hand and two-hand scenarios, hand-only and hand-object interactions, as well as RGB and depth-based estimation. DF-Mamba outperforms the latest image backbones, including VMamba and Spatial-Mamba, on all datasets and achieves state-of-the-art performance. Read More
Pianist Transformer: Towards Expressive Piano Performance Rendering via Scalable Self-Supervised Pre-Trainingcs.AI updates on arXiv.org arXiv:2512.02652v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Existing methods for expressive music performance rendering rely on supervised learning over small labeled datasets, which limits scaling of both data volume and model size, despite the availability of vast unlabeled music, as in vision and language. To address this gap, we introduce Pianist Transformer, with four key contributions: 1) a unified Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI) data representation for learning the shared principles of musical structure and expression without explicit annotation; 2) an efficient asymmetric architecture, enabling longer contexts and faster inference without sacrificing rendering quality; 3) a self-supervised pre-training pipeline with 10B tokens and 135M-parameter model, unlocking data and model scaling advantages for expressive performance rendering; 4) a state-of-the-art performance model, which achieves strong objective metrics and human-level subjective ratings. Overall, Pianist Transformer establishes a scalable path toward human-like performance synthesis in the music domain.
arXiv:2512.02652v1 Announce Type: cross
Abstract: Existing methods for expressive music performance rendering rely on supervised learning over small labeled datasets, which limits scaling of both data volume and model size, despite the availability of vast unlabeled music, as in vision and language. To address this gap, we introduce Pianist Transformer, with four key contributions: 1) a unified Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI) data representation for learning the shared principles of musical structure and expression without explicit annotation; 2) an efficient asymmetric architecture, enabling longer contexts and faster inference without sacrificing rendering quality; 3) a self-supervised pre-training pipeline with 10B tokens and 135M-parameter model, unlocking data and model scaling advantages for expressive performance rendering; 4) a state-of-the-art performance model, which achieves strong objective metrics and human-level subjective ratings. Overall, Pianist Transformer establishes a scalable path toward human-like performance synthesis in the music domain. Read More