Building health care agents using Amazon Bedrock AgentCoreArtificial Intelligenceon September 26, 2025 at 4:03 pm In this solution, we demonstrate how the user (a parent) can interact with a Strands or LangGraph agent in conversational style and get information about the immunization history and schedule of their child, inquire about the available slots, and book appointments. With some changes, AI agents can be made event-driven so that they can automatically send reminders, book appointments, and so on.
In this solution, we demonstrate how the user (a parent) can interact with a Strands or LangGraph agent in conversational style and get information about the immunization history and schedule of their child, inquire about the available slots, and book appointments. With some changes, AI agents can be made event-driven so that they can automatically send reminders, book appointments, and so on. Read More
Why MissForest Fails in Prediction Tasks: A Key Limitation You Need to Keep in MindTowards Data Scienceon September 26, 2025 at 2:00 pm Why the original MissForest algorithm cannot be directly applied for predictive modeling, and how MissForestPredict solves this problem
The post Why MissForest Fails in Prediction Tasks: A Key Limitation You Need to Keep in Mind appeared first on Towards Data Science.
Why the original MissForest algorithm cannot be directly applied for predictive modeling, and how MissForestPredict solves this problem
The post Why MissForest Fails in Prediction Tasks: A Key Limitation You Need to Keep in Mind appeared first on Towards Data Science. Read More
US investigators are using AI to detect child abuse images made by AIMIT Technology Reviewon September 26, 2025 at 7:03 pm Generative AI has enabled the production of child sexual abuse images to skyrocket. Now the leading investigator of child exploitation in the US is experimenting with using AI to distinguish AI-generated images from material depicting real victims, according to a new government filing. The Department of Homeland Security’s Cyber Crimes Center, which investigates child exploitation…
Generative AI has enabled the production of child sexual abuse images to skyrocket. Now the leading investigator of child exploitation in the US is experimenting with using AI to distinguish AI-generated images from material depicting real victims, according to a new government filing. The Department of Homeland Security’s Cyber Crimes Center, which investigates child exploitation… Read More
Hugging Face Releases Smol2Operator: A Fully Open-Source Pipeline to Train a 2.2B VLM into an Agentic GUI CoderMarkTechPoston September 26, 2025 at 8:51 pm Hugging Face (HF) has released Smol2Operator, a reproducible, end-to-end recipe that turns a small vision-language model (VLM) with no prior UI grounding into a GUI-operating, tool-using agent. The release covers data transformation utilities, training scripts, transformed datasets, and the resulting 2.2B-parameter model checkpoint—positioned as a complete blueprint for building GUI agents from scratch rather than
The post Hugging Face Releases Smol2Operator: A Fully Open-Source Pipeline to Train a 2.2B VLM into an Agentic GUI Coder appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Hugging Face (HF) has released Smol2Operator, a reproducible, end-to-end recipe that turns a small vision-language model (VLM) with no prior UI grounding into a GUI-operating, tool-using agent. The release covers data transformation utilities, training scripts, transformed datasets, and the resulting 2.2B-parameter model checkpoint—positioned as a complete blueprint for building GUI agents from scratch rather than
The post Hugging Face Releases Smol2Operator: A Fully Open-Source Pipeline to Train a 2.2B VLM into an Agentic GUI Coder appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
AI News September 26 2025: Robots, AI Videos & $30M Funding Executive Summary AI News Roundup: Robots Get Smarter, Meta Pushes AI Videos, and Recruiting Goes LLM The AI world took a breather yesterday. No mega-rounds. No AGI announcements. Just three developments worth your attention. Google’s Robots Can Now Think Ahead (And Google Things) Yesterday […]
CLIPin: A Non-contrastive Plug-in to CLIP for Multimodal Semantic Alignmentcs.AI updates on arXiv.orgon September 26, 2025 at 4:00 am arXiv:2508.06434v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Large-scale natural image-text datasets, especially those automatically collected from the web, often suffer from loose semantic alignment due to weak supervision, while medical datasets tend to have high cross-modal correlation but low content diversity. These properties pose a common challenge for contrastive language-image pretraining (CLIP): they hinder the model’s ability to learn robust and generalizable representations. In this work, we propose CLIPin, a unified non-contrastive plug-in that can be seamlessly integrated into CLIP-style architectures to improve multimodal semantic alignment, providing stronger supervision and enhancing alignment robustness. Furthermore, two shared pre-projectors are designed for image and text modalities respectively to facilitate the integration of contrastive and non-contrastive learning in a parameter-compromise manner. Extensive experiments on diverse downstream tasks demonstrate the effectiveness and generality of CLIPin as a plug-and-play component compatible with various contrastive frameworks. Code is available at https://github.com/T6Yang/CLIPin.
arXiv:2508.06434v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Large-scale natural image-text datasets, especially those automatically collected from the web, often suffer from loose semantic alignment due to weak supervision, while medical datasets tend to have high cross-modal correlation but low content diversity. These properties pose a common challenge for contrastive language-image pretraining (CLIP): they hinder the model’s ability to learn robust and generalizable representations. In this work, we propose CLIPin, a unified non-contrastive plug-in that can be seamlessly integrated into CLIP-style architectures to improve multimodal semantic alignment, providing stronger supervision and enhancing alignment robustness. Furthermore, two shared pre-projectors are designed for image and text modalities respectively to facilitate the integration of contrastive and non-contrastive learning in a parameter-compromise manner. Extensive experiments on diverse downstream tasks demonstrate the effectiveness and generality of CLIPin as a plug-and-play component compatible with various contrastive frameworks. Code is available at https://github.com/T6Yang/CLIPin. Read More
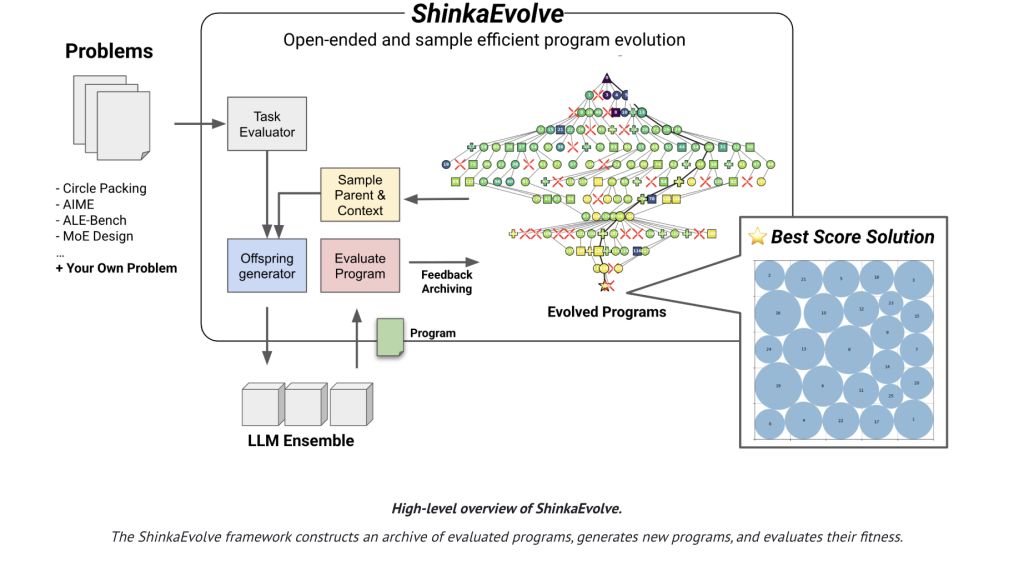
Sakana AI Released ShinkaEvolve: An Open-Source Framework that Evolves Programs for Scientific Discovery with Unprecedented Sample-EfficiencyMarkTechPoston September 26, 2025 at 9:15 am Sakana AI has released ShinkaEvolve, an open-sourced framework that uses large language models (LLMs) as mutation operators in an evolutionary loop to evolve programs for scientific and engineering problems—while drastically cutting the number of evaluations needed to reach strong solutions. On the canonical circle-packing benchmark (n=26 in a unit square), ShinkaEvolve reports a new SOTA
The post Sakana AI Released ShinkaEvolve: An Open-Source Framework that Evolves Programs for Scientific Discovery with Unprecedented Sample-Efficiency appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Sakana AI has released ShinkaEvolve, an open-sourced framework that uses large language models (LLMs) as mutation operators in an evolutionary loop to evolve programs for scientific and engineering problems—while drastically cutting the number of evaluations needed to reach strong solutions. On the canonical circle-packing benchmark (n=26 in a unit square), ShinkaEvolve reports a new SOTA
The post Sakana AI Released ShinkaEvolve: An Open-Source Framework that Evolves Programs for Scientific Discovery with Unprecedented Sample-Efficiency appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
AnyPlace: Learning Generalized Object Placement for Robot Manipulationcs.AI updates on arXiv.orgon September 26, 2025 at 4:00 am arXiv:2502.04531v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Object placement in robotic tasks is inherently challenging due to the diversity of object geometries and placement configurations. To address this, we propose AnyPlace, a two-stage method trained entirely on synthetic data, capable of predicting a wide range of feasible placement poses for real-world tasks. Our key insight is that by leveraging a Vision-Language Model (VLM) to identify rough placement locations, we focus only on the relevant regions for local placement, which enables us to train the low-level placement-pose-prediction model to capture diverse placements efficiently. For training, we generate a fully synthetic dataset of randomly generated objects in different placement configurations (insertion, stacking, hanging) and train local placement-prediction models. We conduct extensive evaluations in simulation, demonstrating that our method outperforms baselines in terms of success rate, coverage of possible placement modes, and precision. In real-world experiments, we show how our approach directly transfers models trained purely on synthetic data to the real world, where it successfully performs placements in scenarios where other models struggle — such as with varying object geometries, diverse placement modes, and achieving high precision for fine placement. More at: https://any-place.github.io.
arXiv:2502.04531v2 Announce Type: replace-cross
Abstract: Object placement in robotic tasks is inherently challenging due to the diversity of object geometries and placement configurations. To address this, we propose AnyPlace, a two-stage method trained entirely on synthetic data, capable of predicting a wide range of feasible placement poses for real-world tasks. Our key insight is that by leveraging a Vision-Language Model (VLM) to identify rough placement locations, we focus only on the relevant regions for local placement, which enables us to train the low-level placement-pose-prediction model to capture diverse placements efficiently. For training, we generate a fully synthetic dataset of randomly generated objects in different placement configurations (insertion, stacking, hanging) and train local placement-prediction models. We conduct extensive evaluations in simulation, demonstrating that our method outperforms baselines in terms of success rate, coverage of possible placement modes, and precision. In real-world experiments, we show how our approach directly transfers models trained purely on synthetic data to the real world, where it successfully performs placements in scenarios where other models struggle — such as with varying object geometries, diverse placement modes, and achieving high precision for fine placement. More at: https://any-place.github.io. Read More
Google AI Ships a Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server for Data Commons, Giving AI Agents First-Class Access to Public StatsMarkTechPoston September 26, 2025 at 8:05 am Google released a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server for Data Commons, exposing the project’s interconnected public datasets—census, health, climate, economics—through a standards-based interface that agentic systems can query in natural language. The Data Commons MCP Server is available now with quickstarts for Gemini CLI and Google’s Agent Development Kit (ADK). What was released Why MCP
The post Google AI Ships a Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server for Data Commons, Giving AI Agents First-Class Access to Public Stats appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Google released a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server for Data Commons, exposing the project’s interconnected public datasets—census, health, climate, economics—through a standards-based interface that agentic systems can query in natural language. The Data Commons MCP Server is available now with quickstarts for Gemini CLI and Google’s Agent Development Kit (ADK). What was released Why MCP
The post Google AI Ships a Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server for Data Commons, Giving AI Agents First-Class Access to Public Stats appeared first on MarkTechPost. Read More
Nano Banana Practical Prompting & Usage GuideKDnuggetson September 26, 2025 at 12:00 pm In this article we will take a look at what Nano Banana excels at, some tips and tricks for using the model, and lay out a series of example prompts and promoting strategies for getting the most out of using it.
In this article we will take a look at what Nano Banana excels at, some tips and tricks for using the model, and lay out a series of example prompts and promoting strategies for getting the most out of using it. Read More