Last Updated: February 17, 2026 URL: /careers/ai/ai-governance-administrator/ Category: Careers > AI Tags: entry-level, operations, background-admin, background-project-mgmt Role Overview The AI Governance Administrator is the operational foundation of the AI governance function and the most accessible entry point into this career ecosystem. Where the AI Compliance Manager builds governance frameworks and the CAIO sets strategy, the […]
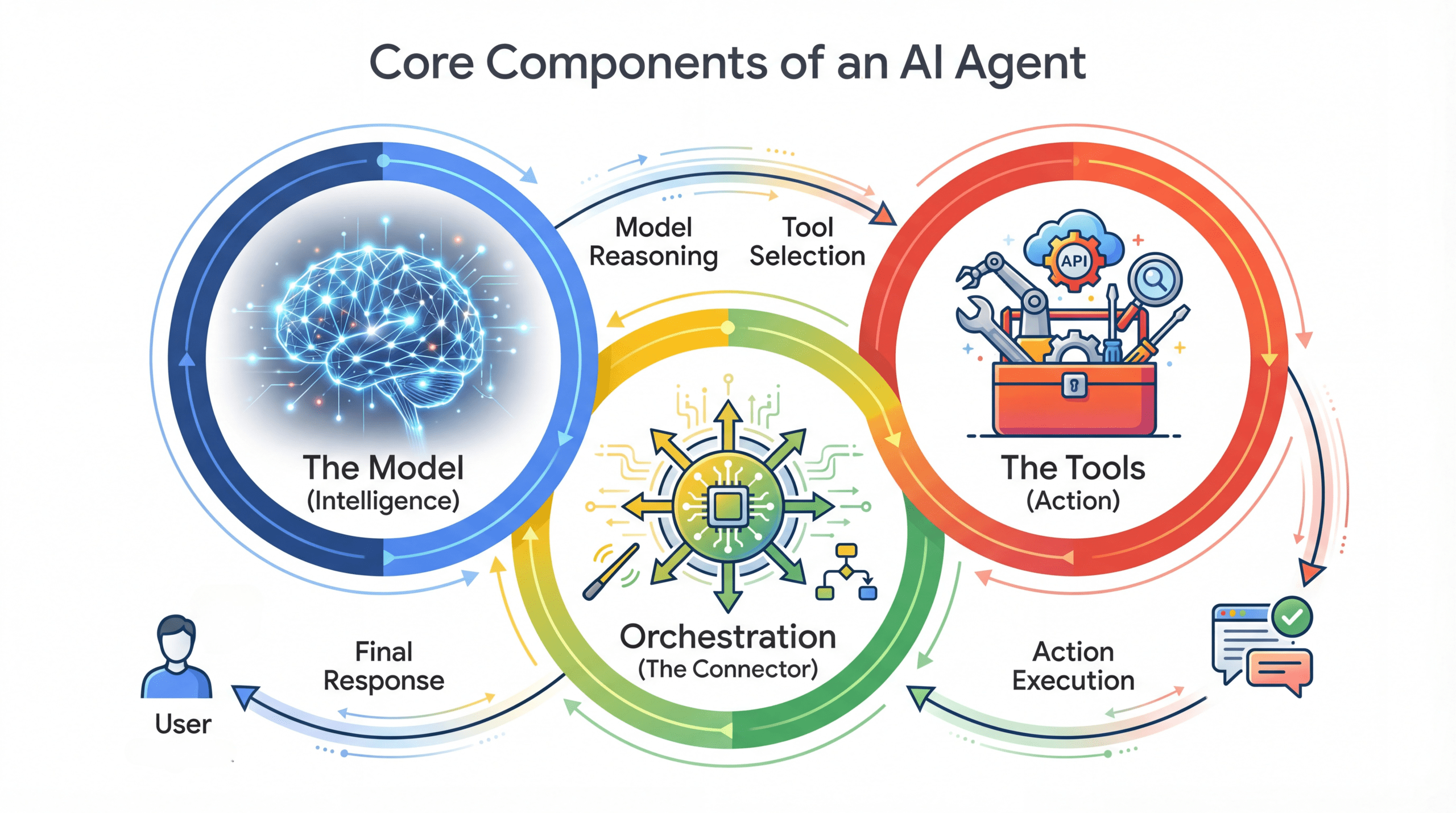
Building Production-Ready AI Agents with Agent Development KitKDnuggets ADK from Google addresses a critical gap in the agentic AI ecosystem by providing a framework that simplifies the construction and deployment of multi-agent systems. Learn more.
ADK from Google addresses a critical gap in the agentic AI ecosystem by providing a framework that simplifies the construction and deployment of multi-agent systems. Learn more. Read More
How AI upgrades enterprise treasury managementAI News The adoption of AI for enterprise treasury management enables businesses to abandon manual spreadsheets for automated data pipelines. Corporate finance departments face pressure from market volatility, regulatory demands, and digital finance requirements. Ashish Kumar, head of Infosys Oracle Sales for North America, and CM Grover, CEO of IBS FinTech, recently discussed the realities of corporate
The post How AI upgrades enterprise treasury management appeared first on AI News.
The adoption of AI for enterprise treasury management enables businesses to abandon manual spreadsheets for automated data pipelines. Corporate finance departments face pressure from market volatility, regulatory demands, and digital finance requirements. Ashish Kumar, head of Infosys Oracle Sales for North America, and CM Grover, CEO of IBS FinTech, recently discussed the realities of corporate
The post How AI upgrades enterprise treasury management appeared first on AI News. Read More
AlpamayoR1: Large Causal Reasoning Models for Autonomous DrivingTowards Data Science All you need to know about Chain of Causation reasoning and the current state of Autonomous Driving!
The post AlpamayoR1: Large Causal Reasoning Models for Autonomous Driving appeared first on Towards Data Science.
All you need to know about Chain of Causation reasoning and the current state of Autonomous Driving!
The post AlpamayoR1: Large Causal Reasoning Models for Autonomous Driving appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
5 Lightweight and Secure OpenClaw Alternatives to Try Right NowKDnuggets Want a smaller, faster, more secure agent stack than OpenClaw?
Want a smaller, faster, more secure agent stack than OpenClaw? Read More
AI in Multiple GPUs: How GPUs CommunicateTowards Data Science A deep dive into the hardware infrastructure that enables multi-GPU communication for AI workloads
The post AI in Multiple GPUs: How GPUs Communicate appeared first on Towards Data Science.
A deep dive into the hardware infrastructure that enables multi-GPU communication for AI workloads
The post AI in Multiple GPUs: How GPUs Communicate appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
FastMCP: The Pythonic Way to Build MCP Servers and ClientsKDnuggets Learn how to build MCP servers and clients using FastMCP, which is comprehensive, complete with error handling, best practices, and deployment strategies, making it ideal for both beginners and intermediate developers.
Learn how to build MCP servers and clients using FastMCP, which is comprehensive, complete with error handling, best practices, and deployment strategies, making it ideal for both beginners and intermediate developers. Read More
Build AI workflows on Amazon EKS with Union.ai and FlyteArtificial Intelligence In this post, we explain how you can use the Flyte Python SDK to orchestrate and scale AI/ML workflows. We explore how the Union.ai 2.0 system enables deployment of Flyte on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS), integrating seamlessly with AWS services like Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), Amazon Aurora, AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), and Amazon CloudWatch. We explore the solution through an AI workflow example, using the new Amazon S3 Vectors service.
In this post, we explain how you can use the Flyte Python SDK to orchestrate and scale AI/ML workflows. We explore how the Union.ai 2.0 system enables deployment of Flyte on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS), integrating seamlessly with AWS services like Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), Amazon Aurora, AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), and Amazon CloudWatch. We explore the solution through an AI workflow example, using the new Amazon S3 Vectors service. Read More
Amazon Quick Suite now supports key pair authentication to Snowflake data sourceArtificial Intelligence In this blog post, we will guide you through establishing data source connectivity between Amazon Quick Sight and Snowflake through secure key pair authentication.
In this blog post, we will guide you through establishing data source connectivity between Amazon Quick Sight and Snowflake through secure key pair authentication. Read More
Gemini 3.1 Pro: A smarter model for your most complex tasksGoogle DeepMind News 3.1 Pro is designed for tasks where a simple answer isn’t enough.
3.1 Pro is designed for tasks where a simple answer isn’t enough. Read More