Free Agentic AI Compliance & Governance Assessment Spreadsheet
A structured, formula-driven self-assessment tool designed to support organizations evaluating agentic AI systems across 12 governance domains and 117 checklist items, drawing on principles from the EU AI Act, NIST AI RMF, ISO/IEC 42001, ISO/IEC 38507, and broader AI safety research.
CTA Button: [Download Now]
Agentic AI systems don’t just answer questions. They take actions, call APIs, make decisions, and operate with varying degrees of independence from human oversight. That changes the governance equation entirely. The controls you’d apply to a traditional ML model don’t cover scope drift detection, kill-switch mechanisms, or decision provenance graphs.
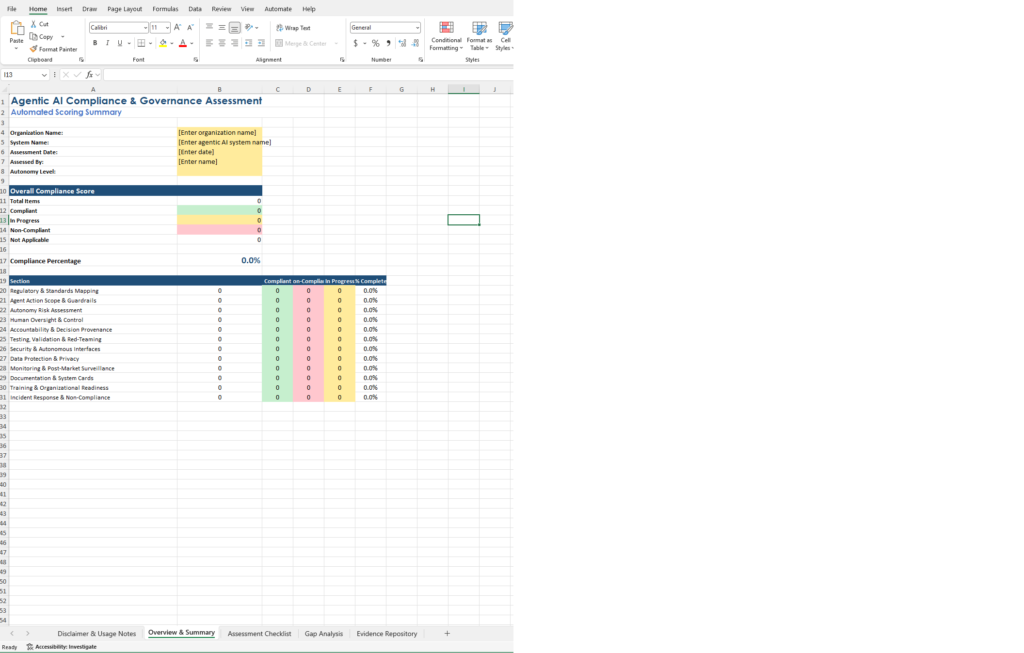
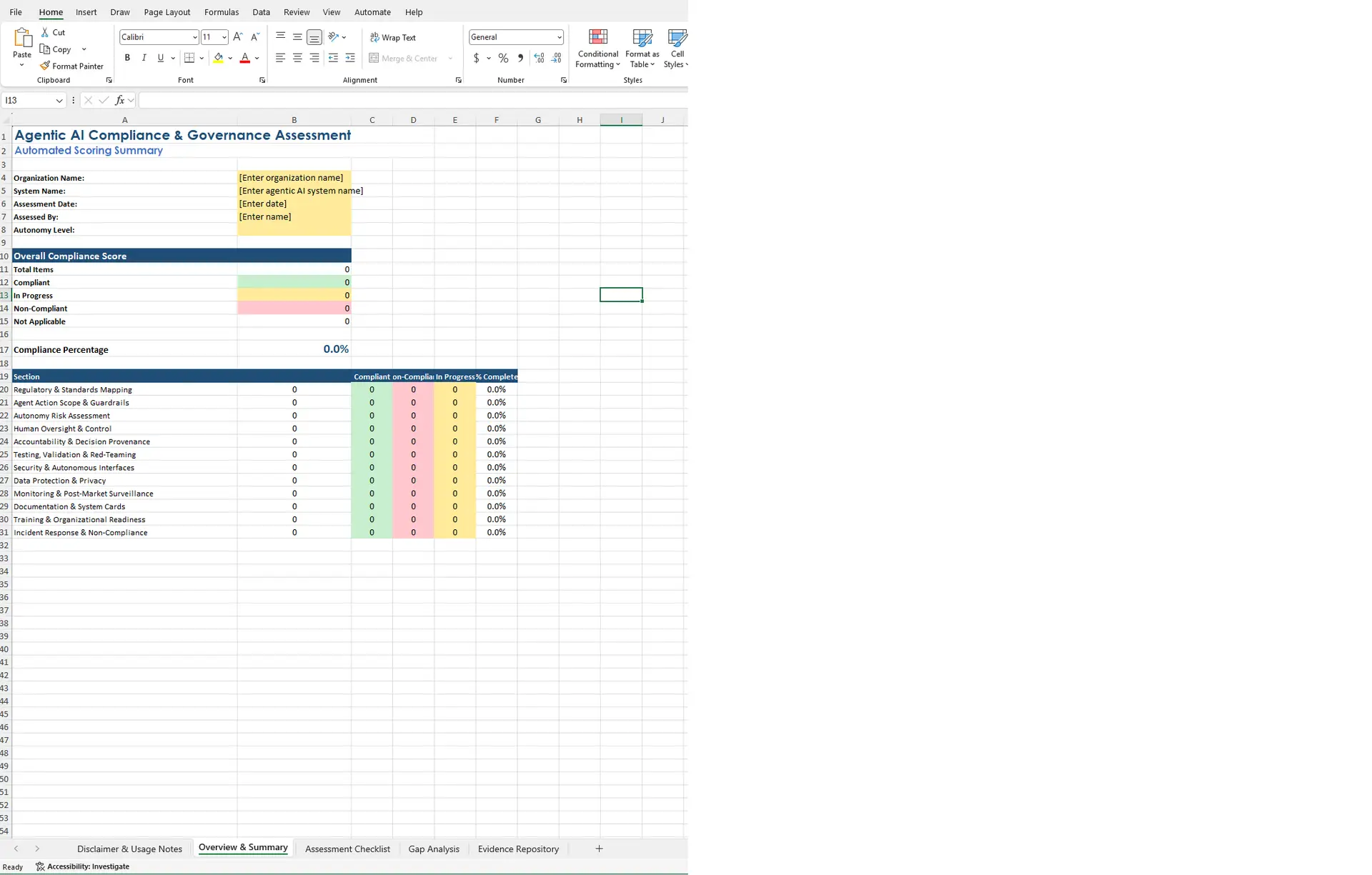
This spreadsheet provides a structured framework for evaluating agentic AI systems across 117 assessment items organized into 12 governance domains. The scoring updates automatically as you work through the checklist. Items you mark “Non-Compliant” or “In Progress” populate the gap analysis sheet without manual filtering. Priority ratings auto-calculate based on status: Non-Compliant flags as High, In Progress flags as Medium.
The tool requires organizational customization. It provides the assessment structure and scoring methodology, not a finished compliance determination. You’ll need to evaluate each item against your specific agentic system’s capabilities, document your evidence, and build remediation plans where gaps exist.
Key Benefits
- Includes 117 assessment items organized across 12 governance domains with dropdown status fields (Compliant, In Progress, Non-Compliant, N/A)
- Provides automated compliance percentage that updates in real time as statuses are entered
- Features auto-calculated priority ratings: Non-Compliant = High, In Progress = Medium, Compliant = None, N/A = N/A
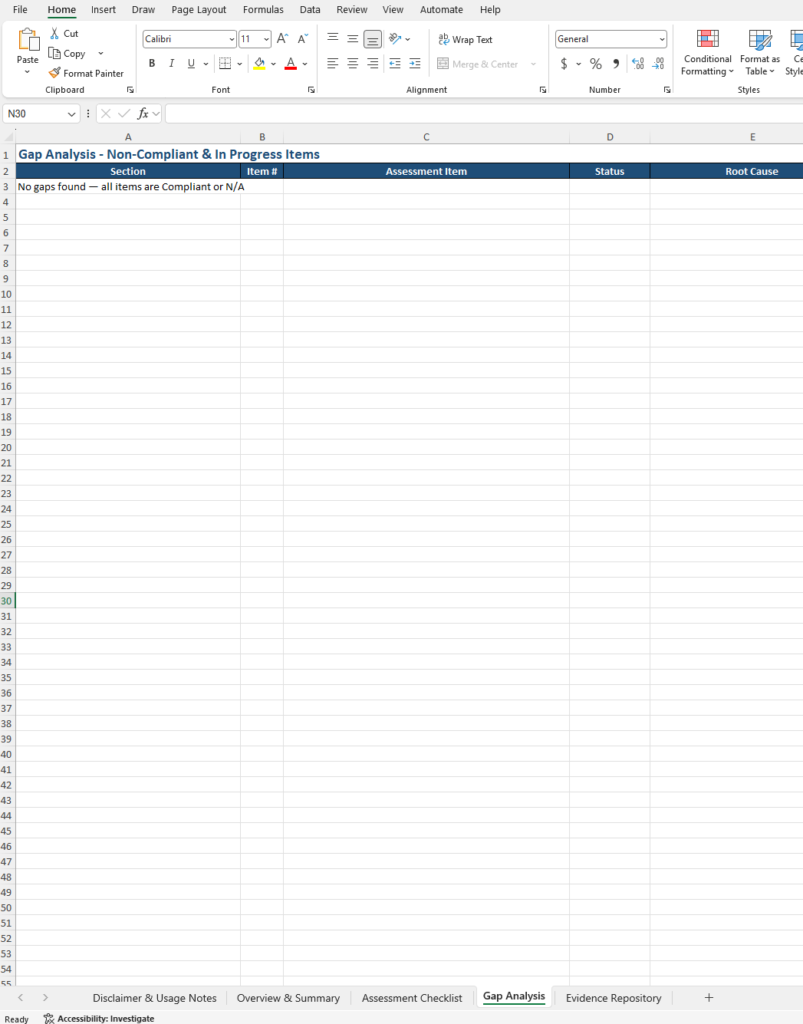
- Includes a gap analysis tracker that automatically populates Non-Compliant and In Progress items via FILTER formulas, with columns for Root Cause and Remediation Action
- Features an evidence repository with 24 pre-built evidence types organized by governance domain
- Covers agentic-specific concerns including kill-switch mechanisms, scope drift detection, decision provenance, prompt injection testing, multi-agent interaction risks, and SBOM-AI
- Applicable to all autonomy levels: Fully Autonomous (no human in the loop), Semi-Autonomous (human on the loop), and Human Supervised (human in the loop)
- Draws on principles from the EU AI Act, NIST AI RMF, ISO/IEC 42001, ISO/IEC 38507, and broader AI safety research
- Free for personal, educational, and organizational use
Who Uses This?
Designed for:
- AI governance teams and compliance officers overseeing agentic AI deployments
- Risk managers evaluating autonomous system risks including multi-agent interaction, scope drift, and reward hacking
- CISOs and security teams assessing agent-specific attack surfaces (prompt injection, tool-calling abuse, memory sandboxing)
- CTOs and product managers responsible for deploying agentic AI systems
- AI safety researchers evaluating alignment, oversight, and control mechanisms
- Auditors conducting governance assessments of autonomous AI systems
What’s Inside
The spreadsheet contains 5 sheets:
- Disclaimer & Usage Notes – Publisher information, legal disclaimer, scope definition, 7-step usage workflow, scoring methodology, sheet descriptions, and community attribution details
- Overview & Summary – Organization details, autonomy level selection, overall compliance score dashboard, and section-by-section breakdown with dynamic item counts and percentage complete per domain
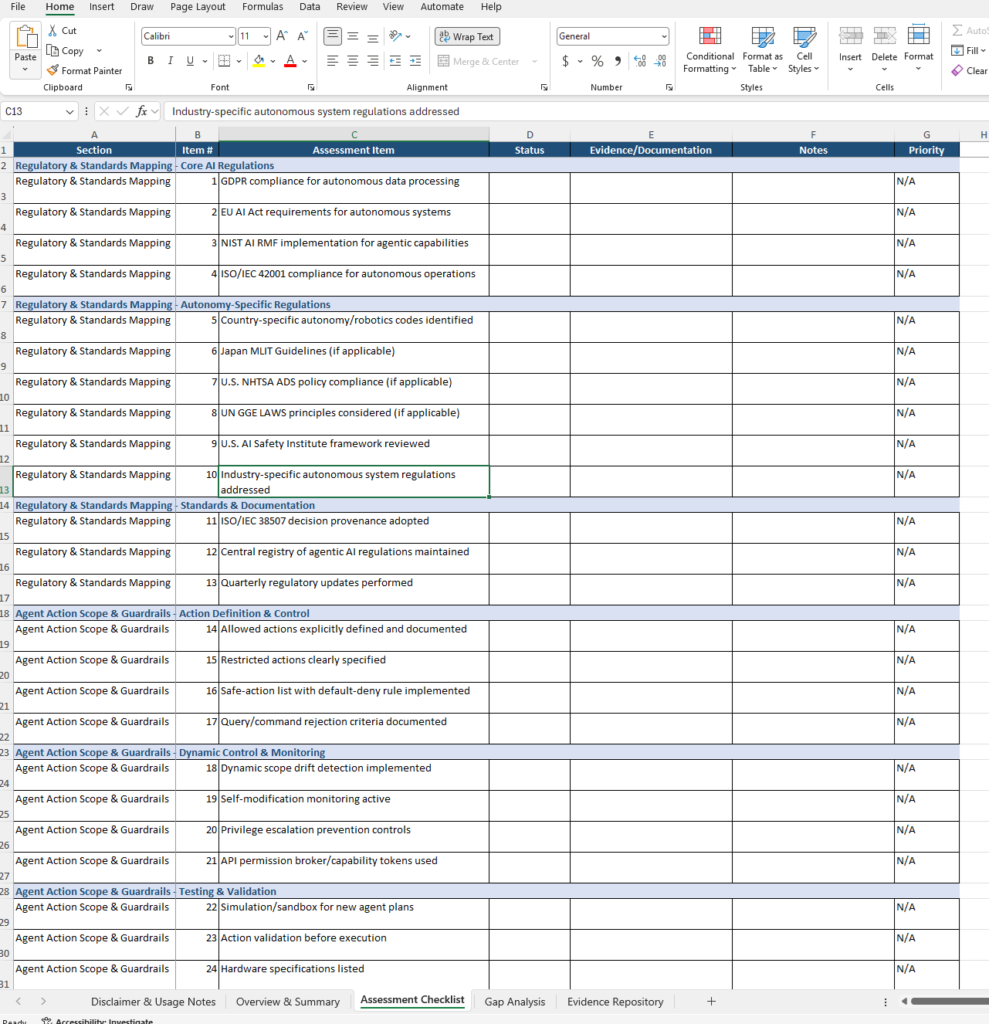
- Assessment Checklist – The core 117-item assessment across 12 domains with columns for Section (A), Item # (B), Assessment Item (C), Status (D, your input), Evidence/Documentation (E, your input), Notes (F, your input), and Priority (G, auto-calculated)
- Gap Analysis – Automatically populated via FILTER formula showing only Non-Compliant and In Progress items, with columns for Root Cause and Remediation Action for planning your remediation roadmap
- Evidence Repository – Pre-built template with 24 evidence types organized by governance domain, including columns for Document/Location, Collection Date, and Notes
Why This Matters
Agentic AI introduces governance challenges that traditional AI compliance frameworks weren’t built for. When an AI system can autonomously call external APIs, execute multi-step plans, and modify its own approach based on intermediate results, the risk surface expands well beyond model accuracy and bias testing.
Consider what’s different about governing an agent versus a standard predictive model: the agent can escalate its own privileges if guardrails are weak, drift outside its defined action scope, exhaust resources through runaway loops, or be manipulated via prompt injection into taking unauthorized actions. These aren’t theoretical edge cases. They’re documented failure modes that organizations deploying agentic systems need to assess and address.
The EU AI Act addresses high-risk AI systems with requirements around human oversight, transparency, and risk management. The NIST AI RMF provides a voluntary governance structure. ISO/IEC 42001 establishes management system requirements. ISO/IEC 38507 covers governance of IT and AI decision-making. But none of these frameworks were written specifically for agents that take autonomous actions, call tools, and chain decisions together. This assessment bridges that gap by mapping agentic-specific governance concerns to established regulatory principles.
Framework Alignment
This assessment draws on principles from:
- EU AI Act – High-risk system requirements, conformity assessment, human oversight obligations, and transparency requirements applied to autonomous system contexts
- NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF) – Risk identification and management structures adapted for agentic capabilities
- ISO/IEC 42001 – AI management system requirements including documentation, monitoring, and continual improvement for autonomous operations
- ISO/IEC 38507 – Governance of IT, including decision provenance and accountability structures
- GDPR – Data protection compliance for autonomous data processing, consent management, data subject rights, and privacy impact assessments
- Broader AI safety research – Reward hacking, specification gaming, alignment evaluation, and emergent risk identification
Additional regulatory references within the checklist include Japan MLIT Guidelines, U.S. NHTSA ADS policy, UN GGE LAWS principles, and U.S. AI Safety Institute framework.
Key Features
- 117 assessment items across 12 governance domains:
- Regulatory & Standards Mapping (13 items) – Core AI regulations, autonomy-specific regulations, standards and documentation
- Agent Action Scope & Guardrails (12 items) – Action definition and control, dynamic control and monitoring, testing and validation
- Autonomy Risk Assessment & Management (14 items) – Core risk identification, advanced risk types, risk management process
- Human Oversight & Control Mechanisms (13 items) – Oversight structure, kill-switch and emergency controls, monitoring and feedback
- Accountability & Decision Provenance (8 items) – Decision tracking, chain-of-thought logging, RACI definitions, forensic review
- Testing, Validation & Red-Teaming (13 items) – Core testing, security and adversarial testing, bias and impact testing
- Security & Autonomous Interfaces (8 items) – Access controls, API permission brokers, capability tokens, SBOM-AI
- Data Protection & Privacy (7 items) – Privacy compliance, consent management, data minimization, data subject rights
- Monitoring & Post-Market Surveillance (8 items) – Continuous monitoring, behavior anomaly detection, KPIs/KRIs, audit logs
- Documentation & System Cards (9 items) – System cards, tool calling documentation, prompt template catalogs, technical files
- Training & Organizational Readiness (5 items) – Agent-specific compliance training, supervisor role training, prompt/tool designer training
- Incident Response & Non-Compliance (7 items) – Agent-specific IR plans, graded response levels, kill-switch activation criteria
- Automated scoring methodology – Compliant = full credit, In Progress = 50% credit, Non-Compliant = zero credit, N/A excluded from denominator
- Auto-calculated priority ratings in Column G based on status values
- Section-by-section dashboard with dynamic item counts and percentage complete per domain
- Autonomy level capture on the Overview sheet (Fully Autonomous, Semi-Autonomous, Human Supervised)
- Sub-categorized domains – Assessment items are organized into sub-categories within each domain (e.g., Regulatory & Standards Mapping breaks into Core AI Regulations, Autonomy-Specific Regulations, and Standards & Documentation)
Comparison Table: Building Your Own vs. Using This Template
| Feature | Building From Scratch | Free Agentic AI Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Assessment structure | You define domains and items | 117 items across 12 domains pre-built |
| Agentic-specific coverage | Requires deep research into agent risks | Includes kill-switch, scope drift, decision provenance, prompt injection, multi-agent risks |
| Scoring automation | Manual calculation required | Formula-driven, updates in real time |
| Priority calculation | Manual triage | Auto-calculated from status (High/Medium/None/N/A) |
| Gap tracking | Separate process or manual filtering | Automated via FILTER formula with Root Cause and Remediation columns |
| Framework coverage | Limited to your team’s awareness | Draws on EU AI Act, NIST AI RMF, ISO/IEC 42001, ISO/IEC 38507, GDPR, and additional frameworks |
| Evidence management | Ad hoc documentation | 24 pre-built evidence types organized by domain |
| Autonomy level handling | One-size-fits-all | N/A status allows scoping to your system’s autonomy level |
| Cost | Internal staff time to research and build | Free |
FAQ Section
Q: Does completing this assessment certify my organization as compliant with the EU AI Act, NIST AI RMF, or any other regulation? A: No. This is a self-assessment tool for informational and educational purposes. Completing it does not constitute compliance certification with any regulation, standard, or framework. It is designed to help identify gaps and guide improvement efforts. Organizations should consult qualified legal counsel and compliance professionals before making governance decisions.
Q: What file format is this delivered in? A: The tool is delivered as a Microsoft Excel (.xlsx) file. Documents are optimized for Microsoft Excel to ensure proper formatting, formula functionality, and collaborative editing capabilities.
Q: Is this tool designed for all types of AI systems? A: No. This assessment is specifically designed for agentic AI systems, meaning AI systems that can take autonomous actions, make decisions, call tools/APIs, and operate with varying degrees of independence. It does not cover traditional (non-agentic) AI/ML model governance in depth. Organizations should supplement with standard ML governance frameworks as needed for non-agentic systems.
Q: How does the tool handle different levels of autonomy? A: The assessment is applicable to all autonomy levels: Fully Autonomous (no human in the loop), Semi-Autonomous (human on the loop), and Human Supervised (human in the loop). Not all items apply equally to every autonomy level. Use the N/A status where items don’t apply to your system’s specific autonomy configuration.
Q: How often should I run this assessment? A: The tool recommends an initial assessment before deployment, quarterly reviews during active operation, and ad-hoc reassessment after significant system changes, incidents, or regulatory updates.
Q: What’s the difference between the Evidence/Documentation column on the Assessment Checklist and the Evidence Repository sheet? A: The Evidence/Documentation column (E) on the Assessment Checklist captures specific evidence references for individual assessment items. The Evidence Repository sheet provides a centralized catalog of all supporting documentation organized by governance domain, with fields for document location, collection date, and notes.
Ideal For
- Organizations deploying agentic AI systems that need a structured governance baseline
- AI governance teams conducting initial or periodic assessments of autonomous AI capabilities
- Security teams evaluating agent-specific attack surfaces and control mechanisms
- Risk management professionals assessing autonomy-related risks (scope drift, reward hacking, multi-agent collusion, resource exhaustion)
- Compliance teams preparing documentation ahead of regulatory reviews for autonomous AI systems
- AI safety researchers evaluating alignment, oversight, and control mechanisms in deployed agents
- Consultants supporting client agentic AI governance programs
Pricing Strategy
Single Template: Free for personal, educational, and organizational use. Attribution to Tech Jacks Solutions is appreciated but not required. Commercial redistribution or resale is prohibited.
Bundle Option: May be combined with additional Tech Jacks Solutions governance and compliance templates depending on organizational needs.
Enterprise Option: Available as part of comprehensive AI governance documentation suites. Contact Tech Jacks Solutions for organizational licensing and customization.
Differentiator
This assessment tool covers 117 items across 12 governance domains built specifically for agentic AI systems. That’s the distinction worth paying attention to. Most AI compliance checklists evaluate traditional model governance: bias testing, data quality, transparency disclosures. Those matter, but they don’t address what happens when an AI system can autonomously call APIs, chain multi-step decisions, escalate its own privileges, or drift outside its defined scope. This tool covers agentic-specific concerns including kill-switch mechanisms, decision provenance graphs, scope drift detection, prompt injection testing, multi-agent interaction risks, reward hacking assessments, and SBOM-AI requirements. It includes automated scoring, auto-calculated priority ratings, formula-driven gap analysis, and a pre-built evidence repository with 24 evidence types. The tool requires organizational customization and does not guarantee compliance outcomes, but it provides the structured framework that the current regulatory landscape hasn’t yet fully addressed for autonomous AI systems.